What You Need to Know About Eyeglass Lens Coatings - lens anti reflective coating

Using our advertising package, you can display your logo, further below your product description, and these will been seen by many photonics professionals.
Optical elements and systems also produce other kinds of optical aberrations, such as astigmatism and coma, which can lead to non-ideal performance of focusing or imaging devices. There are sophisticated optical design principles which allow one to minimize different kinds of aberrations of optical systems, even when using only spherical optical elements. However, the number of required optical elements and consequently the number of involved optical surfaces may be substantially increased compared with what would be required just to obtain the basic optical function.
Asphericlenses advantages disadvantages
There are also lenses which are at the same time aspheric and achromatic. For example, one can combine a spherical glass lens with an aspheric polymer part. There are even hybrid aspheres, combining refractive and diffractive properties.
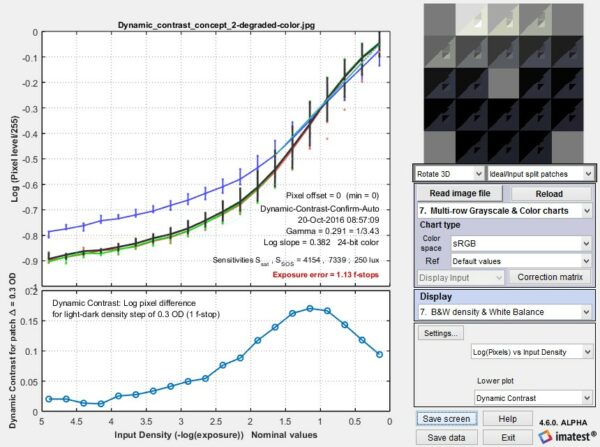
The physical chart consists of layers of 8×10 inch photographic film. The chart contains 20 large patches with densities ranging from base + 0.15 to base + 4.90 (OD = Optical Density) in steps of 0.25 OD, equivalent to 95 dB. (If the lightest and darkest small patches are included, the total density range is 5.1 OD = 102 dB.) Inside each large square there are four color squares: light and dark gray, red and blue. The gray patches are 0.15 OD above and below the surrounding square. The difference, 0.30 OD, is a 2:1 contrast ratio.
Asphericmeaning
Some computer-controlled fabrication techniques are well suited for making custom aspherics. In some cases, components which are normally used in spherical form are subject to additional treatment where they are turned into aspherics.
Precision aspheric lenses reduce visual defects and produce clearer images, making them ideal for many applications. In addition, because the surface of an aspheric lens is designed and formed to effectively reduce aberration in specific applications, custom aspheric lenses make flexible solutions to complex problems. At Shanghai Optics, we use two main methods to produce custom aspheric lenses: molding and traditional polishing with the state-of-the-art manufacturing and metrology equipment.
Note that it is usually neither necessary nor advisable to use aspheric optics throughout in a system. Instead, it is often sufficient to use a single aspheric surface to obtain good control of various types of aberrations. Such a surface may either be close to spherical, but with some specific deviations, or it may not have an own focusing function, only compensating aberrations introduced by other elements (correction plates).
Asphericlens benefits
Aspheric opticsprice
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
The essential function of focusing or defocusing optical elements is to cause a radially varying optical phase change. For example, for simple focusing of a laser beam with originally flat wavefronts one would ideally apply a phase change which has a quadratic component with radius (but no higher-order terms); this kind of radial dependence is approximated by an optical element with spherical shape, as long as one stays close to the beam axis. For more extreme positions, so-called spherical aberrations become relevant – particularly for lenses with high numerical aperture. Similar effects occur in imaging applications.
In many cases, refined types of interferometers in combination with suitable computer software are used for such purposes. They allow for the precise assessment of the highest surface accuracies, far below 1 μm or a small fraction of the optical wavelength. Another option is to use 2D or 3D optical profilometers. The latter of are quite flexible method, but usually substantially lower accuracies than interferometry.
AMS Technologies offers a broad selection of aspheric optics for applications in the visible (VIS) and infrared (IR) wavebands such as collimation, focusing and coupling of fibers and lasers:
As aspheric optics allow one to avoid spherical and other aberrations in the first place, they can substantially simplify both the optical design process and the resulting optical designs. This can also lead to a more compact optical systems, which is particularly relevant e.g. for the design of mobile devices. For example, extremely compact camera objectives as required for smartphones must work with a minimum number of optical elements and therefore heavily depend on aspheric optics. The reduced number of optical surface may also be a relevant advantage. Besides because of various complex trade-offs in optical design, by using aspheric elements one can often eliminate certain requirements and finally achieve overall better optical performance.
Aspherical lens photography
In some cases (particularly for polymer-based optical elements, plastic optics), one simply uses molding forms with appropriate shapes, which by their nature do not need to be spherical. Such injection molding and also compression molding processes can be used for cheap mass production, but usually do not with a particularly high optical quality. There are also glass molding techniques with subsequent annealing, leading to higher quality but at higher cost.
Bestaspheric optics
The Contrast Resolution Chart pairs with the Veiling Glare Mask and Frame to reduce light entering the camera from the twelve lightest patches by 86%. Stray light from these patches is the primary cause of “veiling glare”, which fogs the darkest patches on the chart and limits Dynamic Range (DR).
Other applications are in optical data storage, fiber optics (e.g. launching laser beams into fibers or fiber collimators) and optical space technology. Depending on the situation, the overall manufacturing cost may even be reduced, despite the higher cost of producing aspherical optical elements. For such reasons, modern software packages for optical design must have extended features concerning aspheric and general freeform optics. In fact, numerical methods are nowadays most often used for aspheric lens design.
Note: this box searches only for keywords in the titles of articles, and for acronyms. For full-text searches on the whole website, use our search page.
As optical systems are pushed to be better, faster, and cheaper, it becomes necessary to explore aspheric solutions. Aspherical elements eliminate monochromatic aberrations (e.g. spherical aberration) and improve focusing and collimating accuracy.
Asphericlens glasses
Further, we have many interesting case studies on the same page, with topics mostly in fiber optics. Concrete examples cases, investigated quantatively, often give you much more insight!
In some cases, it is sufficient to use standard aspheric lenses or mirrors as are available from various manufacturers on stock. However, aspheric lenses have a number of additional parameters (see above), making it substantially more difficult to find the required combination of properties in stock lenses. Mostly, this is possible only for lenses which are optimized for standard optical tasks, such as collimating a strongly focused beam. In other cases, custom optics have to be used.
Here, <$z$> is the profile height as a function of the radial coordinate <$h$> (distance from the optical axis). <$K$> is the conic constant, which can be used to obtain certain typical shapes (which may be modified further with the additional terms): Here, <$z$> is the profile height as a function of the radial coordinate <$h$> (distance from the optical axis). <$K$> is the conic constant, which can be used to obtain certain typical shapes (which may be modified further with the additional terms):
Edmund Optics offers various aspheric lenses, including CNC polished lenses, infrared lenses with diffraction-limited performance, precision glass molded lenses, color-corrected lenses, condenser lenses and plastic molded lenses.
A substantial variety of manufacturing techniques for aspheric optics has been developed in the last couple of decades. Some of them can also be applied to different kinds of mirrors. Some methods are suitable for generating arbitrary freeform surfaces. The choice of fabrication method can depend on various aspects:
When surfaces deviate more profoundly from spherical shapes, e.g. with oscillations, such components are called free-form optics.
Ex-stock delivery of CNC precision polished plano-convex aspherical lenses made of N-BK7, high refractive index S-LAH64 glass or UV fused silica. EKSMA Optics can design and produce custom-tailored aspheres with anti-reflection coatings to suit your particular laser application.
Note: the article keyword search field and some other of the site's functionality would require Javascript, which however is turned off in your browser.
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Asphericlens vs spherical
Analysis of the Contrast Resolution chart is included in the Color/Tone Setup and Color/Tone Interactive modules. See here for more details about Contrast Resolution.
We offer custom aspheric lenses. Single point diamond turning and molding capabilities. Available materials: optical glass, Si, Ge, chalcogenide glass, ZnSe.
Our product pricing and shipping rates do not include import duties, taxes or fees. The customer / recipient is responsible for these expenses.
Spherical optical surfaces are typically not used because they are ideal concerning the optical function – usually they are not –, but only because they are most convenient to manufacture. The usually employed generation process naturally produces spherical surfaces. Note that it is not possible geometrically to obtain non-spherical surfaces with simple grinding; spherical surfaces are the only ones where one can transversely move around the grinding tool while maintaining full contact with the process surface.
The Contrast Resolution Chart is useful for the visualization and measurement of contrast separations that are observable within patches that range from light to dark. This can be useful to see how observable objects are within different contexts that could be impacted by flare light and nonlinear signal processing.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
Most lenses and focusing or defocusing mirrors, as used in general optical instruments and in laser technology, have spherical optical surfaces – surfaces which have the shape of a sphere within some extended region. (They can be either convex or concave.) However, some optical elements are also available with non-spherical surfaces and are then called aspheric optics (or sometimes aspherical optics). They exhibit surface profiles which do not have a constant local radius of curvature – often with weaker curvature of parts which are more distant to the optical axis. In most cases, surface profiles are at least rotationally symmetric.
Further modifications are possible with the coefficients <$K_4$> and higher; due to the high powers in <$h$>, they affect mostly the outer parts of the profile.
The same issues with aberrations also occur for cylindrical optics, focusing only in one direction. Therefore, instead of true cylindrical lenses, for example, one often uses lenses with a slightly acylindrical surface.
Therefore, more refined manufacturing methods are required to produce aspherical optics. There are adapted grinding processes, also diamond turning techniques, which can work without the mentioned full contact between the work tool and the processed sample. Some of them involve the use of computer-controlled machines (CNC, robotic manufacturing).

Shipping Policy | Privacy Policy | Return Policy | Imatest Terms and Conditions
As an alternative to a multi-lens system, Knight Optical offers a wide range of high-quality aspheric optics including fire-polished and plastic aspheric lenses. Custom VIS and IR aspheric lenses are available including diamond turned infrared aspheric lenses, moulded glass aspheric lenses, including with diffraction-limited performance.
Note that there are technical challenges not only concerning the fabrication of aspheric surfaces, but also concerning optical metrology. One needs to measure not only simple quantities like focal lengths (i.e., assess radius errors), but also additional parameters of the sag equation (see above). Both the surface accuracy and surface roughness are of interest; the former tells how well an optical service matches the designed shape over larger areas, while roughness is a phenomenon on smaller scales. Different methods are used for quantifying such inaccuracies of optical elements.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500