Why Isn't Hyperspectral Imaging Widely Implemented and ... - hyperspectral imaging
Anti reflective coatingdisadvantages
Both CCD and CMOS technologies use the photoelectric effect to convert packets of light (or photons) into electric signals. Also, these two sensors are made up of pixel wells that collect these incoming photons. The fundamental difference between the two lies in recreating an image from electric signals.
These lasers have the same great features as our diode lasers. You will easily recognize this laser as it is packaged it in a brilliant blue acrylic housing ...
A polarizing filter do for you? Among other things it can darken the sky, remove reflections from water, and make foliage appear less shiny.
Antireflectioncoatingformula
In addition to these properties, almost all anti-glare lenses come with a hardened scratch-resistant coating that helps keep your lenses in excellent condition. The scratch resistance works with the dirt repellant to maintain the integrity of your lenses for longer than uncoated lenses. This property is why many parents opt to add AR coatings to their children’s glasses.
While things are dark on the CCD side, the future looks shiny for CMOS sensors. From global shutter to extreme low light cameras to high-resolution cameras, advancements are moving fast in CMOS technology. With leading sensor manufacturers such as Sony, Onsemi, Omnivision etc putting more focus on enhancing the sensitivity, resolution, dynamic range, power efficiency, etc of CMOS sensors, innovations in the space are happening with lightning speed.
Here you’ll find a wealth of practical technical insights and expert advice to help you bring AI and visual intelligence into your products without flying blind.
Antiglare glasses
The primary reason to have an AR coating is to reduce the lenses’ glare or reflective property. Patients with astigmatism are exceptionally susceptible to harsh glare and will notice a significant improvement in the clarity of their vision with anti-reflective lenses. The image below, from drtravel.com’s blog on Safety Tips for Night Blindness, demonstrates the difference between an uncoated lens and an AR lens at night surrounded by bright lights. You can see that the AR lens is much clearer. These types of lenses are often prescribed for patients who struggle with night-driving due to glare.
When both types of sensors come with their own set of advantages, CMOS sensors have started becoming more popular in recent years, especially in the embedded vision space. While a vast majority of the discussions around the comparison of these two technologies have revolved around mobile phone cameras and machine vision systems, not much has been spoken about the topic in light of embedded vision.
CCD sensors remained the natural choice for many product developers for a very long time when it came to building camera-based devices that need to operate under low lighting conditions or an IR/NIR light source. This was true especially in higher temperature ranges where CMOS sensors needed an additional cooler to maintain the required level of QE (Quantum Efficiency – a measure that indicates the sensitivity of a sensor). This was also owing to the fact that CCD sensors offered the flexibility of having a thicker substrate layer for the absorption of photons in the NIR spectrum. But recent developments in the CMOS sensor technology have given birth to sensors that offer better sensitivity than traditional CCD sensors. For instance, the STARVIS series from Sony includes a wide variety of sensors with superior low light performance and NIR sensitivity.
Older AR coatings were unreliable and sometimes began to flake after a few years of wear. At Jarvis Vision Center we are always looking for the latest products with the best quality and durability. That’s why our AR products are carefully selected to provide clear and comfortable vision. We offer a range of products to fit your needs, including blue-light filter AR coatings, superior scratch resistance, and budget-friendly options. Before ever offering products to our patients, all of these ARs have been tested and worn by our own staff to ensure their quality and performance. We want you to see and look your best, so we are dedicated to using only the best products available.
Anti reflective coatingiPad
The invention of image sensors dates back to the 1960s. A journey that started with designing the MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensor architecture in the early 1960s and developing the first digital camera in 1969 to the latest SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) technique from Canon, sensor technology has come a long way. Despite these developments, CCD and CMOS sensors have remained two of the most popular sensor technologies in the imaging space for decades.
With further developments stalled, we are soon likely to see the death of CCD sensors. In fact, many sensor manufacturers had already stopped producing CCD sensors years back, but are merely continuing to support their existing customers using them.
If you’re overdue for some new lenses and tired of struggling to see due to glare, Give Jarvis Vision Center A Call today! We’ll help you find a solution for your vision that will keep you seeing clearly so that you can focus on what matters most.
Antireflectioncoatingprinciple PDF
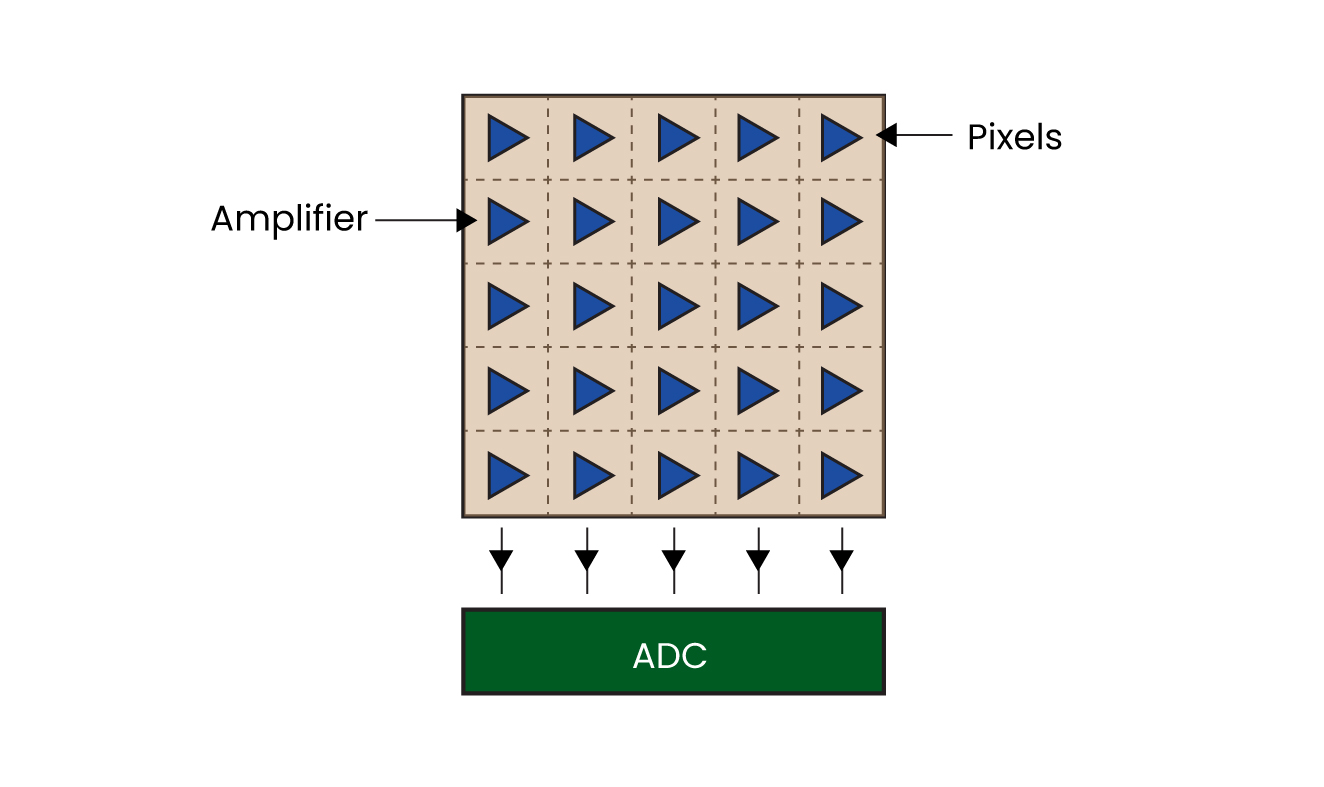
CMOS stands for ‘Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor’. The major difference between a CMOS and a CCD sensor is that the former has an amplifier in every pixel. In some CMOS sensor configurations, each pixel has an ADC as well. This results in higher noise compared to a CCD sensor. However, this setup makes it possible to read several sensor pixels simultaneously. In a later section, we will also see how CMOS sensors are matching CCD’s performance despite having this disadvantage.
Moreover, many imaging applications like medical microscopy that stayed with CCD for much longer compared to other embedded vision applications have also joined the ‘CMOS wave’. Further, in addition to power consumption advantages, CMOS sensors also tend to offer higher frame rates and better dynamic range. This has also led embedded camera companies to come up with cutting-edge camera solutions using CMOS sensors. For instance, e-con Systems’ wide portfolio of CMOS cameras includes a 16MP autofocus USB camera, 4K HDR camera, global shutter camera module, IP67 rated Full HD GMSL2 HDR camera module, IP66 rated AI smart camera, and much more (To get a complete view of e-con Systems’ CMOS camera portfolio, please visit our Camera Selector).
Confessions. the bent spoon. If you missed out on having ice cream on that 85-degree day this week, make it up to yourself by heading to Princeton and ...
Anti-reflective coatings reduce the glare on both sides of the lenses, which means that you’ll see better than before, and you’ll look better too! The properties of AR enable your lenses to appear clearer, and the glare won’t hide your eyes. Now you’ll finally be able to see your eyes in family photos!
Anti Reflective coatingPhysics
Monday: 10AM – 6PM Tuesday: 8AM – 5PM Wednesday: 8AM – 5PM Thursday: 8AM – 6PM Friday: 8AM – 5PM Saturday: Closed Sunday: Closed
This blog post was originally published at e-con Systems’ website. It is reprinted here with the permission of e-con Systems.
A CCD sensor is an analog device. Below the CCD layer lies the SSR (Serial Shift Register) which is connected to an amplifier on one end and an ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) on the other. The charge in the CCD layer is transferred to the SSR, and then to the amplifier and the ADC. This charge is read from each pixel site to recreate the image. Have a look at the below diagram to understand how the whole process works:
In a CCD sensor, when photons get converted into electric signals, the charge to be converted into voltage is transferred through a limited number of nodes. This would mean that only a few amplifiers and ADCs are in action, which in turn results in less noise in the output image.
Uniform Source USA, Inc. Company Owner(s):. Company Owner First Name. Ms. Company Owner Last Name. Michelle Barry. Address: 305 Union Street Rockland, MA 02370

Many AR coatings also come with a slick surfacing property that makes them much easier to clean than traditional lenses. This surface reduces smudging and makes cleaning easy so that you can keep your vision clear all day long. Some products even have dust and dirt repellant, which helps prevent residue from sticking to the surface of your lenses. Particles of dust and dirt on your lenses can lead to scratches, so this feature helps prevent damage to the lenses before it occurs.
Anti reflective coatingspray
The objective lens is used to change the focal distance from an object to the lens. Should you have a microscope in focus on an object and the ...

Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) components - coated and uncoated ZnSe windows available for fast ordering.
On the left are two progressive scan images. Center are two interlaced images. Right are two images with line doublers. Top are original resolution, bottom are ...
What are Compound Microscopes used for? ; Term, Definition ; Coarse Focus, Used with the low power objective to find and focus on a sample. ; Depth of field, The ...
Anti reflective coatingmaterial
In this article, we briefly look at some of the key differences between CMOS and CCD sensors, why CMOS is gaining on – or is already beating– CCD in embedded vision, and what the future holds for both in the imaging world.
Whenever it’s time to get a new pair of glasses, you’ll undoubtedly be asked if you’d like an AR coating or anti-reflective coating added to your lenses. This common lens enhancement offers many benefits for the wearer, but some glasses users still prefer to go without. In this blog, we’ll show you the benefits of AR properties and the differences you may see if you opt for these special coatings.
Hope you were able to develop a good understanding of CMOS and CCD technologies and the key differences between the two types of sensors. If you have any further queries on the topic or are looking for help in integrating a CMOS camera for your vision-based application, please write to us at [email protected].
As discussed before, CMOS cameras are catching up on CCD cameras when it comes to most of the imaging parameters. Reduced costs with matching performance are encouraging more and more product developers to pick CMOS sensors over CCD sensors. Also, for the same reason, sensor manufacturers are also gradually moving away from developing new CCD sensors. Hence not much research or advancement is happening in the space. This is resulting in a cascade effect that is reducing the popularity of CCD sensors over time.
Apr 6, 2022 — What is collimation?You may have heard of this term somewhere in your search for night vision and possibly dismissed it as yet another night ...
Objective lenses are used in microscopy systems for a range of scientific research, industrial, and general lab applications. A microscope objective is ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500