Understanding camera focal length and why it matters. - short focal length
And at a time of increasing gridlock on Capitol Hill, many on both the left and the right think the outcome of political negotiations between Obama and Republican leaders should be that their side gets more of what it wants.
To be sure, there are areas of consensus. Most Americans, regardless of their ideological preferences, value communities in which they would live close to extended family and high-quality schools. But far more liberals than conservatives think it is important that a community have racial and ethnic diversity (76% vs. 20%). At the same time, conservatives are more likely than liberals to attach importance to living in a place where many people share their religious faith (57% vs. 17% of liberals).
The data in this report are based on two independent survey administrations with the same randomly selected, nationally representative group of respondents. The first is the center’s largest survey on domestic politics to date: the 2014 Political Polarization and Typology Survey, a national telephone survey of 10,013 adults, on landlines and cell phones, from January through March of this year. The second involved impaneling a subset of these respondents into the newly created American Trends Panel and following up with them via a survey conducted by web and telephone. The two surveys are described separately, in further detail, in the About the Surveys section of the report.
Note that depth of field only sets a maximum value for the circle of confusion, and does not describe what happens to regions once they become out of focus. These regions are also called "bokeh," from Japanese (pronounced bo-ké). Two images with identical depth of field may have significantly different bokeh, as this depends on the shape of the lens diaphragm. In reality, the circle of confusion is usually not actually a circle, but is only approximated as such when it is very small. When it becomes large, most lenses will render it as a polygonal shape with 5-8 sides.
Later, the project will explore the various factors that contribute to political polarization, or stem from it. A September report will examine how political polarization is linked to people’s information environments: Their news sources, social media habits and interpersonal communication networks. Other reports will look at how political polarization relates to where people live, to their political environments, to how they view themselves and others around them, to their socioeconomic circumstances, to generational changes and to broader sociological and psychological personality traits.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300Washington, DC 20004USA(+1) 202-419-4300 | Main(+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax(+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Stateof polarization of light
On the other hand, when standing in the same place and focusing on a subject at the same distance, a longer focal length lens will have a shallower depth of field (even though the pictures will frame the subject entirely differently). This is more representative of everyday use, but is an effect due to higher magnification, not focal length.
“Ideological silos” are now common on both the left and right. People with down-the-line ideological positions – especially conservatives – are more likely than others to say that most of their close friends share their political views. Liberals and conservatives disagree over where they want to live, the kind of people they want to live around and even whom they would welcome into their families.
Polarised stateof neuron
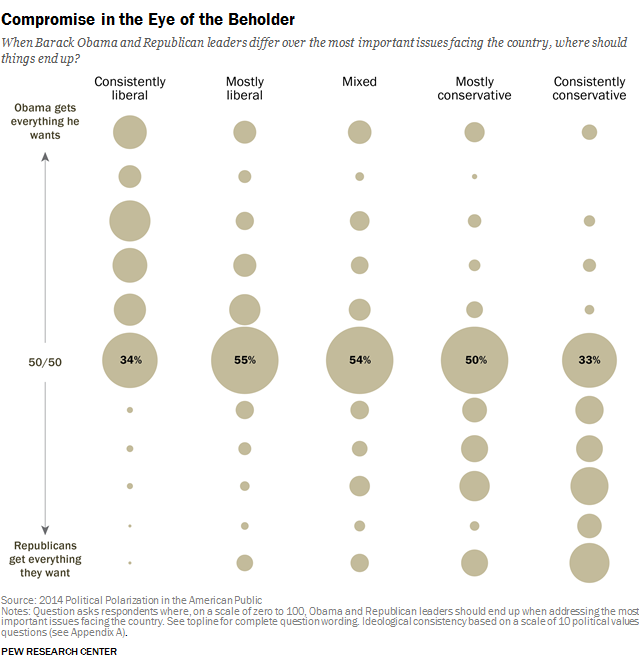
Yet an equitable deal is in the eye of the beholder, as both liberals and conservatives define the optimal political outcome as one in which their side gets more of what it wants. A majority of consistent conservatives (57%) say the ideal agreement between President Obama and congressional Republicans is one in which GOP leaders hold out for more of their goals. Consistent liberals take the opposite view: Their preferred terms (favored by 62%) end up closer to Obama’s position than the GOP’s.
Nearly two-thirds (63%) of consistent conservatives and about half (49%) of consistent liberals say most of their close friends share their political views. Among those with mixed ideological values, just 25% say the same. People on the right and left also are more likely to say it is important to them to live in a place where most people share their political views, though again, that desire is more widespread on the right (50%) than on the left (35%).
On measure after measure – whether primary voting, writing letters to officials, volunteering for or donating to a campaign – the most politically polarized are more actively involved in politics, amplifying the voices that are the least willing to see the parties meet each other halfway.
However, there is as much ideological uniformity on the left as the right. The share of Democrats holding consistently liberal views has grown steadily over the past 20 years, quadrupling from 5% in 1994 to 23% today. Social issues like homosexuality and immigration that once drove deep divides within the Democratic Party are now areas of relative consensus. And Democrats have become more uniformly critical of business and more supportive of government.
Depth of field also appears shallower for SLR cameras than for compact digital cameras, because SLR cameras require a longer focal length to achieve the same field of view (see the tutorial on digital camera sensor sizes for more on this topic).
Polarised statemeaning in hindi
Liberals and conservatives share a passion for politics. They are far more likely than those with more mixed ideological views to discuss politics on a weekly or daily basis. But for many, particularly on the right, those conversations may not include much in the way of opposing opinions.
Polarised stateexamples
Consistent liberals and conservatives define ideal political compromise as one in which their side gets more of what it wants
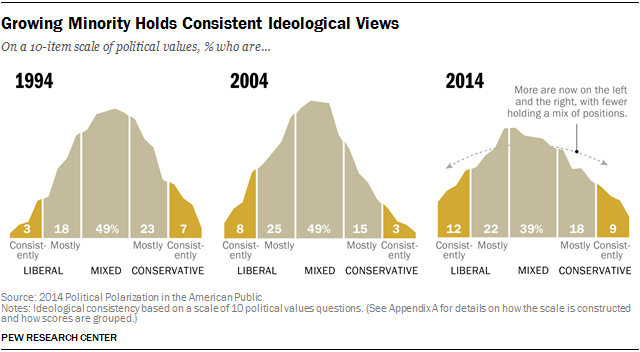
To chart the progression of ideological thinking, responses to 10 political values questions asked on multiple Pew Research surveys since 1994 have been combined to create a measure of ideological consistency. Over the past twenty years, the number of Americans in the “tails” of this ideological distribution has doubled from 10% to 21%. Meanwhile, the center has shrunk: 39% currently take a roughly equal number of liberal and conservative positions. That is down from about half (49%) of the public in surveys conducted in 1994 and 2004.
For macro photography (high magnification), the depth of field is actually influenced by another factor: pupil magnification. This is equal to one for lenses which are internally symmetric, although for wide angle and telephoto lenses this is greater or less than one, respectively. A greater depth of field is achieved (than would be ordinarily calculated) for a pupil magnification less than one, whereas the pupil magnification does not change the calculation when it is equal to one. The problem is that the pupil magnification is usually not provided by lens manufacturers, and one can only roughly estimate it visually.
Many of those in the center remain on the edges of the political playing field … while the most ideologically oriented and politically rancorous Americans make their voices heard
These sentiments are not shared by all – or even most – Americans. The majority do not have uniformly conservative or liberal views. Most do not see either party as a threat to the nation. And more believe their representatives in government should meet halfway to resolve contentious disputes rather than hold out for more of what they want.
This exposes a limitation of the traditional DoF concept: it only accounts for the total DoF and not its distribution around the focal plane, even though both may contribute to the perception of sharpness. Note how a wide angle lens provides a more gradually fading DoF behind the focal plane than in front, which is important for traditional landscape photographs.
The current report is divided into five parts: The first two focus on measuring the nature and scope of political polarization, emphasizing the difference between growing ideological consistency and rising partisan antipathy. The third looks closely at how polarization manifests itself in people’s personal lives. The fourth looks at the relationship between polarization and practical policymaking, and the fifth digs deeper into how political participation both amplifies and reflects polarization.
The rise of ideological uniformity has been much more pronounced among those who are the most politically active. Today, almost four-in-ten (38%) politically engaged Democrats are consistent liberals, up from just 8% in 1994. The change among Republicans since then appears less dramatic – 33% express consistently conservative views, up from 23% in the midst of the 1994 “Republican Revolution.” But a decade ago, just 10% of politically engaged Republicans had across-the-board conservative attitudes.
Note that focal length has not been listed as influencing depth of field, contrary to popular belief. Even though telephoto lenses appear to create a much shallower depth of field, this is mainly because they are often used to magnify the subject when one is unable to get closer. If the subject occupies the same fraction of the image (constant magnification) for both a telephoto and a wide angle lens, the total depth of field is virtually* constant with focal length! This would of course require you to either get much closer with a wide angle lens or much farther with a telephoto lens, as demonstrated in the following chart:
Diagram depicting depth of focus versus camera aperture. The purple lines comprising the edge of each shaded region represent the extreme angles at which light could potentially enter the aperture. The interior of the purple shaded regions represents all other possible angles.
Note how there is indeed a subtle change for the smallest focal lengths. This is a real effect, but is negligible compared to both aperture and focusing distance. Even though the total depth of field is virtually constant, the fraction of the depth of field which is in front of and behind the focus distance does change with focal length, as demonstrated below:
A different maximum circle of confusion also applies for each print size and viewing distance combination. In the earlier example of blurred dots, the circle of confusion is actually smaller than the resolution of your screen for the two dots on either side of the focal point, and so these are considered within the depth of field. Alternatively, the depth of field can be based on when the circle of confusion becomes larger than the size of your digital camera's pixels.
Polarised stateof neuron meaning
Another implication of the circle of confusion is the concept of depth of focus (also called the "focus spread"). It differs from depth of field because it describes the distance over which light is focused at the camera's sensor, as opposed to the subject:
The signs of political polarization are evident on both ends of the political spectrum, though the trajectory, nature and extent differ from left to right.
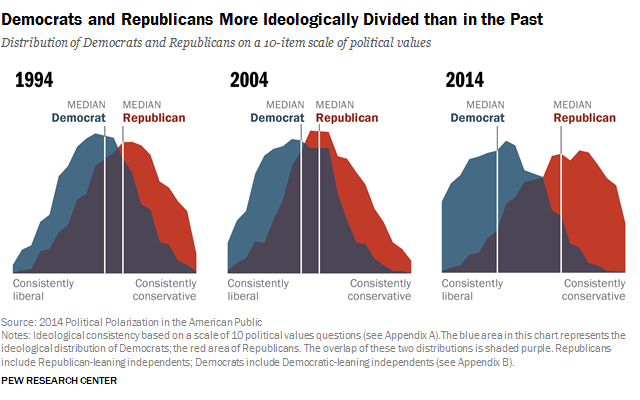
And this shift represents both Democrats moving to the left and Republicans moving to the right, with less and less overlap between the parties. Today, 92% of Republicans are to the right of the median (middle) Democrat, compared with 64% twenty years ago. And 94% of Democrats are to the left of the median Republican, up from 70% in 1994.
Among all Democrats, 27% say GOP policies are a threat to the well-being of the country; among all Republicans, more than a third (36%) think Democratic policies threaten the nation.
Although print size and viewing distance influence how large the circle of confusion appears to our eyes, aperture and focusing distance are the two main factors that determine how big the circle of confusion will be on your camera's sensor. Larger apertures (smaller F-stop number) and closer focusing distances produce a shallower depth of field. The following test maintains the same focus distance, but changes the aperture setting:
This is the first report of a multi-part series based on a national survey of 10,013 adults nationwide, conducted January 23-March 16, 2014 by the Pew Research Center. The survey, funded in part through grants from the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation and supported by the generosity of Don C. and Jeane M. Bertsch, is aimed at understanding the nature and scope of political polarization in the American public, and how it interrelates with government, society and people’s personal lives.
In order to calculate the depth of field, one needs to first decide on an appropriate value for the maximum allowable circle of confusion. This is based on both the camera type (sensor or film size), and on the viewing distance / print size combination. Needless to say, knowing what this will be ahead of time often isn't straightforward. Try out the depth of field calculator tool to help you find this for your specific situation.
In 1994, hardly a time of amicable partisan relations, a majority of Republicans had unfavorable impressions of the Democratic Party, but just 17% had very unfavorable opinions. Similarly, while most Democrats viewed the GOP unfavorably, just 16% had very unfavorable views. Since then, highly negative views have more than doubled: 43% of Republicans and 38% of Democrats now view the opposite party in strongly negative terms.
When they look at a political system in which little seems to get done, most Americans in the center of the electorate think that Obama and Republican leaders should simply meet each other halfway in addressing the issues facing the nation.
Today 92% of Republicans are to the right of the median Democrat, and 94% of Democrats are to the left of the median Republican
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder.
Polarised statemeaning in biology
Since there is no critical point of transition, a more rigorous term called the "circle of confusion" is used to define how much a point needs to be blurred in order to be perceived as unsharp. When the circle of confusion becomes perceptible to our eyes, this region is said to be outside the depth of field and thus no longer "acceptably sharp." The circle of confusion above has been exaggerated for clarity; in reality this would be only a tiny fraction of the camera sensor's area.
Even these numbers tell only part of the story. Those who have a very unfavorable impression of each party were asked: “Would you say the party’s policies are so misguided that they threaten the nation’s well-being, or wouldn’t you go that far?” Most who were asked the question said yes, they would go that far. Among all Democrats, 27% say the GOP is a threat to the well-being of the country. That figure is even higher among Republicans, 36% of whom think Democratic policies threaten the nation.
These are among the findings of the largest study of U.S. political attitudes ever undertaken by the Pew Research Center. Data are drawn from a national telephone survey of 10,013 adults, conducted from January through March of this year, and an ongoing series of follow-up surveys. This rich dataset, coupled with trends and insights from two decades of Pew Research Center polling, reveals a complex picture of partisan polarization and how it manifests itself in political behaviors, policy debates, election dynamics and everyday life.
Note: Depth of field calculations are at f/4.0 on a camera with a 1.6X crop factor,using a circle of confusion of 0.0206 mm.
Why not just use the smallest aperture (largest number) to achieve the best possible depth of field? Other than the fact that this may require prohibitively long shutter speeds without a camera tripod, too small of an aperture softens the image by creating a larger circle of confusion (or "Airy disk") due to an effect called diffraction — even within the plane of focus. Diffraction quickly becomes more of a limiting factor than depth of field as the aperture gets smaller. Despite their extreme depth of field, this is also why "pinhole cameras" have limited resolution.
And the differences between right and left go beyond disagreements over politics, friends and neighbors. If they could choose anywhere to live, three-quarters of consistent conservatives prefer a community where “the houses are larger and farther apart, but schools, stores, and restaurants are several miles away.” The preferences of consistent liberals are almost the exact inverse, with 77% saying they’d chose to live where “the houses are smaller and closer to each other, but schools, stores, and restaurants are within walking distance.”
The second report, coming in a few weeks, is the new Pew Research Center Political Typology. The typology – the sixth such study since 1987 – looks beyond Red vs. Blue divisions to gain a clearer understanding of the dynamic nature of the “center” of the American electorate, and the internal divides on both the left and the right.
And while few Americans overall go so far as to voice disappointment with the prospect of a family member marrying a Democrat (8%) or a Republican (9%), that sentiment is not uncommon on the left or the right. Three-out-of-ten (30%) consistent conservatives say they would be unhappy if an immediate family member married a Democrat and about a quarter (23%) of across-the-board liberals say the same about the prospect of a Republican in-law.
People on the right and left are more likely to say it is important to them to live in a place where most people share their political views
The overall share of Americans who express consistently conservative or consistently liberal opinions has doubled over the past two decades from 10% to 21%. And ideological thinking is now much more closely aligned with partisanship than in the past. As a result, ideological overlap between the two parties has diminished: Today, 92% of Republicans are to the right of the median Democrat, and 94% of Democrats are to the left of the median Republican.
Republicans and Democrats are more divided along ideological lines – and partisan antipathy is deeper and more extensive – than at any point in the last two decades. These trends manifest themselves in myriad ways, both in politics and in everyday life. And a new survey of 10,000 adults nationwide finds that these divisions are greatest among those who are the most engaged and active in the political process.
Polarizedstateof cell
The depth of field does not abruptly change from sharp to unsharp, but instead occurs as a gradual transition. In fact, everything immediately in front of or in back of the focusing distance begins to lose sharpness — even if this is not perceived by our eyes or by the resolution of the camera.
At this viewing distance and print size, camera manufacturers assume a circle of confusion is negligible if no larger than 0.01 inches (when enlarged). As a result, camera manufacturers use the 0.01 inch standard when providing lens depth of field markers (shown below for f/22 on a 50mm lens). In reality, a person with 20/20 vision or better can distinguish features 1/3 this size, and so the circle of confusion has to be even smaller than this to achieve acceptable sharpness throughout.
Polarised statemeaning
When does the circle of confusion become perceptible to our eyes? An acceptably sharp circle of confusion is loosely defined as one which would go unnoticed when enlarged to a standard 8x10 inch print, and observed from a standard viewing distance of about 1 foot.
Yet many of those in the center remain on the edges of the political playing field, relatively distant and disengaged, while the most ideologically oriented and politically rancorous Americans make their voices heard through greater participation in every stage of the political process.
The key concept is this: when an object is in focus, light rays originating from that point converge at a point on the camera's sensor. If the light rays hit the sensor at slightly different locations (arriving at a disc instead of a point), then this object will be rendered as out of focus — and increasingly so depending on how far apart the light rays are.
Partisan animosity has increased substantially over the same period. In each party, the share with a highly negative view of the opposing party has more than doubled since 1994. Most of these intense partisans believe the opposing party’s policies “are so misguided that they threaten the nation’s well-being.”
Beyond the rise in ideological consistency, another major element in polarization has been the growing contempt that many Republicans and Democrats have for the opposing party. To be sure, disliking the other party is nothing new in politics. But today, these sentiments are broader and deeper than in the recent past.
Longer focal lengths may also appear to have a shallower depth of field because they enlarge the background relative to the foreground (due to their narrower angle of view). This can make an out of focus background look even more out of focus because its blur has become enlarged. However, this is another concept entirely, since depth of field only describes the sharp region of a photo — not the blurred regions.
*Technical Note: We describe depth of field as being virtually constant because there are limiting cases where this does not hold true. For focal distances resulting in high magnification, or very near the hyperfocal distance, wide angle lenses may provide a greater DoF than telephoto lenses. On the other hand, at high magnification the traditional DoF calculation becomes inaccurate due to another factor: pupil magnification. This reduces the DoF advantage for most wide angle lenses, and increases it for telephoto and macro lenses. At the other limiting case, near the hyperfocal distance, the increase in DoF arises because the wide angle lens has a greater rear DoF, and can thus more easily attain critical sharpness at infinity.
With Barack Obama in the White House, partisan antipathy is more pronounced among Republicans, especially consistently conservative Republicans. Overall, more Republicans than Democrats see the opposing party’s policies as a threat and the differences are even greater when ideology is taken into account. Fully 66% of consistently conservative Republicans think the Democrats’ policies threaten the nation’s well-being. By comparison, half (50%) of consistently liberal Democrats say Republican policies jeopardize the nation’s well-being. Conservatives also exhibit more partisan behavior in their personal lives; they are the most likely to have friends and prefer communities of like-minded people.
Changes in ideological consistency on the right have followed a different course. In 1994, during the “Republican Revolution,” 13% of Republicans were consistent conservatives. That figure fell to 6% a decade later during George W. Bush’s presidency, before rebounding to 20% today. This increase has come despite more moderate views among Republicans on issues like homosexuality and immigration, as GOP thinking on issues related to government and the economy has veered sharply to the right.
Depth of field refers to the range of distance that appears acceptably sharp. It varies depending on camera type, aperture and focusing distance, although print size and viewing distance can also influence our perception of depth of field. This tutorial is designed to give a better intuitive and technical understanding for photography, and provides a depth of field calculator to show how it varies with your camera settings.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500