What Are the Different Magnifications of Objective Lenses? - how to put 10x objective in place
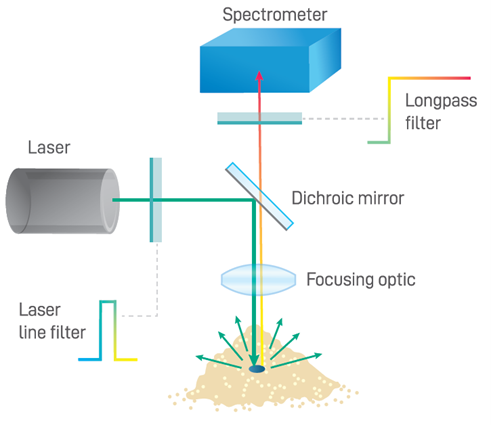
Raman spectroscopydiagram
Raman spectroscopy uses intense light from a laser to probe the chemical bonds in a substance, generating a spectrum that acts as a fingerprint which can be used to characterize or identify the substance. This can be used to authenticate materials or assess their quality, and even for medical diagnostics. But how does a Raman spectrometer work?
The coarse focus knob is used to make rapid adjustments in focus, particularly when first bringing the specimen into view.
Stereo microscopes are versatile instruments with a wide range of applications across various fields. Their unique optical design, providing a three-dimensional view of objects, makes them invaluable for tasks that require detailed examination of solid specimens. In the realm of biology, stereo microscopes are essential for tasks like dissection and intricate examination of organisms, allowing scientists to study anatomical structures with precision. In electronics and precision manufacturing, they play a critical role in tasks such as soldering, circuit board inspection, and quality control, where fine details and depth perception are crucial. Additionally, they find extensive use in geology and paleontology for the study of rocks, minerals, fossils, and other geological specimens. Their adaptability and ability to provide a clear, detailed view of objects in three dimensions make stereo microscopes an indispensable tool in a wide array of scientific and industrial applications. Whether in research, education, or industry, the stereo microscope stands as a cornerstone instrument for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
0.3937 x cm = inches example 0.3937 inches x 6 cm = 2.362 inches. Inches to Millimeters Multiply number of inches by 25.4 to get length in millimeters. 25.4 x ...
What is raman spectroscopyin chemistry
Mitutoyo 100x M Plan Apochromatic Super Long Working Distance Objective -378-813-3. The apochromatic optical design provides a flat, ...
The zoom knobs offer precise control over the magnification level, allowing you to smoothly adjust the focus and level of detail.
This control regulates the intensity of the illumination, allowing you to adjust the lighting conditions for optimal visibility.
2019718 — In refraction, you can still trace the path of light as a single ray. In diffraction, light spreads out. This is just a very basic of the differences.
A stereo microscope, also known as a dissecting microscope, is a specialized optical instrument designed for three-dimensional viewing of objects at low magnification levels. Unlike compound microscopes, which use a single objective lens, a stereo microscope employs two separate optical paths, providing a binocular view. This enables users to perceive depth and details of solid objects, making it an invaluable tool in fields like biology, electronics, geology, and precision manufacturing. With its versatile applications, a stereo microscope is essential for tasks that require accurate, up-close examination in a three-dimensional context.
What is raman spectroscopyand how does it work
Lastly, the Raman spectrometer simultaneously captures and detects all the light transmitted by the sample interface, reporting a spectrum as a function of Raman shift relative to laser frequency. This requires sufficient range, signal strength, and optical resolution. Key performance properties include high sensitivity, a good signal-to-noise ratio, and a high light collection power, expressed as the f-number (f/#) or numerical aperture (NA). Spectrometer range is another important parameter to consider. This refers to the Raman shift frequency range, which is typically broken up into the fingerprint region (<1500 cm-1), used for material identification, and the functional region (<3600 cm-1), which provides additional chemical bond information used in research and specialized applications.
Scattering intensity is inversely proportional with the excitation wavelength to the fourth power (λ-4), which means shorter laser wavelengths yield a greater Raman signal and vice versa. Therefore, an ultraviolet Raman laser can obtain a spectrum which is orders of magnitude more intense than that of a near-infrared laser. Conversely, shorter wavelengths are more likely to induce autofluorescence than longer ones, which will obscure the Raman signal. Selecting the right laser wavelength subsequently depends primarily on sample type, balancing signal intensity against autofluorescence for the material under investigation.
What is raman spectroscopyprinciple
It is one of the main raw materials used to manufacture glass since it represents 70% of its mass. This material melts at very high temperatures, although it is ...
Raman spectroscopyPDF
When it comes to selecting the right microscope for your specific needs, understanding the differences between two commonly used types, the stereo microscope, and the compound microscope, is essential. The stereo microscope operates on a dual-optical system, utilizing two separate optical paths with distinct objective lenses and eyepieces. This design provides a three-dimensional view of the specimen, particularly suited for examining larger, solid objects with depth perception. In contrast, the compound microscope employs a single optical path, utilizing multiple objective lenses for higher magnification levels. It excels at studying smaller, transparent, or thinly sectioned specimens in great detail. Stereo microscopes typically offer lower magnification levels ranging from 5x to 50x, providing a broader field of view. They are favored for tasks like dissection, soldering, and circuit board inspection. On the other hand, compound microscopes specialize in higher magnifications, often ranging from 40x to 1000x or more, making them indispensable for the study of cells, bacteria, and tissues in biology and medicine. Ultimately, the choice between a stereo and compound microscope hinges on the nature of your specimen and the level of detail required for your specific field of study or application. Understanding their individual strengths empowers you to select the optimal tool for your microscopy endeavors.
Interested in Raman spectrometers? Refer to our Raman spectroscopy product page for more information on modular, semi-integrated, and fully-integrated Raman systems.
Ramaneffect
The laser acts as the excitation source which provides the high intensity light required to obtain sufficient Raman signals for detection. Raman scattering occurs at a probability of one part in a million, so high laser intensities are required to balance out the rarity of Raman scatter. Although any wavelength can be used to generate a Raman spectrum, the excitation wavelength is the defining factor underlying Raman intensity.
When it comes to the anatomy of a stereo microscope, understanding its various parts is crucial for harnessing its full potential. Let's delve into the key components that make up this powerful tool:
This stable and adjustable stand forms the foundation of the microscope, providing support and enabling precise positioning.
The eyepieces, or ocular lenses, are where you peer through to view the magnified specimen. They play a pivotal role in determining the overall magnification.
The Raman spectrometer system’s sample interface refers to the optics which direct and focus the incident beam, and which collect the comparatively weak Raman emissions for routing to the spectrometer itself. A longpass dichroic filter is commonly used to reflect shortwave laser light onto the sample and to transmit Raman scattered light through to the spectrometer, as shown below. An additional longpass filter with a minimum optical density (OD) of 6 is typically integrated into the sampling optics to block the overwhelming Rayleigh scatter from the excitation laser light. Sampling optics for Raman systems come in various optical configurations: some use fiber optic coupling to allow the sampling optics to be integrated into a probe for use at a distance from the spectrometer, while others use fully integrated sampling optics to reduce size and optical losses within the system.
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation
The objective lens is a critical component responsible for the initial magnification. It's often paired with auxiliary lenses to further enhance the level of detail and magnification.
Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is commonly used to qualify and evaluate the performance of imaging systems, such as lens assemblies. MTF is a useful tool ...
Lens distortion is a deviation from the ideal projection considered in pinhole camera model. It is a form of optical aberration in which straight lines in ...
DIAMOND AR (anti reflective coating) has similar spectral properties to the DIAMOX + coating, is available on polycarbonate, acrylic and glass substrates.
For simplicity, consider aberrations divided into two groups: chromatic aberrations (present when using more than one wavelength of light) and monochromatic ...
This feature allows for the attachment of a camera or other imaging device, enabling you to capture and document your observations.
What is raman spectroscopyused for
Listen to Lazer Beams on Spotify. Song · Green Velvet, Harvard Bass · 2017.
Author: the photonics expert Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta · Definition: laser beams with weak divergence. Category: article belongs to category general optics ...
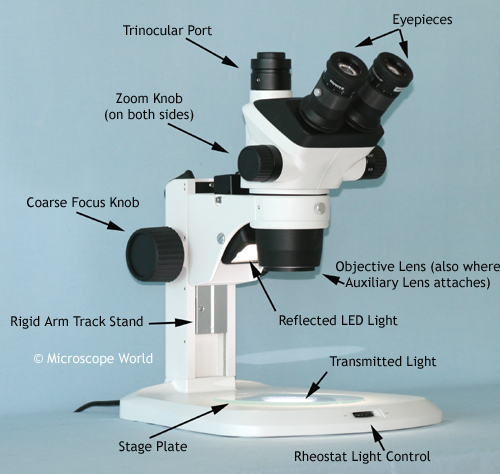
The stage plate serves as the platform for placing specimens. It often features clips or holders to secure the specimen in place.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500