How to read an USAF1951 target? - OptoWiki Knowledge Base - usaf test target
Types ofmicroscope
Hilarious, but useful. Thanks for your input. I think I shall use some rods fashioned from materials I have or can easily obtain. This is for a generalised guide, it'll be as accurate as I need it to be.
If you are set on lasers, at that distance, I'd use the laser rangefinder I use for shooting . That one's a bit expensive for what you want but there are many for less than £80
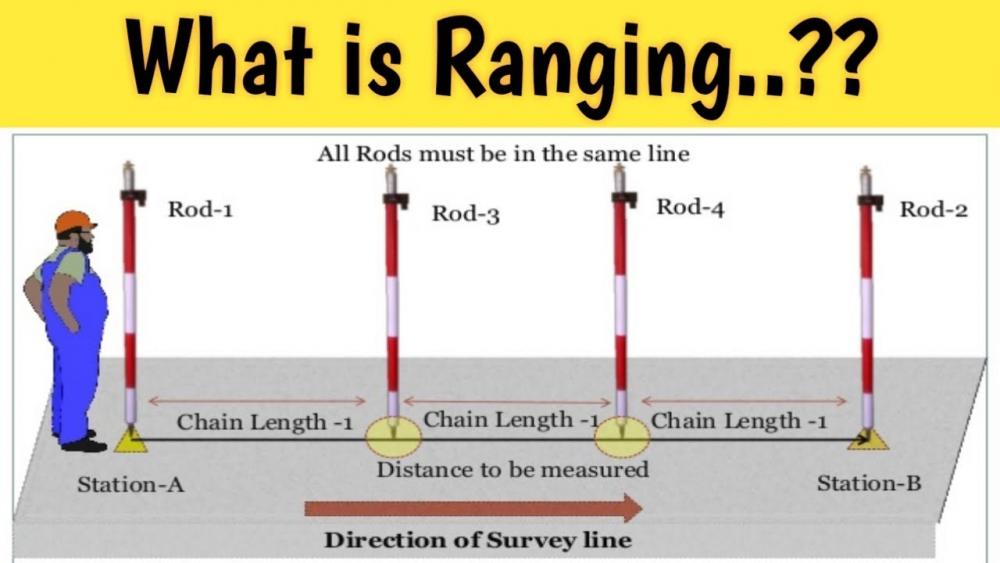
They are not expensive, can be found in sectional form (for storage and to make extra high) , and are handy for any marking out....so handy for other people that they keep disappearing.
Whatis amicroscopeused for
There are two main types of electron microscope – the transmission EM (TEM) and the scanning EM (SEM). The transmission electron microscope is used to view thin specimens (tissue sections, molecules, etc) through which electrons can pass generating a projection image. The TEM is analogous in many ways to the conventional (compound) light microscope. TEM is used, among other things, to image the interior of cells (in thin sections), the structure of protein molecules (contrasted by metal shadowing), the organization of molecules in viruses and cytoskeletal filaments (prepared by the negative staining technique), and the arrangement of protein molecules in cell membranes (by freeze-fracture).
As for water levels recommended above They are invaluable in confined spaces. I spent 2 uncomfortable days under a Boots pharma factory, but there was no other way with 4 ft headroom.
I am having our land surveyor back for other stuff but I'd ideally like him to survey the fence once completed, as opposed to him coming earlier to peg out the position.
Lightmicroscope
3. Buy rods that are in sections so can go higher.https://www.yorksurvey.co.uk/1m-point-jointed-pole-section-c2x23061987
Laser levelling can go wrong too. The modern groundworker uses them, but doesn't know the principles of levelling. So if it is out of adjustment, and using long and short sightings, big errors can arise.
Being old school I prefer string/line, I have a roll of electric fence wire (platted nylon with wire ) which is very strong and does not stretch .
Microscopediagram
Everything needs to be looked over, just by eye and perhaps pacing to check for anomalies. For example here, if the satellite guided positions of 4 posts don't look straight.
Why do I resist modern methods? I don't, but they are so easy to use that they are used by some people who don't really understand what they are doing , and mistakes are missed.
They are not expensive, can be found in sectional form (for storage and to make extra high) , and are handy for any marking out....so handy for other people that they keep disappearing.
3. Buy rods that are in sections so can go higher.https://www.yorksurvey.co.uk/1m-point-jointed-pole-section-c2x23061987
Sometimes the old ways are best....these are still for sale so plenty people still using them. They look good on your site too, and are a good way to wind up the neighbours that a road is coming through..
Compoundmicroscope
You can use a garden hose(s) and just attach some clear sections each end with jubilee clips etc. Just make sure the air's all out.
I can see both points and have clear line of sight, but it'll be hard to run a string, not to mention keep it taught. Does a laser pointer exist that will do this? I don't need it to measure or level, just show me a line. Once I have that, I can get some markers down to ground level.
Sometimes the old ways are best....these are still for sale so plenty people still using them. They look good on your site too, and are a good way to wind up the neighbours that a road is coming through..
I'm not set on anything specific. As I said, I'm not concerned with anything other than the position and straightness of the line. I need to put a marker in, on the line about halfway along and only need the physical position on the ground, so the visual line-of-sight method will work I think, as long as I can see it over that distance.
Modern equipment and methods are very easy and precise. So on this post it would be feasible to get a land surveyor with a fancy machine to mark your points out for half a day's pay...£300. You should be in attendance for banging posts and any decisions.
If you want it for legal purposes then get the surveyor to map it with a GPS marker and then transpose this to the floor with pegs. He will be able to do it within 30cm.
In a nutshell, we are splitting the property perpendicular to the longest boundary of the whole plot. That long boundary has 'slipped' by a fairly substantial amount (over a metre along its entire 70m length), but as we are now going to fit a proper fence I'd like to get the bit on the land we are retaining as close to being on the correct line as possible. The bit on the land we're selling is for the new owners to argue if they wish.
Microscopeparts and functions
1. Cut the hedge locally....you will know where when you start. For first approximation you can have someone hold it high.
Whatismicroscopein science
1. Cut the hedge locally....you will know where when you start. For first approximation you can have someone hold it high.
But it is much more fun and satisfying to do it yourself, and in doing so you might also notice any quirks in the landscape, and change your mind where to put this new boundary.
10 uses ofmicroscope
Electron microscopy (EM) is a technique for obtaining high resolution images of biological and non-biological specimens. It is used in biomedical research to investigate the detailed structure of tissues, cells, organelles and macromolecular complexes. The high resolution of EM images results from the use of electrons (which have very short wavelengths) as the source of illuminating radiation. Electron microscopy is used in conjunction with a variety of ancillary techniques (e.g. thin sectioning, immuno-labeling, negative staining) to answer specific questions. EM images provide key information on the structural basis of cell function and of cell disease.
Conventional scanning electron microscopy depends on the emission of secondary electrons from the surface of a specimen. Because of its great depth of focus, a scanning electron microscope is the EM analog of a stereo light microscope. It provides detailed images of the surfaces of cells and whole organisms that are not possible by TEM. It can also be used for particle counting and size determination, and for process control. It is termed a scanning electron microscope because the image is formed by scanning a focused electron beam onto the surface of the specimen in a raster pattern. The interaction of the primary electron beam with the atoms near the surface causes the emission of particles at each point in the raster (e.g., low energy secondary electrons, high energy back scatter electrons, X-rays and even photons). These can be collected with a variety of detectors, and their relative number translated to brightness at each equivalent point on a cathode ray tube. Because the size of the raster at the specimen is much smaller than the viewing screen of the CRT, the final picture is a magnified image of the specimen. Appropriately equipped SEMs (with secondary, backscatter and X-ray detectors) can be used to study the topography and atomic composition of specimens, and also, for example, the surface distribution of immuno-labels.

If you are set on lasers, at that distance, I'd use the laser rangefinder I use for shooting . That one's a bit expensive for what you want but there are many for less than £80
For the cost, everyone should have one. This one is £10, and if you fix it to timbers, as the following pic, you have control .You can get a hydraulic oil version with digital readout of level difference for £400.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500