This New Autonomous Drone for Cops Can Track You In ... - can police use drones
The strategic use of fire hoses enhances the agility and reach of firefighting efforts, enabling responders to address fires in diverse environments and mitigate potential challenges posed by the fire’s scale and intensity.
In smoke filled environments, these devices play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of firefighters by providing a continuous supply of clean air.
Constructed from fire-resistant materials, fire blankets emerge as versatile tools in firefighting and emergency response.
The strategic and well-coordinated utilisation of firefighting equipment remains a cornerstone in the battle against the unpredictable and destructive force of fires.
Beyond their mobility, the specialised equipment on these vehicles equips firefighters with the resources needed to combat fires of varying scales.
By offering real-time insights into the intensity and distribution of heat, these devices empower firefighters with the ability to make informed decisions, optimise resource allocation, and execute targeted strategies for suppressing fires and conducting search and rescue operations.
Only dangerous goods that are unstable decompose violently or could react dangerously will need to be segregated. Generally, dangerous goods that are unstable are not allowed to be transported in a mixed load or in the same package.
Visible tape with the clear directive “Do Not Cross” is utilised to cordon off unsafe areas and control access to the fire scene.
IATADG segregation chart
Protective gear, including fire suits and gloves, plays a pivotal role in ensuring firefighters’ safety as they confront flames.
One prominent trend is the integration of smart technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, into firefighting gear.
An innovative self-activating fire suppression system, the Fire Extinguisher Ball offers a unique approach to firefighting.
Imdgsegregation chart
The specialised design of firefighter gloves prioritises both dexterity and protection, allowing firefighters to navigate challenging situations while safeguarding their hands from the formidable heat generated in the course of combating fires.
Beyond enhancing visibility, the removal of smoke and toxins creates a safer working environment, allowing firefighters to operate more efficiently and with reduced exposure to hazardous substances.
Positioned strategically, these buckets serve as immediate response tools, offering a swift and accessible means to douse small fires or control sparks.
Some firefighting equipment is not directly used to directly put out fires, but it used to improve the safety and efficiency of firefighters.
As technology advances, so does our ability to respond effectively to fire emergencies, ensuring a safer and more resilient future for communities worldwide.
Their ability to swiftly survey large areas and capture critical information aids in strategizing and responding effectively to incidents.
The continuous advancements in firefighting equipment underscore a commitment to improving the efficiency, safety, and overall effectiveness of firefighting operations.
The Fire Extinguisher Ball’s ability to initiate fire suppression independently makes it a valuable addition to fire safety measures, ensuring a rapid response even in scenarios where immediate human intervention may be difficult.
The future of firefighting equipment holds exciting possibilities, driven by advancements in technology, materials, and design.
This includes wearable sensors and augmented reality visors that provide real-time data to firefighters, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making.
The reliability and functionality of these apparatuses exemplify their vital role in preserving the well-being of firefighters and ensuring their ability to execute effective firefighting and rescue operations in environments where clean air is a precious commodity.
The carrier should have a safe operating procedure (SOP) for “load planning” which includes segregation of consignments when multiple consignments will be collected en route. Meanwhile, if a consignor is preparing packages with multiple dangerous goods (e.g., consolidation bins or overpacks), then the consignor’s SOP must include instructions on how to manage the packaging of incompatible dangerous goods.

With layers designed to withstand the harsh conditions of a fire, these suits are crucial in ensuring the safety and well-being of firefighters.
Centurian Media Limited (CML) is committed to creating a diverse environment and is proud to be an equal opportunity employer. Our clients, suppliers, along with all qualified applicants that we receive for employment, fixed contract or freelance projects receive consideration without regard to race, colour, religion, gender, gender identity or expression, sexual orientation, national origin, genetics, disability, age, or veteran status. CML is also committed to compliance with all fair employment practices regarding citizenship and immigration status.
Dangerous goods loadingchartfor air FedEx
In emergency situations, they offer protection by wrapping around individuals, creating a temporary shield against flames and heat.
By generating a controlled and directed flow of air, these fans contribute significantly to improving visibility for firefighters within confined areas.
Comprising a multi-layered construction, these suits act as an impermeable barrier, creating a formidable shield between the firefighter and potentially harmful substances.
Firefighters undergo rigorous training to understand the capabilities and limitations of each tool, ensuring a synchronised and effective response to diverse fire scenarios.
Firefighters select the appropriate extinguisher based on the fire’s nature and discharge the firefighting agent with precision, aiming at the fire’s base.
The continuous evolution of firefighting equipment reflects a commitment to enhancing the capabilities of those who bravely confront the unpredictable nature of fires.
Crafted from materials resistant to high temperatures, they enable firefighters to handle hot surfaces and materials with confidence.
This versatile and effective tool finds particular utility in scenarios involving hazardous materials or potential chemical fires, where the quick containment of flammable liquids is essential to mitigate the risk of fire escalation.
The specialised construction of fire suits exemplifies the commitment to providing a robust defence against the hazards encountered in the line of duty, reinforcing the resilience of those who bravely confront the flames.
These signs delineate evacuation routes and indicate the locations of firefighting equipment, guiding occupants to safety during fire emergencies.
Each tool plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of firefighters and the effectiveness of fire suppression efforts.
Deployed to manage traffic and create clear pathways for emergency vehicles, traffic cones are essential in ensuring unimpeded access for firefighting teams.
Crafted from fire-resistant materials, these suits envelop firefighters in a protective barrier during the most intense operations.
Compact and portable, light pumps are indispensable for transporting water to areas inaccessible to larger firefighting vehicles.
Hose Jets represent heightened firefighting capabilities, requiring the collaboration of two firefighters to handle their extra power.
This adaptability allows firefighters and individuals to employ the most suitable extinguishing agent, enhancing the effectiveness of fire suppression efforts across a wide range of fire scenarios.
These crucial elements are essential for firefighters in their mission to extinguish flames, rescue individuals, and mitigate the impact of fire emergencies.
Specialised fire doors are meticulously designed to resist fire and smoke, acting as effective barriers to limit their spread within a building.
Except for specific requirements about the loading of explosives, the TDG Regulations do NOT directly address the transportation of incompatible dangerous goods. However, Section 5.4 in Part 5 of the TDG Regulation states:
These specialised tools offer an elevated force and flow, allowing firefighters to exert increased control over the extinguishing process.
Positive pressure ventilation fans are devices designed to create airflow that effectively removes smoke and toxins from enclosed spaces.
Segregation applies to the means of containment (MOC), package, an overpack, and the means of transport (MOT). The general guidance for dangerous goods that are allowed to be shipped (i.e., they are not forbidden) includes the following:
Note: The information below is provided as guidance only. Always check with Transport Canada and the TDG Act and Regulations to ensure compliance.
This ingenious device is particularly advantageous in confined spaces or areas with limited accessibility, where traditional firefighting methods might face challenges.
A means of containment (MOC) should be segregated according to the carrier’s loading plan. The carrier’s TDG specialist should determine the incompatibility between the dangerous goods that are intended to be transported. As different consignments are loaded, the loader or driver should follow the safe operating procedure (SOP). The SOP should include information on how to carry out a segregation check:
In this article, we’ll explore the diverse list of firefighting equipment, shedding light on their functions and importance in the face of fire emergencies.
Drones not only contribute to the safety and efficiency of firefighting operations but also offer a technological edge, elevating the precision and speed with which responders can assess, plan, and execute strategies in the dynamic context of firefighting scenarios.
Flamezorb’s ability to address such specific challenges makes it a valuable asset in the firefighting arsenal, contributing to the overall effectiveness of fire suppression efforts in diverse and complex situations.
DGcompatibilitychart
5.4 A person must load and secure dangerous goods in a means of containment and must load and secure the means of containment on a means of transport in such a way as to prevent, under normal conditions of transport, damage to the means of containment or to the means of transport that could lead to a release of the dangerous goods.
Firefighting equipment is the lifeline for those who risk their lives to protect communities and properties from the devastating impact of fires.
This may involve the development of specialised tools for wildfires and improved strategies for early detection and prevention.
Dangerous goodsSegregation Chartuk
Their portability and adaptability make them fundamental in addressing the diverse challenges posed by fires in varying structures and scenarios, contributing to the overall success and safety of firefighting operations.
The collaborative efforts of researchers, engineers, and firefighters promise a future where technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of firefighting operations, ultimately better equipping first responders to address evolving challenges.
Their simplicity makes them an essential first line of defence, providing an uncomplicated yet crucial tool in the initial stages of firefighting.
Specially designed for the demanding challenges of firefighting, a fire suit is more than a mere uniform – it’s a shield against extreme heat and flames.
The diversity in extinguisher types ensures flexibility in addressing different classes of fires—whether involving ordinary combustibles, flammable liquids, electrical equipment, or gases.
Explosives are assigned a compatibility group. See Column 3 in Schedule 1. The compatibility groups are described in Appendix 2 of Part 2 in the TDG Regulations. The Table from Section 5.7 in Part 5 of the TDG Regulation lists the explosives compatibility groups that can be transported together. It is reproduced below with some minor modifications of the column titles.
Chemicalsegregation Chart
From traditional tools that have stood the test of time to cutting-edge technology ensuring efficiency and safety, each item plays a crucial role in combating fires and protecting lives.
These specialised garments shield against extreme heat, providing a critical barrier between the firefighter and the hazardous environment.
From traditional tools like fire extinguishers to cutting-edge technology such as thermal imaging cameras, each item plays a crucial role in a firefighter’s arsenal.
For example: the assigned compatibility group for UN0004 in Schedule 1 is 1.1D. This explosive can be transported together with other explosives that have the following assigned compatibility letter/group: C, D, E, N, S. NOTE: If an explosive (e.g., UN0074) is assigned to the compatibility group “A”, then such an explosive cannot be transported with any other explosive.
These doors are critical components of passive fire protection systems, providing crucial time for evacuation and minimising the potential for fire extension.
Whether extending to reach upper floors of buildings or providing a stable platform for rescue operations, ladders enhance the agility and effectiveness of firefighting teams.
As one of the most prevalent tools in large-scale firefighting, fire hoses are indispensable for firefighters combating significant flames.
They play a crucial role in extrication operations, enabling swift and precise interventions in situations where immediate access is essential.
Additionally, the use of robotics in firefighting, ranging from autonomous vehicles to robotic firefighting assistants, is on the horizon.
Their purpose extends beyond conventional firefighting gear, addressing the specific challenges posed by chemical fires and the release of dangerous gases.
With the ability to adjust the jet stream, firefighters enhance precision in directing water onto the flames, addressing specific firefighting requirements.
These versatile devices play a pivotal role in firefighting operations by enabling firefighters to access elevated areas, conduct rescues, and navigate challenging environments.
As climate change intensifies, firefighting equipment is likely to evolve to cope with more frequent and severe wildfires.
Protective gear, such as fire suits and gloves, shields firefighters from extreme heat, allowing them to navigate hazardous environments.
(3) Unless able to separate properly, do NOT transport Class 4.3 dangerous goods with any aqueous (water-containing) solutions together.
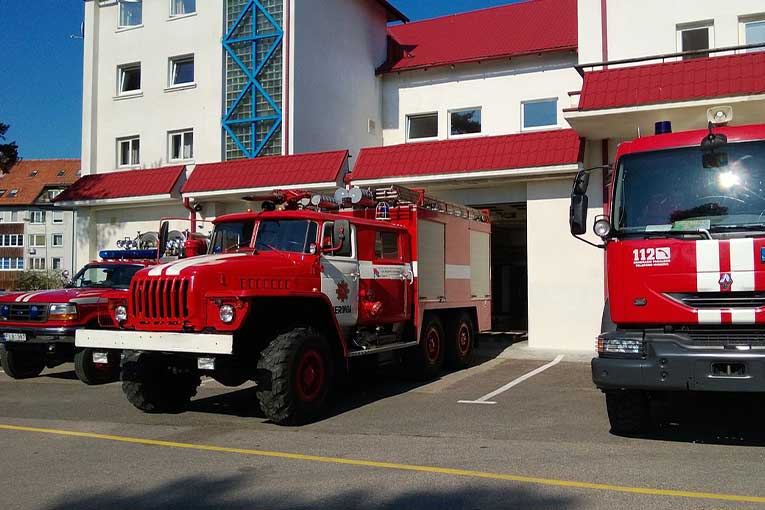
These vehicles carry essential firefighting tools, water tanks, and hoses, ensuring a swift and effective response to fire emergencies.
Flamezorb, a granular substance, serves as a rapid-response tool in firefighting by efficiently absorbing flammable liquids.
Although every effort is made to ensure the accuracy, currency and completeness of the information, CCOHS does not guarantee, warrant, represent or undertake that the information provided is correct, accurate or current. CCOHS is not liable for any loss, claim, or demand arising directly or indirectly from any use or reliance upon the information.
The term segregation is used to mean “to put apart from the rest,” “isolate,” or “physically separate from the rest.” Dangerous goods might need to be segregated when:
Their robust construction and power make them essential for situations where conventional access methods are insufficient.
The letter “S” indicates that dangerous may not be loaded, transported, or stored together in the same transport vehicle during the course of transportation unless they are separated in a manner so the dangerous goods will not come into contact with one another in case of an incident where the packages will be leaking. NOTE: Even if separation methods are used, Class 8 (corrosive) liquids may not be loaded above or adjacent to Class 4 (flammable) or Class 5 (oxidizing) materials. However, this requirement does not apply to Class 4 and Class 5 dangerous goods that, when in contact, are known NOT to cause a fire or a dangerous evolution of heat or gas.
Segregation does not necessarily refer to keeping dangerous good package A away from dangerous good package B, such as the opposite side of a truck trailer. An accident with A may cause a release of B, or a reaction from one might affect the other.

Strategically positioned, their rapid response significantly contributes to controlling fires, preventing their escalation, and protecting lives and property within structures.
By providing an encapsulating defence, gas-tight suits empower firefighters to navigate complex and perilous environments, ensuring their safety while enabling effective response and mitigation in the face of chemical hazards.
The adaptability of fire blankets extends their utility beyond traditional firefighting scenarios, making them valuable assets in various emergency situations where rapid response and versatile tools are paramount to ensuring the safety of individuals and effectively addressing evolving challenges.
There are many different types of fire extinguisher, each containing specific firefighting agents such as water, foam, dry powder, or CO2.
These cones play a crucial role in maintaining order and facilitating the rapid movement of emergency vehicles to and from the incident scene.
When exposed to flames, the ball bursts autonomously, releasing a fine powder that swiftly and effectively extinguishes the fire.
NOTE: Some incompatible dangerous goods may be allowed to be transported together when their quantity is below a specific threshold limit or when limited quantity packaging is used. A threshold limit can be established by a safety engineer and in consultation with the TDG Directorate.
Their length and adaptability empower firefighters to reach remote or challenging locations, providing a versatile means of effectively delivering water to suppress fires.
The use of firefighting equipment is not only reliant on the tools themselves but also on the skill, training, and coordination of firefighting teams.
Canada’s TDG Regulations do not include a compatibility table for dangerous goods (the Regulations do include a compatibility table for consignments that consist of explosives only).
Firefighting equipment is what helps firefighters to extinguish flames, ensuring the safety of lives and property, and the varied list of firefighting equipment shows how diverse firefighting really is.
Thermal imaging cameras aid in locating individuals trapped in smoke-filled environments and identifying hotspots that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Firefighting equipment encompasses a diverse range of tools, devices, and protective gear specifically designed to combat and manage fires effectively.
Drones provide aerial views, enhancing situational awareness for better decision-making, while thermal imaging cameras aid in locating individuals and identifying hotspots within a fire.
Innovations in materials science are shaping the development of more lightweight yet durable protective gear, addressing comfort and mobility concerns for firefighters.
It manages the entry and exit procedures of firefighters equipped with breathing apparatus, ensuring systematic and safe operations in environments with compromised air quality.
Firefighters, equipped with a diverse array of tools, employ a systematic approach to address different scales and types of fires.
This course is updated to meet Transport Canada's educational requirements under the TDG Act and Regulations, for all persons who handle, offer for transport, or transport dangerous goods by road. This course includes the SOR/2020-23 TDG regulatory amendment.
These unmanned aerial vehicles, equipped with advanced cameras, offer invaluable aerial views that significantly enhance fire assessment capabilities.
Essential components of early warning systems, smoke detectors are devices that promptly detect smoke, alerting occupants to potential fire hazards.
This updated course provides an overview of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) Act and Regulations. It reflects the most recent regulatory amendments in (SOR/2023-155) and (SOR/2023-206) published in the Canada Gazette, and other significant content updates.
Yes. There are a number of commercial software applications available for loading that take into account the compatibility of dangerous goods. These applications are mode (e.g., air, marine, road) and jurisdiction-specific (e.g., Canada, USA). Thus, when deciding to use an application, the software application needs to be selected carefully.
(2) Do NOT transport dangerous goods together with food, feeds or other edible materials on the same means of transport (e.g., vehicle).
These gloves are essential for firefighters, offering crucial hand protection in the dynamic and intense environments encountered during firefighting operations.
Whether used by trained personnel or as part of fire safety measures in public spaces, fire buckets play a fundamental role in empowering individuals to take immediate action and contribute to fire containment efforts.
When transporting dangerous goods, there is always a risk of spills. If incompatible substances mix because the packages get damaged in an incident, a chemical reaction may produce enough heat to cause fire or explosion or possibly release dangerous gases. For example, chlorine gas is released when a spill of sodium hypochlorite solution comes into contact with a sulphuric acid spill. Chlorine gas is classified with the following TDG class and subsidiary classes in Schedule I of the TDG Regulations: 2.3 (5.1) (8). Thus, chlorine gas is dangerous because it is toxic, can oxidize other materials, and is corrosive.
Note: The compatibility letter for the dangerous good "UN0029 DETONATORS, NON-ELECTRIC for blasting" is next to the TDG Class (see Column 3 in Schedule 1). The letter "B" next to "1.1" is the compatibility letter.
Table 1: Sample segregation and separation chart for road transportation of dangerous goods (1,2,3)NOTE: The following table is provided as informational only. It is not an interpretation of the TDG Act or regulations. Always consult with TDG professionals and reliable chemical information sources when making your determination regarding compatibility.
Dangerous goodssegregation chartPDF
These pumps enhance operational flexibility, providing firefighting teams with the ability to establish water supply points in diverse environments.
The collaborative use of Hose Jets reflects a strategic approach, amplifying the effectiveness of firefighting efforts in scenarios where a more robust and targeted water delivery is essential to combat fires of greater scale or intensity.
Registered office: 71-75 Shelton Street London Greater London WC2H 9JQ UNITED KINGDOMOperating office: The Maidstone Studios, New Cut Road, Vinters Park, Maidstone Kent ME14 5NZ
This tape ensures the safety of both emergency responders and the public by preventing unauthorised entry into potentially hazardous zones.
Although Canada has not issued a compatibility or segregation chart, a number of different international jurisdictions have compiled such charts in their dangerous goods or hazardous material transport regulations. Caution must be used when following these charts as they are based on the dangerous good’s TDG class. Accurate compatibility charts are those that are based on the chemical properties of the dangerous goods.
(***) Class 9 dangerous goods have varied properties, and thus, it is best to check the SDS regarding hazards and get advice from the supplier.
IATADG segregation chart2024
Ideally compatibility charts for loading plans are created by using multiple sources, such as the reactivity section in the dangerous good’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS), chemical reference books on reactivity, and consultation with the supplier or shipper. For example, both hydrochloric acid (UN1789) and sodium hydroxide (UN1823 for solids and UN1824 for solutions) are dangerous goods with an assigned TDG Class 8 in Schedule 1 of the TDG Regulations. Although hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are assigned to the same TDG class, they are NOT compatible. If these two dangerous goods come into contact with one another, there will be a generation of considerable heat, which could result in the creation or sputtering of corrosive vapours and mists.
Firefighting equipment is not only about extinguishing flames but also about ensuring the safety of those on the front lines.
Whether navigating through urban environments or remote locations, these vehicles enhance the reach and capabilities of firefighting teams, playing a vital role in the timely containment and suppression of fires to protect lives and property.
The hoses allow firefighters to direct water effectively, reaching inaccessible areas, while sprinklers automatically release water upon detecting excessive heat, contributing to fire containment.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500