Application of appearance defect inspection for automobile brake discs
I. Introduction: The Necessity of Defect Inspection and Technical Selection
In the field of automotive manufacturing, brake discs, as key safety components of the vehicle's braking system, their quality directly affects the driving safety of drivers. During the production process of brake discs, due to various factors such as different production techniques, production environments, and manual operations, the finished products often have multiple defects. Surface defects mainly include scratches, sand holes, pits, rust, bumps, cracks, foreign objects in the air duct, etc. These defects will directly affect multiple technical indicators of the brake disc, such as strength, hardness, stress, and load-bearing capacity, thereby shortening its service life and bringing serious safety hazards. Therefore, it is particularly important to conduct precise inspection of the appearance defects of brake discs.
At present, the commonly used techniques for detecting surface defects of brake discs include eddy current testing, magnetic particle inspection, infrared testing, X-ray testing and machine vision testing, etc. Compared with other contact measuring tools or manual visual inspection, machine vision inspection, with its non-destructive and non-contact characteristics; With advantages such as high accuracy of inspection data, high efficiency, and significant reduction in labor costs, it is gradually being widely applied in this industry. This technology can quickly capture high-resolution images of the surface of brake discs and use powerful deep learning image processing algorithms to achieve the identification, differentiation of various appearance defects and precise measurement of key dimensions.
2. The Importance of Machine Vision Light Sources
Machine vision technology mainly involves two links: image acquisition and image processing. The quality of the image directly affects the success or failure of the entire system. By taking advantage of the optical characteristics of different types of light sources, such as coaxial light, tricolor light, and ultra-bright frequency flash sources, etc., the contrast between the detected target and the background can be significantly enhanced, ensuring the stability of the imaging quality. This provides a basis for accurate and efficient analysis for subsequent image processing.
In the inspection of appearance defects of brake discs, the light source plays a crucial role in improving image quality. Brake discs have complex curved surface structures. The strong lighting in the workshop can cause ambient light interference. The diverse and tiny defect forms all pose considerable challenges to the imaging quality of the visual system. Inappropriate lighting schemes may lead to problems such as overexposure of the image, uneven brightness, and insufficient contrast, thereby causing the loss or misjudgment of key defect information. Even the most advanced algorithms cannot play their due role.
This article mainly introduces the lighting scheme for 360° all-round appearance defect inspection of air duct brake discs, which can simultaneously meet the requirements of three inspection workstations. Therefore, it is necessary to combine multiple cameras and multiple light sources in a reasonable layout to ensure the acquisition of stable and complete images.
3. Application
To verify the effectiveness of the lighting scheme, special tests were conducted on the defects in different areas of the air duct brake disc. The key schemes and effects are as follows.
3-1.Positive defect inspection effect
The front of the brake disc is large in size (with a diameter of 30-40cm) and has heat dissipation fins (with a height difference of 1-2cm). Ordinary light sources are prone to causing shadows. The combination of a "large depth of field short focal length lens combined with an open-hole surface light source" is adopted. The lens covers the height difference area to avoid out-of-focus, and the surface light source provides uniform illumination to eliminate shadows. Tests show that the 0.5mm scratch and 0.3mm sand hole are clearly black, contrasting sharply with the light gray background without any missed detecments (as shown in Figure 1).
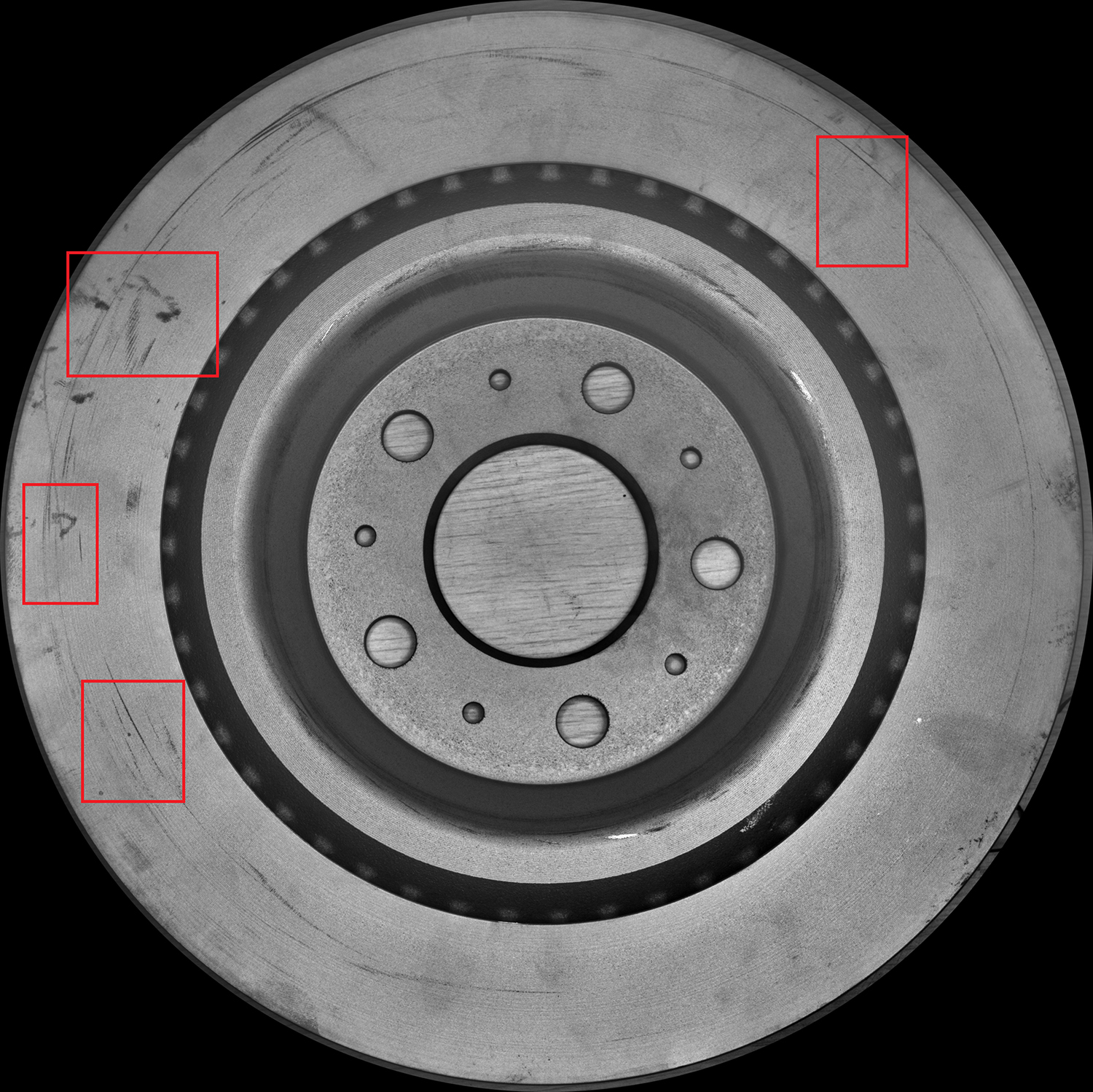
Figure 1 shows the effect of the front defect
3-2.The inspection effect of forward and inclined plane defects
The inclined plane is the transition zone between the front and the side, with a large curvature and many blind spots. Six high-resolution cameras are installed at a 45° Angle around each other, with a 10% overlap in the shooting range. They are combined with a circular shadowless light source to achieve uniform illumination. After image stitching, a panoramic image is formed, and the defect contours are clear (as shown in Figure 2, it is a local image of a single camera).
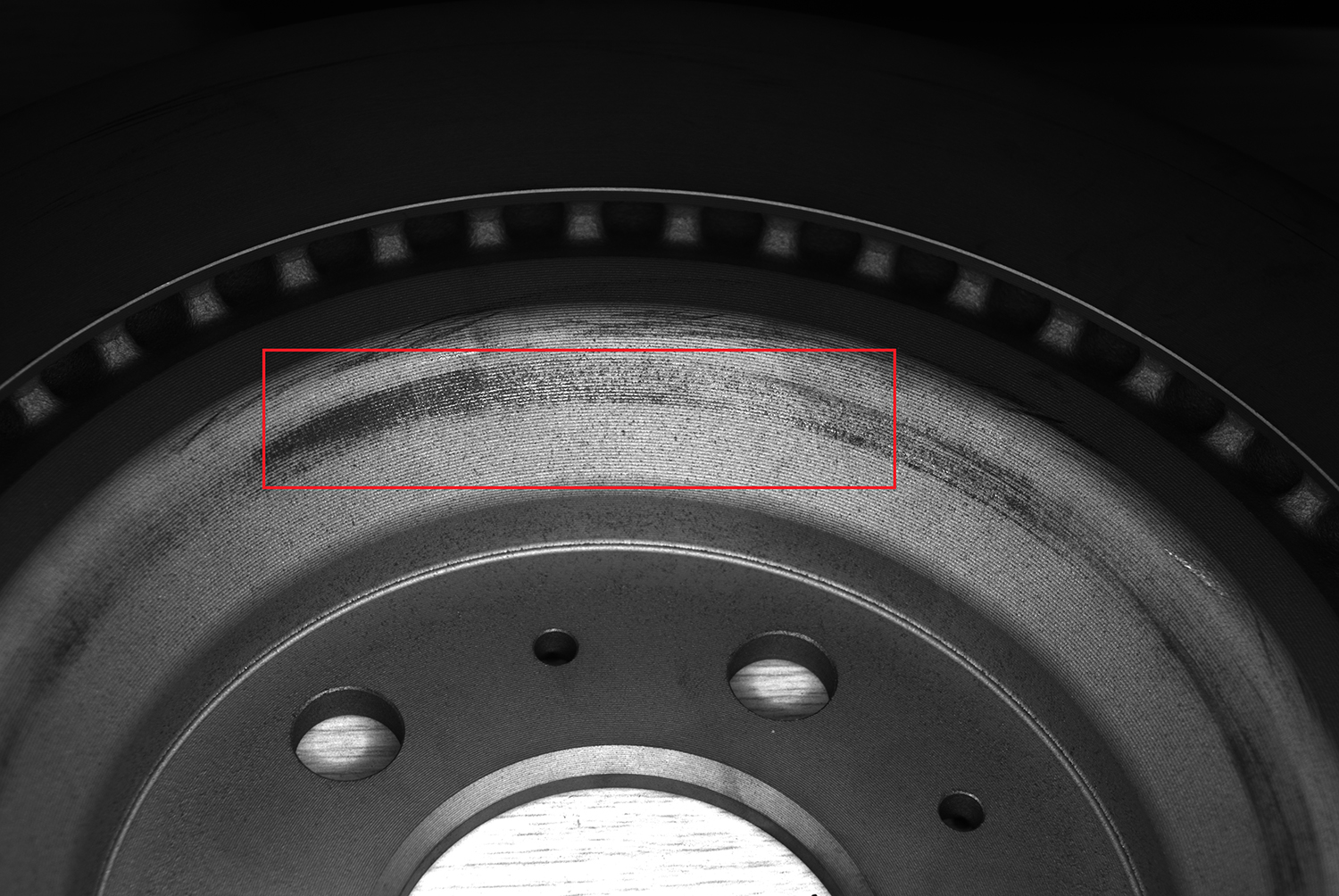

Figure 2 shows the partial image effect of a single camera
3-3.The inspection effect of scratches on the inclined surface of the air duct
The space on the inclined surface of the air duct is narrow (1-2cm wide and 3-5cm deep), making it difficult for ordinary light sources to penetrate deeply. Multiple cameras are installed in a surrounding manner to work in coordination, sharing a single light source for illumination and synchronously controlling the acquisition of images. The contrast with the inner wall of the air duct is obvious, avoiding the missed judgment caused by insufficient light (as shown in Figure 3).
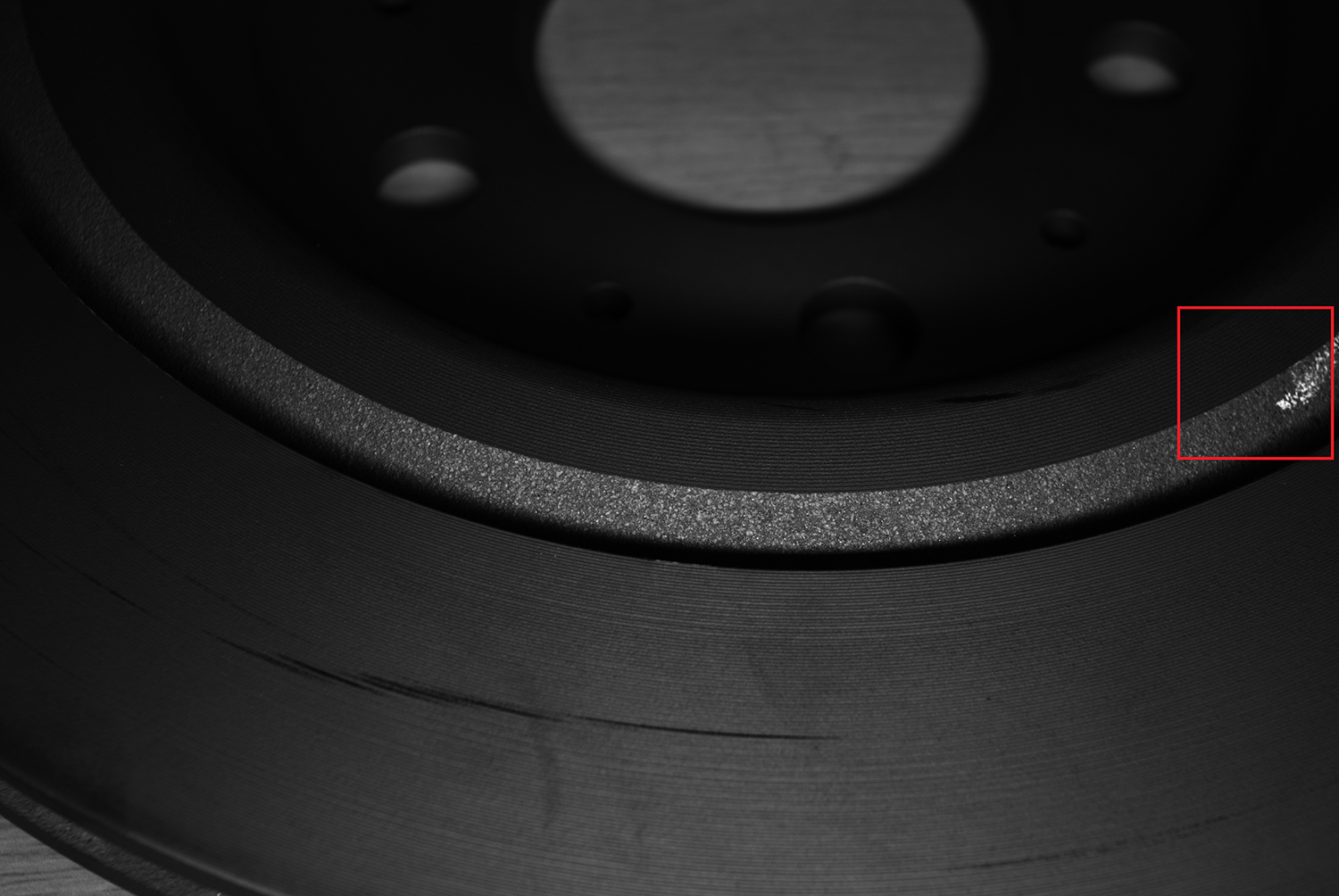

Figure 3 shows the scratch effect at the inclined surface of the air duct
3-4.The inspection effect of back defects
The back needs to be inspected for defects such as sand holes and rust, and its structure is similar to that of the front. The scheme of "large depth of field short focal length lens combined with open-hole surface light source" is adopted. The vertical illumination of the light source is bright enough, shortening the exposure time and avoiding reflection. During the test, the rusted areas and sand holes were all black, the background was light gray and uniform, and the recognition accuracy was consistent with the front (as shown in Figure 4).
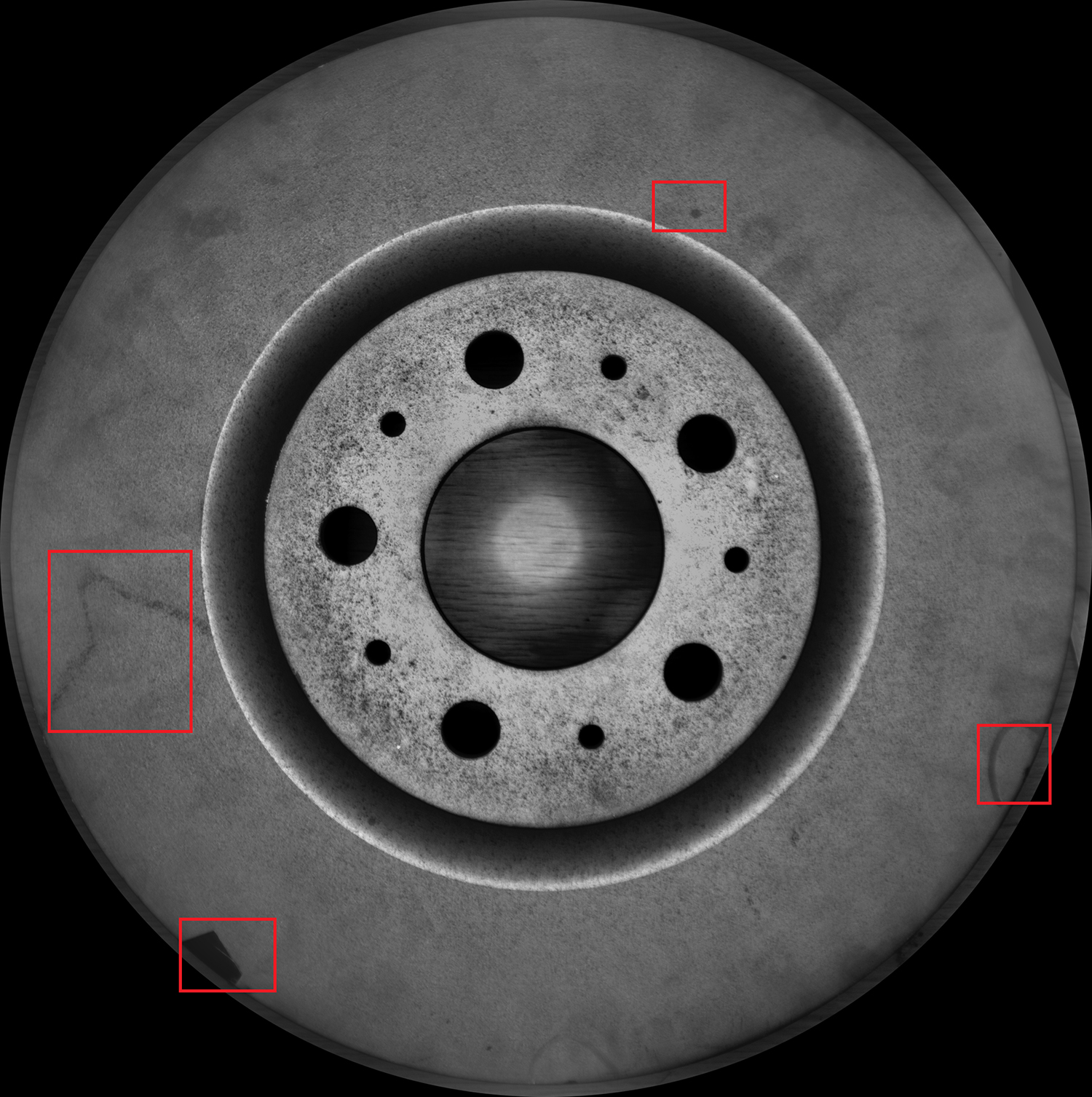

Figure 4 shows the effect of the defect on the back
3-5.The inspection effect of defects on the back, side and inclined surfaces
The inspection range of the back side and back inclined plane is wide and the angles are complex. Six cameras (three for the back side and three for the back inclined) are installed at the same workstation. The angles are adjusted according to the curvature, and they share a single annular shadowless light source. After image denoising processing, dirt and abnormal colors are visible, and the image has no shadows (as shown in Figure 5).
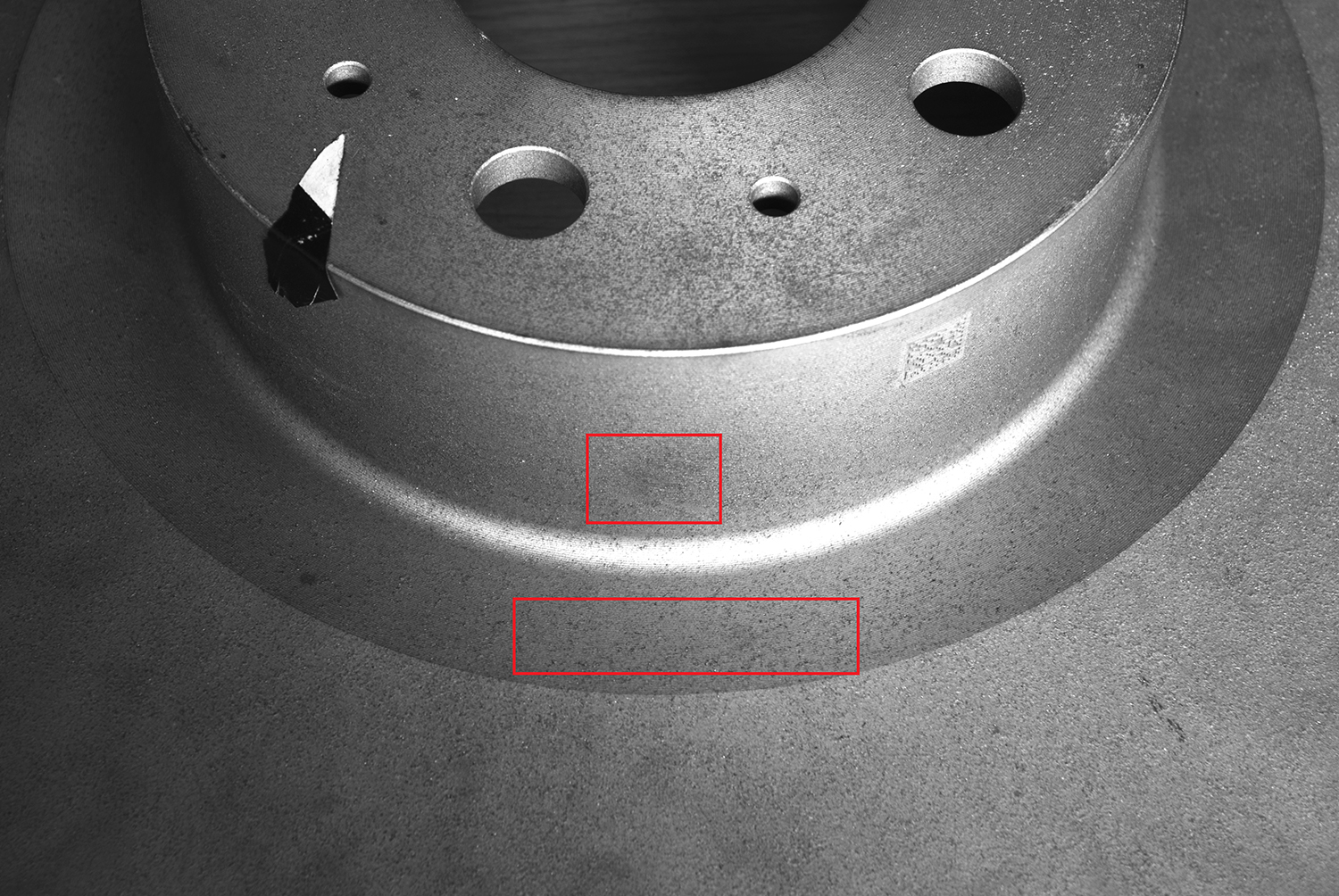
Figure 5 shows the side and slope effects of the back
3-6.The inspection effect of foreign objects in the air duct
The line scanning camera is used in conjunction with the brake disc rotation for shooting, and is equipped with an ultra-bright coaxial light source. Foreign objects within a depth of 3cm in the air duct are detected. The foreign objects appear irregular white and are clearly distinguishable from the background. (As shown in Figure 6)

Figure 6: Foreign object effect in the air duct
4.End
In machine vision inspection, some test conditions for the spatial limits of structures are often encountered. In order to provide customers with the best optical imaging lighting solution, within the limited conditions, the size of the light source, the irradiation Angle, and the feasibility of static or dynamic inspection should be comprehensively considered. In this scheme, for example, although the defects of the brake disc relatively obvious, but due to large size, a single workstation at the same time realize the face inspection requirements, to save the space station, so the installation of the light source structure is particularly important. Since the optical imaging lighting scheme is a key upfront step that determines the performance of the system, the correct selection of the light source imaging scheme can lay a solid foundation for subsequent image processing and defect identification. LOTS at the beginning of the optical imaging scheme evaluation field with rich experience, can provide professional technical support for different test scenarios.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500