Telecentric Industrial Lens Selection
Telecentric lenses are mainly designed to correct the parallax of traditional industrial lenses. They can keep the image magnification constant within a certain object distance range, thereby compensating for the visual effect of "large near and small far" of ordinary industrial lenses and meeting the requirements of precision measurement. Telecentric lenses can be divided into: image-side telecentric optical path, object-side telecentric optical path and bilateral telecentric optical path according to the design principle.
1.Optical Path Principle
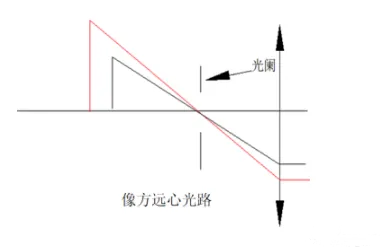
1-1.Like Fang Yuanxin optical path
The optical path diagram of the image-side telecentric optical path is shown in the figure below. It places the aperture stop on the object-side focal plane, and the image-side principal ray is parallel to the optical axis. The convergence center of the principal ray is located at infinity on the image side. The characteristic of this lens is that the magnification is independent of the image distance, which can eliminate the measurement error introduced by inaccurate focusing on the image side.
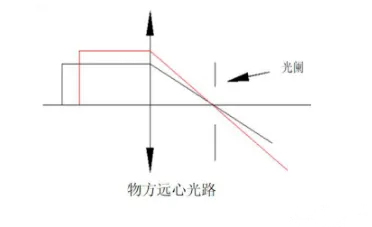
1-2. Object side telecentric optical path
The optical path diagram of the object telecentric optical path is shown below. It places the aperture stop on the image focal plane of the optical system, and the convergence center of the object principal ray parallel to the optical axis principal ray is located at infinity on the object side. The characteristic of this lens is that within a reasonable range of motion, the magnification of the object has nothing to do with the object distance. Even if the object distance changes, the image height will not change, that is, the measured object size will not change. The lens designed according to this principle is an object telecentric lens, or telecentric lens for short.
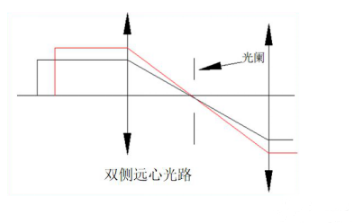
1-3. Bilateral telecentric optical path
The double-sided telecentric optical path is what we often call the double telecentric optical path. The optical path diagram is shown in the figure below. It combines the dual advantages of image-side telecentricity and object-side telecentricity. Within the depth of field, the distance of the object or the distance of the camera will not affect the magnification of the imaging system, that is, the image does not change with the change of object distance and phase distance. The lens designed according to the double-sided telecentric optical path is a double telecentric lens.
2.Lens prototype
2-1. Object-side telecentric lens
As mentioned earlier, the object-space telecentric lens is referred to as a telecentric lens. Common parameters of telecentric lenses include magnification, working distance, object-space resolution, depth of field, numerical aperture NA, etc. Among the many parameters, the most confusing one is probably the numerical aperture NA.
The numerical aperture NA mentioned in the telecentric lens refers to the image-side numerical aperture. The larger the numerical aperture NA value, the better the lens resolution and brightness. The corresponding relationship between the numerical aperture NA and the object-side resolution is:
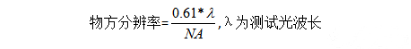
2-2.Bi-telecentric lens
The common parameters of bi-telecentric lenses are easier to understand than those of telecentric lenses. They include magnification, object resolution, working distance, depth of field, telecentricity, etc. Among these parameters, the corresponding relationship of each parameter is consistent with the corresponding relationship of telecentric lenses. The only one that needs special explanation is probably telecentricity. It is one of the important parameters for evaluating the quality of telecentric lenses and bi-telecentric lenses.
Telecentricity refers to the angle at which the main light deviates from the optical axis. The smaller the angle, the better the telecentricity and the smaller the magnification error of the lens. In the measurement process, it is manifested as: within the depth of field, the magnification of the object is the same at different working distances. It is an important factor to make up for the disadvantage of ordinary industrial lenses that they are "larger near and smaller far".
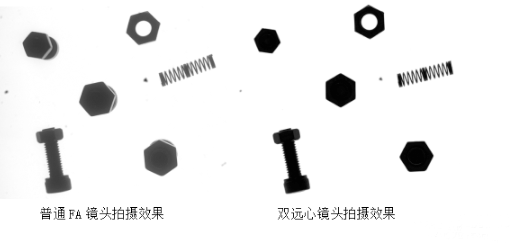
3.Advantages of Bi-telecentric Lenses
Telecentric lenses and bi-telecentric lenses are often used in the field of precision measurement. Bi-telecentric lenses have a greater depth of field than telecentric lenses. When other parameters are the same, the working range of bi-telecentric lenses is larger than that of telecentric lenses, and the observable range is wider. When the height difference of the objects we need to observe is relatively large, bi-telecentric lenses can be given priority.
Compared with telecentric lenses, bi-telecentric lenses have higher telecentricity. In the selection process for precision measurement, if the accuracy of the observed object is very high, bi-telecentric lenses will be a better choice.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500