Laser therapy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia - what are lasers used for
Whatis objective lens inmicroscope
It is expressed in millimeter (mm) units. A lens with a short focal length is a wide-angle lens and one with a long focal length is a telephoto lens. The angle ...
Microscope Objectivesmagnification
Both methods can be used to estimate distortion, but they can be more applicable in certain situations. F-Tan (Theta) is preferred when the focus is on object size and magnification changes due to distortion. And the F(Theta) method is used to get the angular relationship of distorted image points without needing magnification information.
Plan objective–These objectives produces a flat image across the field of view. The three objectives discussed above all produce a curved image. A plan-achromat, plan-fluorite or plan-apochromat are corrected.
Diagonal Field of View (FOV) at a Specific Image Distance: Values provided at different image distances (e.g., 124° @ 10mm)
Prabu is the Chief Technology Officer and Head of Camera Products at e-con Systems, and comes with a rich experience of more than 15 years in the embedded vision space. He brings to the table a deep knowledge in USB cameras, embedded vision cameras, vision algorithms and FPGAs. He has built 50+ camera solutions spanning various domains such as medical, industrial, agriculture, retail, biometrics, and more. He also comes with expertise in device driver development and BSP development. Currently, Prabu’s focus is to build smart camera solutions that power new age AI based applications.
May 21, 2020 — Yes the double slit is just a special case of the grating. The equations for the angular separation are the same. The difference here is because ...
Whatdoesthestagedo on a microscope
The magnification of the image depends on the combination of the eyepiece and the objective used. This combination also affects the field of view. This example shows how these factors inter-relate.
Mathematically, distortion can be represented in three different ways in the lens datasheet; let us look at each of them in detail.
The first image shows the eyepiece view when using a 1.0X objective with a 10X eyepiece. It has a 34mm field of view. The second image shows the video field of view of about 16–4.7mm (COLCAM-NTSC camera with a 0.5X coupler). The third image shows the video view that approximates the eyepiece view. It uses a 0.5X objective with a 20X eyepiece.
Whatdoesthestage clipsdo on a microscope
TIP: On the trinocular version of the PZMIII or PZMIV stereo microscope with the standard configuration (1.0X objective, 10X eyepieces) and with the optimal camera adaptor (0.5X on a ½” CCD camera) the video capture field of view is up to 40% less than the visual field. By using a 0.5X objective with 20X eyepieces the video capture area doubles, and the resulting video capture more closely matches the visual field of view.
The F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tangent function to relate the angle to object size and magnification. Whereas the F(Theta) method focuses on the angular position of the image point relative to the centre. Both the methods require the focal length (F) and the diagonal FOV (degrees). But in the F(Theta) method the FOV in degrees is converted to radians.
In this blog, we break down distortion parameters in lens datasheets and the three ways in which distortion is represented.
The formula calculates the difference between the expected height of an object based on the sensor size and its actual distorted height based on the distortion values and field of view. This difference is then expressed as a percentage of the vertical sensor size to provide a measure of barrel distortion.
F(Theta) method focuses on the angular relationship between the ideal undistorted image point and the actual distorted image point without needing magnification information.
... reflective surfaces, shrink mirrors, and the exclusive GiantMirror. Our easy to use mirror foils and holographic materials are a versatile alternative to ...
F-Theta lenses are specifically designed to maintain a constant image size (or spot size for lasers) across a scan field. The F-Theta calculation helps ensure the accuracy of this constant size by measuring deviations from the ideal. These lenses are used in various applications like laser marking and engraving, laser cutting, 3D printing and LiDAR.
Whatdoestheocular lensdo on a microscope
F-Tan (Theta) method uses the tan(theta) relationship to calculate a reference height based on magnification, and the F(Theta) method uses F*theta (radians) to represent the ideal image point location based on its angular position.
Problem: The PZMIII or PZMIV stereo zoom microscope normally comes with a 1.0X objective and a 10X pair of eyepieces. The magnification is 6X to 50X, however the concept of magnification is difficult to visualize. Let's discuss what can be seen at the two zoom extremes. Imagine the visual circle to be a range of 34–4.2 mm. This microscope has a working distance of 100mm. Researchers working with small animals will have difficulty working in this tight space.
Infinity Correction–When measuring from the back end of the objective to the primary focal plane, many microscopes are limited to a specific distance (160mm). More expensive microscope use a different series of lenses, prisms and mirrors to allow for an "infinite" distance between those two points. This is called infinity correction.
Aims ofmicroscopepractical
Magnification = Image size (with ruler) ÷ Actual size (according to scale bar).
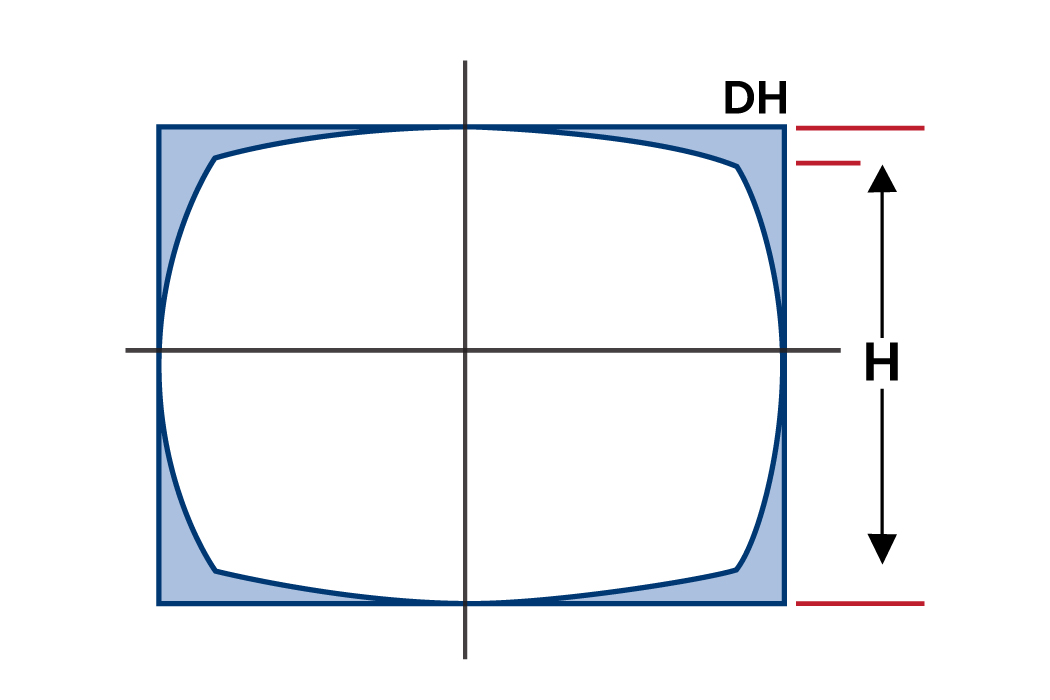
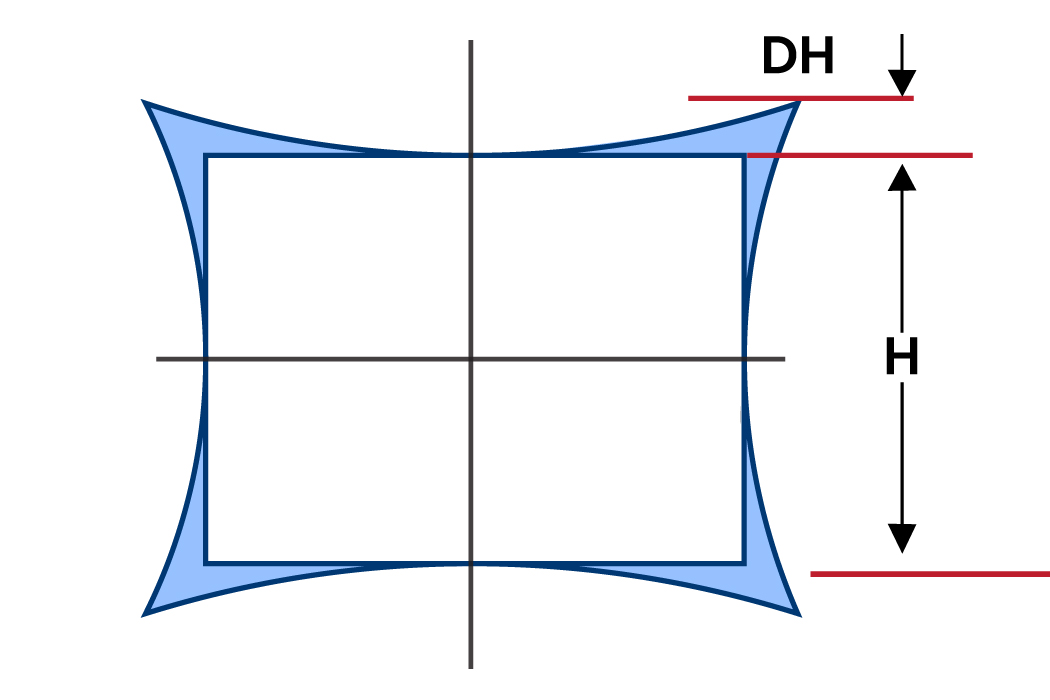
Imagine a scene with a square grid. In barrel distortion, the grid would bulge outwards, making the squares appear wider on the edges. Meanwhile, in pincushion distortion, the grid would sink inwards, making the squares appear narrower on the edges. Mustache distortion would cause the grid lines to become wavy.
The F*tan(theta) method is a more general approach to calculating distortion. It’s often used for initial distortion assessment in various lenses, including photographic lenses. This method helps understand how straight lines deviate from their ideal positions due to distortion.
Fluorite or semi-apochromat objectives–These lenses are chromatically corrected for red and blue, and the green focus is also close. They are spherically corrected for blue and green. This objective is better suited for color viewing or recording than achromatic objectives.
Apochromatic objective–This is the most expensive objective. It is chromatically adjusted for four colors (deep blue, blue, green and red) and spherically corrected for deep blue, blue and sometimes green. This is the best choice for color viewing. These have a higher numerical aperture (N.A.) than achromats or fluorites.
A negative value indicates barrel distortion (objects appear smaller towards the edges). In the above example, the calculation shows a higher barrel distortion (-39.5%) at a larger image distance (10mm). As the image distance decreases (9mm and 5mm), the distortion percentages become less negative, indicating a decrease in the barrel effect.
F*tan(theta) calculations are used in camera calibration processes, where distortion parameters are estimated for correcting captured images. Lens designers often utilize F*tan(theta) calculations during the design phase to predict and minimize distortion in the final lens. This helps create lenses with minimal image curvature and ensures accurate image reproduction.
Types ofmicroscope objectives
TV Distortion, as the name suggests, originated in the context of television applications. It can be calculated using the following formula:
HeNe Laser Systems are in stock at DigiKey. Order Now! Optoelectronics ship same day.
Optical distortion represents the overall distortion parameter of the optical system. F-Tan theta or optical distortion can be calculated using the following formula.
Microscopeparts
NOTE: If a 1/3” inch camera (6mm diagonal) is used on the 0.5X microscope adaptor you can apply the ratio of 6/8 for the reduction in the captured field.
We also provide various customization services, including camera enclosures, resolution, frame rate, and sensors of your choice, to ensure our cameras fit perfectly into your embedded vision applications.
A variety of microscope objectives are available. All objectives use lenses to focus light. Light is broken down into various wavelengths (colors) as it travels through a lens. The various wavelengths have different focal points. That means that red, green and blue appears to focus at different points. This is called chromatic aberration. Spherical aberrations are focal mismatches caused by the shape of the lens. Quality lenses are designed correct for chromatic and spherical aberration to bring the primary colors to a common focal point. These terms may help you determine the best objective for your application:
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Lens datasheets often include distortion information to help photographers and engineers understand how the lens behaves. Lens distortion refers to the phenomenon where straight lines in a scene appear curved in the final image. This happens because lenses don’t perfectly focus light from all parts of the field of view.
This cable provides a transfer rate of up to 4.8 Gbps when connected with a USB 3.0 compliant host and device. Foil and braid shielding reduces EMI/RFI ...
Lee Filters Opal Frost 24x21" Diffusion Filter Sheet #410S ; Part · 410S. ; Est. delivery. Thu, Nov 7 - Tue, Nov 12. From Elizabeth, New Jersey, United States.

Generally, f-numbers are used to indicate the amount of light that passes through the lens. The smaller the number, the greater the amount of light passing ...
Achromatic objectives–This objective brings red and blue light to a common focus, and is corrected for spherical aberrations for green. It is excellent for black and white viewing. If an objective is not labeled, it is achromatic.
Solution: Instead of the standard configuration, setup the microscope with a 0.5X objective to increase the working distance to 187 mm. The result of using this lower power objective is that the magnification range decreases by one half and at the same time the field of view double. To restore the microscope system to the original condition (magnification and field of view), replace the 10X eyepieces with 20X eyepieces. The use of these two options restores the visual field of view and magnification range back to the original condition with the added benefit of a larger working distance.
Gain medium (discharge glass tube or glass envelope). The gain medium of a helium-neon laser is made up of the mixture of helium and neon gas contained in a ...
Microscope calculations are a range of formulas used for digital microscopy applications to calculate the depth of field in microscope, field.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500