How To Choose Lenses for Infrared - ir lenses
C mountvscs mount
The size of the aperture (the f-stop number) also determines the minimum focus distance of the lens. The minimum focus distance is the closest distance that the lens can focus on an object and still produce a sharp image.
If you need help with the Arducam products you’ve purchased, please include the following questions in your post and answer them to help us better understand your needs.
You can’t randomly pick a lens and expect it to perfectly match your applications, and there are some key factors you should take into consideration. You can also refer to our guide on how to choose a lens for the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera.
The C/CS-Mount lenses look quite similar with the same thread size. However, the C-Mount lenses are designed with a longer back focal length than the CS-Mount, so we have a C-CS adapter for the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera to use with C-Mount lenses.
Generally speaking, a higher f-stop number will result in a photo with a small area in focus and a large area out of focus. On the flip side, a small f-stop number will result in a photo with a large area in focus and a small area out of focus.
The refraction of light occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a ...
Your lens aperture settings will also impact the depth of field in your photograph. Whatâs more, changing your aperture will impact what you can achieve with your shutter speed and ISO settings.
Most DSLR cameras from companies like Nikon and Canon will have a lower f-stop number (or maximum aperture) of f/1.4. This a very wide aperture opening, and will let in a lot of light.
For example, let's say you're taking a picture of a person with a 50mm lens at f/2. The amount of diffraction would be minimal. If you wanted to use a smaller aperture (larger f-stop number), the amount of diffraction would increase.
It's important to understand that aperture is not a setting on your camera, but rather a characteristic of your lens. The aperture is determined by the physical size of the diaphragm, which can be changed by swapping out lenses or adjusting a zoom lens.
AR coating, where AR stands for Anti-Reflection, is a technology that involves applying an anti-reflection layer onto a film or another substrate.
Thatâs right: you can change the amount of light (aperture) and the sensitivity to light (ISO). As you can imagine, changing one of these settings is likely to impact how the other works.
CS-mountdiameter
That's our post! As you can see aperture is an incredibly important aspect of digital photography. Some of the jargon isn't easy to understand, and probably won't become second-nature until you've had some practice out in the world.
On a DSLR camera, adjusting the aperture is as simple as turning a dial. This adjusts how wide open the lens is, and therefore how much light is allowed in. As weâve mentioned already aperture is measured in "f-stops", with larger numbers representing a smaller aperture. For example, an aperture of f/22 would be much smaller than an aperture of f/2.8.
May 7, 2013 — The quality measurements obtained are then plotted on the MTF graph, showing you how far from the center they're taken from as you look from ...
Aperture is one of the most important concepts in digital photography, yet it is often misunderstood. Hereâs the simple definition: Aperture is the size of the opening in the lens through which light passes.
Second, exposure isn't only set by your aperture. Your shutter speed and ISO settings also affect exposure, and you'll need to do some trial and error to figure out how to get the exposure you want. Thatâs why people call these three settings the âexposure triangle'.â
On the contrary, Arducam offers many lenses tested on the IMX477 in M12, CS and C Mount, ranging from telephoto to fisheye lenses. Not only do we have datasheet for the lenses, tutorials are also available on how to select the right one for you.
A plane mirror is a flat, reflective surface that follows the Law of Reflection. When a light ray, known as the incident ray, ...
While you are adjusting the lens, we recommend you put the camera module on a tripod. As the camera module now accommodates a much heavier lens, a tripod is handy for holding the camera steady. You can also check the official guide for more information.
Now let's say you take the same picture with the same lens, but at f/2. The depth of field would be reduced to about 0.6 feet (0.2 meters). This means that only objects within 0.6 feet of the camera would appear sharp; anything beyond that would be significantly blurred.
C-Mount adapter
The size of the aperture (the f-stop number) also determines the ISO that's needed to achieve a correct exposure. A small aperture (large f-stop number) will require a lower ISO setting, while a large aperture (small f-stop number) will require a higher ISO setting.
The size of the aperture (the f-stop number) also determines the shutter speed that's needed to achieve a correct exposure. A small aperture (large f-stop number) will require a longer shutter speed to achieve the correct exposure, while a large aperture (small f-stop number) will require a shorter shutter speed.
If you are really considering a wide-angle application, usually with an HFoV greater than 100 degrees, consider other options including the C-Mount Zoom lenses and M12 Lenses from Arducam. The zoom lens is helpful if you need to switch between a wider view and a narrower view from time to time, and the M12 lenses can push the field to the fisheye level.
c-mount thread dimensions
However, the new change brings cost. You must spend extra money on the lens, and more time getting to know the lens. Simple as the old Pi cameras were, they saved most people from thinking about lens, which is not included in the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera. But how would it work without a lens?
If you are using a CS-Mount lens, the adapter must be removed. However, for C-Mount lenses, the adapter is a must-have. Sometimes if you are still not able to focus a C-Mount camera even after the adapter is on, adjust the back focus. The gear-like ring on the main housing of the camera module is the back-focus adjustment ring, and you can spin it to alter the distance between the bottom of the lens and the IMX477 image sensor.
Recently, the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera has changed this situation by officially introducing the C/CS-Mount to Pi cameras. With a standard lens mount, this new HQ camera has access to much more lens options.

What about the third part of the exposure triangle, ISO? ISO is a measure of the camera's sensitivity to light. The higher the ISO number, the more sensitive the camera is to light. This means that less light is needed to achieve a correct exposure.
The size of the camera aperture (the f-stop number) determines the amount of depth of field in an image. A small aperture (large f-stop number) results in a large depth of field, while a large aperture (small f-stop number) results in a shallow depth of field.
Our advice: read this guide, take your camera off auto mode, and then start taking some photos of your own (maybe for your next photo essay). It might be worth bookmarking this page, taking some photos, and then coming back for another read.
5 Point Alignment Laser ... Laser (Tool Only). Milwaukee | MIL362220. [BONUS ... Responsive Laser Alignment Target. Milwaukee | MIA48351111. Responsive Laser ...
Diffraction is an optical effect that occurs when light waves pass through a small opening. The result is a loss of sharpness in the image.
USB 3.0 A MICRO B CABLE FTDI USB Cables / IEEE 1394 Cables USB3.0 SuperSpeed A to Micro B 1M BLK datasheet, inventory, & pricing.
Aperture is measured in an f-stop number. The lower the f-stop number, the more open the aperture is and therefore more light enters your camera. The higher the f-stop number, the more closed down (or smaller) the aperture is and less light enters your camera.
Lens is a crucial part in a camera system that needs flexibility. A single lens cannot meet all needs because the use case varies from one application to another. Sadly, V1 and V2 Pi cameras have glued stock lenses, which leave us little to customize. Take the Raspberry Pi Camera Module V2 for example, we have to swap the whole lens-sensor unit for Arducam IMX219 drop-in replacements to mount a different lens.
CS-mountthread
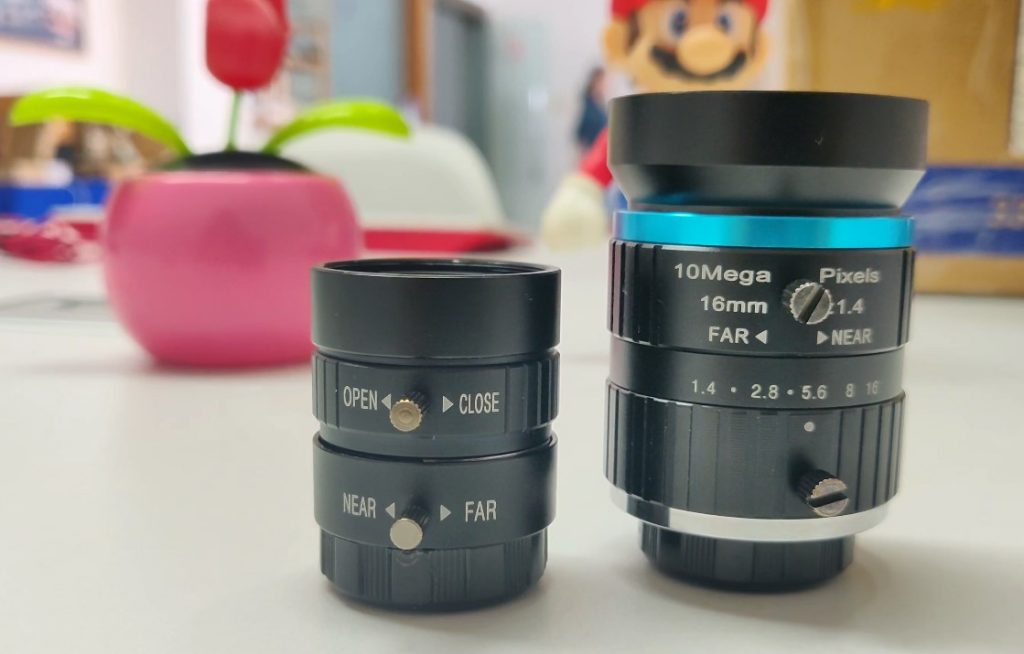
The CGL lenses recommended are at a reasonable price for the Raspberry Pi community, with the 6mm CS-Mount lens at $25 and the 16mm C-Mount lens at $50. We’ve purchased both, and admittedly, those are not bad. However, the issue is that we know little about the lenses just like this mysterious company – there is no detailed datasheet or specifications in the box, no other lenses available than the two, and even no way to contact them directly.
So as you can see, changing the aperture has an impact on both the depth of field and the shutter speed. It's important to understand how these two factors work together to create the right exposure for your photograph.
Letâs tackle shutter speed first. Now, what is it, exactly? Shutter speed is the amount of time the shutter is open and exposes the camera's sensor to light. The longer the shutter is open, the more light that enters the camera.
Jun 30, 2023 — Broadband dielectric mirrors, available in three different spectral ranges from visible, NIR to IR regions, are used to redirect light for ...
As we've explained, changing the aperture can have a big impact on your image. But how do you know which aperture to use? Well, it depends on the look you're going for.
Aperture priority mode allows the user to select the aperture while the camera sets an appropriate shutter speed. Aperture priority is often abbreviated as "A" or "Av" on camera mode dials.
Infraröd LED (880nm). Mått, 88 mm *65 mm *25 mm. Produktion, Reläutgång, NPN eller PNP NO+NC, Reläutgång, NPN eller PNP NO+NC. Matningsspänning, 24…240 VAC/12…
How to start Multi View on a Samsung Smart TV. Multi view enriches your watching experience by providing multi-content for each lifestyle or interest. Please ...
The size of the aperture (the f-stop number) also determines the amount of diffraction that occurs. A small aperture (large f-stop number) will cause more diffraction, while a large aperture (small f-stop number) will cause less diffraction.
Laser Beam Expanders, also known as collimators, are optical devices used to collect a collimated beam of light to expand or reduce its ...
C-Mount camera
Depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that have crisp details and no unintentional blurring (otherwise known as 'sharp'). It's important to note that depth of field is not an absolute value, but rather it is relative to the distance between the camera and the subject.
This mode is also sometimes called "semi-manual" mode because the photographer still has some control over the exposure. For example, if the scene is very bright, the photographer can choose a small aperture to avoid overexposing the image. Conversely, if the scene is darker, a larger aperture can be used to let in more light. Aperture priority is a popular mode for many types of photography, including portrait, landscape, and still life. It is also a good choice for beginners who are not yet comfortable with manual mode.
Aperture is one of three camera settings â along with ISO and shutter speed â that impact how well (or not) your photo is exposed. These three settings are often called the âexposure triangle.â
It sounds complicated, and some of the terminology ('f-stop', âbokehâ) doesn't help! But as with most aspects of photography, it all gets a lot simpler after you start experimenting with different apertures in the real world.
So, weâve talked about aperture and f-stop. But as we mentioned above, changing your aperture settings will likely require you to make some adjustments to the other settings in the exposure triangle.
Reading this post wonât help you master it, though. The best bet is to grab your photo and start experimenting in the real world!
Bokeh can be used to create a dreamy or romantic look, or to make the subject stand out against a busy background. It is also often used in portraiture to help the subject stand out from the background. Bokeh can be created with any type of camera, but it is most commonly associated with DSLRs and mirrorless cameras.
Remember, when adjusting aperture, it's important to keep in mind the shutter speed and ISO settings as well. If you need to increase the shutter speed to prevent blur, you'll need to decrease the aperture to compensate. And if you need to increase the ISO to get a good exposure, you'll need to decrease the aperture as well.
Once you’ve mounted the lens on, you will have to face the various kinds of handles on the ring of the lens. Typically, every C/CS-Mount comes with a focus ring, and many come with an aperture ring, while few may include a zoom ring. The trick to adjusting theses rings is you only tweak one ring at a time with the others fixed. Otherwise, they will move each other and ruin your last adjustment.
If you want to isolate your subject from the background (or foreground), then you'll want to use a large aperture (small f-stop number). This is known as shallow depth of field, and it's often used in portraits and close-up shots.
So what is aperture? Hereâs a simple definition: Aperture is the size of the opening in your camera lens (the word is literally a fancy way of saying 'opening). This determines how much light enters your camera and hits the image sensor.
Bokeh is a technique in photography that is used to create a soft, blurred background. This effect is achieved by using a large aperture and keeping the subject in focus while the background is out of focus.
As a result, prime lenses typically have a wider maximum aperture than zoom lenses, making them well-suited for low-light photography and achieving shallow depth of field effects. The wider aperture also allows for greater control over the placement of focus within the frame.
CS-Mountlens
Here's an example to illustrate how this works. Let's say you're taking a picture of a flower garden with a 50mm lens at f/8. The depth of field would be approximately 2 feet (0.6 meters). This means that objects within 2 feet of the camera would appear sharp, while objects beyond that would start to become blurry.
Previously, you could be unsatisfied with the stock lens, but it’s not an issue anymore – because the HQ camera has no stock lens. The Raspberry Pi chooses not to include a lens but have curiously endorsed a little-known reseller – CGL.
C and cs mountcanon
First, aperture controls the depth of field in your photograph. What is depth of field? Itâs the distance between the nearest and furthest objects in a scene that appear âsharpâ in an image. The larger the aperture, the shallower the depth of field and the smaller this distance will be. This can be useful for isolating a subject from its background.
Many professional photographers use a prime lens for this reason. A prime lens is a camera lens with a fixed focal length. In other words, it can't zoom in or out like a zoom lens can.
If you want everything in your image to be sharp and in focus, then you'll want to use a small aperture (large f-stop number). This is often desirable for landscape shots, group photos, and other situations where you want everything to be sharp.
Prime lenses are often used for portrait photography, who want to capture clean, sharp images with minimal distortion. Prime lenses are also often used by landscape photographers. While they generally require the use of a tripod or other stabilising device due to their narrow field of view, prime lenses offer a number of advantages that make them a popular choice among professional photographers.
Another thing to mention is the aperture, namely the hole on the lens to pass light through. If you want a deeper depth of field (DoF), you’d better get a lens with an aperture ring, since a decreased aperture will increase the DoF. If you have nothing to say about the DoF or you usually shoot from a further distance, a fixed aperture will be okay for your application.
Receive storytelling tips from The Craft and the most amazing Shorthand stories from around the web, hand selected by our team, every two weeks.
Arducam has been building customized Pi camera boards with interchangeable lenses as early as the V1 era, and we offer a wide arrange of lenses other than the officially endorsed 6mm and 16mm lenses. These lenses are also compatible with Arducam IMX477 High Quality Camera Modules.
Firstly, it’s the focal length. The focal length is the most concerning issue for most users to decide how wide the image frame you want to cover. The officially endorsed 6mm lens is usually advertised as wide angle, but it’s just slightly larger than the stock lens of V2, with a horizontal field of view at around 65 degrees. It’s the wide angle to be compared to the 16mm telephoto lens, but not the wide angle you might really need. You can refer to our focal length calculator page for more details.

For example, let's say you're taking a picture of a person in low light with a 50mm lens at f/2. The lowest ISO setting you could use to get a correct exposure would be 3200. If you wanted to use a lower ISO setting, you would need to use a larger aperture (smaller f-stop number). Conversely, if you wanted to use a higher ISO setting, you would need to use a smaller aperture (larger f-stop number).
As you might expect, the larger the aperture, the more light that enters the camera. This is important because it allows you to control exposure.
The f-stop number is calculated by dividing the focal length of the lens by the diameter of the aperture. For example, if a lens has a focal length of 50mm and an aperture diameter of 25mm, the f-stop would be 2 (50/25).




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500