CR1026 6-point metric socket, 1/2" drive Size : 25mm - 25mm size
In optical design, the finite distance between the object and the lens must often be considered. In these cases, the working f-number is used instead. The working f-number is defined by making the approximate relation above exact:
Shenzhen Sopto Technology Co., Ltd Add:2nd Floor Building D Huafeng International Robot Industrial Park,Hangcheng Road, Xixiang Baoan District Shenzhen Service Email:[email protected] Tel: +86-755-23018340 Fax: +86-755-26053449
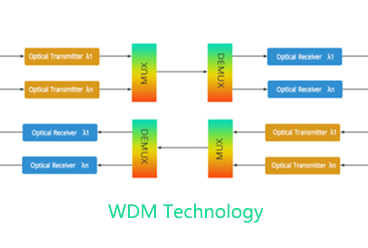
WDM Networking Solution WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technology was developed to expand capacity of networks. WDM system uses a Multiplexer at the transmitter to combine several wavelengths together, each one carry different signal with bite-rate up to 10G and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split them apart.

SFP+ MPO Cable On Sale As a manufacturer of optical modules for data centers,sopto offers optical modules with different data rate to meet the different needs of our customers, and we also accept customized services. All optical transceivers are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP, H3C, Linksys etc

10G SFP Transceiver Series Sopto provides a series of 10G transceiver modules, including SFP+, XFP, BIDI SFP+, BIDI XFP, CWDM/DWDM SFP+; They are designed for using in 10G Ethernet, 10G Fiber Channel, SONET/SDH OC-192/STM-64, and OTN OTU2e links. Digital diagnostics functions. RoHS compliant.
FTTx Solutions âAlong with the fast deployment of FTTX and its worldwide application. Sopto Technology offers an end-to-end infrastructure solution for central office (CO), optical distribution...
Data Center Solutions Construction and operation of data center will break the distributed construction mode. High centralized management of dynamic use of physical resources and virtual resources ...
Numerical apertureunit
LTE Solutions In telecommunication, Long-Term Evolution (LTE) is a standard for high-speed wireless communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and...
where λ0 is the vacuum wavelength of the light, and D is the diameter of the beam at its narrowest spot, measured between the 1/e2 irradiance points ("Full width at e−2 maximum"). Note that this means that a laser beam that is focused to a small spot will spread out quickly as it moves away from the focus, while a large-diameter laser beam can stay roughly the same size over a very long distance.
Fibers can be classified into G.651 fiber (gradient multimode fiber), G.652 fiber (conventional single mode fiber), G.653 fiber (dispersion-shifted fiber), G according to ITU-T recommendations for fiber type classification. .654 fiber (cutoff wavelength fiber) and G.655 (non-zero dispersion shifted fiber) fiber. Among them, G.652 and G.655 are widely used in current projects. G.652, also known as conventional single fiber, can operate at dual wavelengths with minimal dispersion at 1310 nM, with a typical attenuation of 0.34 dB/km. At 1550, the attenuation is at least 0.2 dB/km. G.652 fiber is relatively low in price and mature in technology. It is currently the largest fiber used, accounting for more than 90%.
Numerical apertureof lens
Optical fibers are classified into single-mode fibers and multimode fibers according to the transmission mode of light in the optical fiber.
In multimode fibers, the term equilibrium numerical aperture is sometimes used. This refers to the numerical aperture with respect to the extreme exit angle of a ray emerging from a fiber in which equilibrium mode distribution has been established.
Numerical apertureof objective lens
SFP Module Transceivers Sopto provides standardized transceivers Modules and customized transceivers Modules for data-rate of 1-100G network. Types of Dual fiber/ Single fiber and wavelengths of 850nm/ 1310nm/ 1490nm/ 1550nm/ CWDM 1270 - 1610nm/ DWDM wavelengths and transmitting distance from 30m up to 150km can be selected. Digital Diagnostic Function are also available. All optical transceivers Modules are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP etc.
In most areas of optics, and especially in microscopy, the numerical aperture of an optical system such as an objective lens is defined by
Fiber Optic Patch Cords Fiber patch cords are used to connect one device to another for signal transmission. The fiber jumper is a connector that is installed at both ends for the device; only one end is equipped with a connector, which is a pigtail. Depending on the type of fiber, there are single mode jumpers and multimode jumpers. According to the structure of the connector, it can be divided into FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, MPO, MU, E2000, DIN, and the like.
Optical Fiber is a transparent medium fiber used for guiding light. A practical fiber is composed of a plurality of transparent media. The bare fiber is generally divided into three layers, a central high refractive index glass core (core diameter is generally 50 or 62.5). Îm),in the middle is a low refractive index silica glass cladding (typically 125μm in diameter), the outermost is a resin coating for reinforcement.
Fiber Optic Cable Fiber Optic Cable, also known as an optical fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connect
Numerical aperture definitionin optical
SFP Module On Sale As a manufacturer of optical modules for data centers,sopto offers optical modules with different data rate to meet the different needs of our customers, and we also accept customized services. All optical transceivers are RoHS compliant and could be 100% compatible with branding equipment, such as Cisco, Extreme, Juniper, HP, H3C, Linksys etcPart No.DescriptionPriceDetailsSPT-P131G-10D/20D1.25G 1310nm 10/20km DDM SFP$3.85/PCPDFSPT-PB351G-L20D1.25G 1310nm 20km DDM SFP $4.2/PCPDFSPT-PB531G-L20D1.
When a light ray is incident from a medium of refractive index n to the core of index n1, Snell's law at medium-core interface gives
Light is an electromagnetic wave. The visible light partial wavelength range is 390-760 nm. The portion larger than 760 nm is infrared light, and the portion smaller than 390 nm is ultraviolet light. The applications in the fiber are 850 nm,1300 nm and 1550 nm.
Numerical apertureof microscope
where n is the index of refraction of the medium in which the lens is working (1.0 for air, 1.33 for pure water, and up to 1.56 for oils), and θ is the half-angle of the maximum cone of light that can enter or exit the lens. In general, this is the angle of the real marginal ray in the system. The angular aperture of the lens is approximately twice this value (within the paraxial approximation). The NA is generally measured with respect to a particular object or image point and will vary as that point is moved.
This has the same form as the numerical aperture in other optical systems, so it has become common to define the NA of any type of fiber to be
With an accout for my.bionity.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
Numerical aperture is not typically used in photography. Instead, the angular acceptance of a lens is expressed by the f-number, f/#, which for a thin lens imaging an object at infinity is given by
Numerical apertureformula
In microscopy, NA is important because it indicates the resolving power of a lens. The size of the finest detail that can be resolved is proportional to λ/NA, where λ is the wavelength of the light. A lens with a larger numerical aperture will be able to visualize finer details than a lens with a smaller numerical aperture. Lenses with larger numerical apertures also collect more light and will generally provide a brighter image.
Numerical aperture definitionphysics
The fiber can be divided into Step-Index Fiber (SIF) and Graded-Index Fiber (GIF) according to the difference in refractive index profile on the cross section.
Single mode fiber: The center glass core is thin (the core diameter is generally 9 or 10 μm), and only one mode of light can be transmitted. Therefore, the inter-mode dispersion is small, suitable for remote communication, but its chromatic dispersion plays a major role, so that single-mode fiber has higher requirements on the spectral width and stability of the light source, that is, the spectral width is narrower and the stability is better.
4) Light weight and small size. For example: 900 pairs of twisted pairs with 21,000 channels, 3 inches in diameter and 8 tons / KM. The cable with ten times the communication capacity is 0.5 inches in diameter and weighs 450 P/KM.
where n1 is the refractive index along the central axis of the fiber. Note that when this definition is used, the connection between the NA and the acceptance angle of the fiber becomes only an approximation. In particular, manufacturers often quote "NA" for single-mode fiber based on this formula, even though the acceptance angle for single-mode fiber is quite different and cannot be determined from the indices of refraction alone.
In laser physics, the numerical aperture is defined slightly differently. Laser beams spread out as they propagate, but slowly. Far away from the narrowest part of the beam, the spread is roughly linear with distance—the laser beam forms a cone of light in the "far field". The same relation gives the NA,
Multimode fiber: The center glass core is thicker (50 or 62.5 μm) and can transmit multiple modes of light. However, the dispersion between the modes is large, which limits the frequency at which digital signals are transmitted, and is more severe as the distance increases. For example, a 600MB/KM fiber has a bandwidth of only 300MB at 2KM. Therefore, the distance traveled by multimode fiber is relatively close, usually only a few kilometers.
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics.
XPON ONU Series ONU of user side provides interface for services like data, internet video, CATV and VOIP, wifi. By applying Ethernet, GEM protocol and so on, to implement transparent transmission of user data in PON system.
ONU 1GE Series GPON is the latest generations of access network technology. ITU-T G.984 is the standard protocol of GPON. EPON is the latest generations of access network technology. IEEE802.3ah is the standard protocol of EPON. PON networks provides the reliability and performance expected for business services and provides an attractive way to deliver residential services. GPON enables Fiber To The Home (FTTH) deployments economically resulting to accelerated growth worldwide
Numerical apertureof optical fiber
Multimode optical fiber will only propagate light that enters the fiber within a certain cone, known as the acceptance cone of the fiber. The half-angle of this cone is called the acceptance angle, θmax. For step-index multimode fiber, the acceptance angle is determined only by the indices of refraction:
but θ is defined differently. Laser beams typically do not have sharp edges like the cone of light that passes through the aperture of a lens does. Instead, the irradiance falls off gradually away from the center of the beam. It is very common for the beam to have a Gaussian profile. Laser physicists typically choose to make θ the divergence of the beam: the far-field angle between the propagation direction and the distance from the beam axis for which the irradiance drops to 1/e2 times the wavefront total irradiance. The NA of a Gaussian laser beam is then related to its minimum spot size by
This approximation holds when the numerical aperture is small. The f-number describes the light-gathering ability of the lens in the case where the marginal ray before (or after) the lens is collimated. This case is commonly encountered in photography, where objects being photographed are often far from the camera.
GPON ONU Dual WIFI For 2.4G & 5G Now 5g construction has set off a wave of enthusiasm, 5G networks have significant improvements in throughput, latency and number of conn ections, compared with 4G networks. 5G is the next phase of mobile technology and is widely believed faster, smarter and more efficient than 4G.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500