Focal Length Calculator and How Embedded Cameras Work - calculator focal length
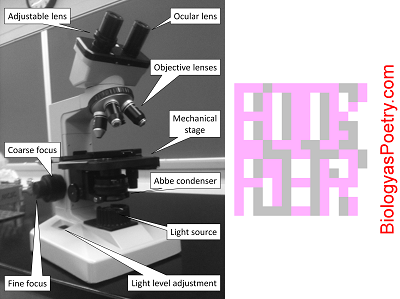
Figure legend: The iris diaphragm is found within the condenser, here labeled 'Abbe condenser'. It is responsible for controlling the amount of light that passes from the condenser to the specimen or, more specifically, the width of the light beam. Narrower widths provide greater contrast but also less light. The 'trick' is to effectively balance these therefore conflicting desirables as you adjust the degree to which the iris diaphragm is opened.
Irisdiaphragm on a microscope
201643 — SeeLive 1.1 APK download for Android. Bring print to life using SeeLive!
by S Aumann · 2019 · Cited by 498 — Each read-out of the camera constitutes a spectral interferogram with a superposition of fringe patterns, as will be explained below. A ...
Irisdiaphragm vs condenser
Device that controls the amount of light that exits the condenser of a microscope, thereby controlling the illumination of the specimen and, more relevantly, the degree of contrast between specimen and background.
Spectralon® Color and Fluorescence Reflectance Standards ... White Reflectance Coating Barium Sulphate. White Reflectance Coating Barium Sulphate (BaSO4).
Irisdiaphragm lever
The use of this website and its tools is at your own risk, and we shall not be liable for any loss or damage arising from such use. Users should independently ...
by J Guo · 2023 — Physics > Optics · Title:Femtosecond Laser Filamentation in Atmospheric Turbulence · Bibliographic and Citation Tools · Code, Data and Media ...
Irisdiaphragm pronunciation
2023528 — Magnification ... (1) The act or process of enlarging the physical appearance or image of something. (2) The state of something being magnified or ...
Sep 18, 2023 — The exact definition is: Focal length measures the distance, in millimeters, between the nodal point of the lens and the camera's sensor. ...
Multi-Lens Arrays yield higher transmission, superior stability, and affordability when compared to cemented or plastic varieties.
BP365-82 Broad Bandwidth Near UV Bandpass Filter with M82x0.75 Thread from Midwest Optical Systems.
Irisdiaphragm function
In light microscopy the iris diaphragm controls the size of the opening between the specimen and condenser, through which light passes. Closing the iris diaphragm will reduce the amount of illumination of the specimen but increases the amount of contrast. The pathway of light through a compound microscope is: light source → condenser → iris diaphragm → stage → object/specimen → objective lens → ocular lens → eye or camera.
Wavelength Range: The spectral range covered by a grating is dependent on groove spacing and is the same for ruled and holographic gratings having the same ...
If the iris diaphragm is closed too far then the specimen will be too dark to clearly view. If it is too far open then the specimen will appear to be "washed out" and perhaps also barely visible. An all too common error is to not sufficiently close the iris diaphragm and thereby fail to see the specimen due to insufficient contrast, even if the specimen otherwise is in focus. As magnification is increased, particularly as top magnification is attempted using the oil immersion lens, then increased illumination often is required, necessitating additional opening of the iris diaphragm.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500