Sensorgröße der Kamera: Welcher ist sinnvoll? - - sensorgrößen
Light intensityformula
This comic book-style video animation series has been developed to help middle school students learn about the 7 SI base measurement units. Don't let her small size fool you, Candela's power over light helps to brighten the whole world. A candela is a measure of brightness about equal to the light given off by a single candle.
Luminousintensity
Becoming Familiar with SI | Everyday Estimation | U.S. Metrication | U.S. Metrication FAQs | Prefixes | Metric Kitchen | SI Education and Training | SI Publications | Understanding Metric | Writing with (SI) Metric Units | National Metric Week | NEST-R (STEM Registry) | NIST Education Resources
Radiation at frequencies other than 540 x 1012 Hz is also measured in candelas in accordance with the standard luminous efficiency, V (λ), curve that peaks at 540 x 1012 Hz (yellow-green). Learn more about the realization of the candela and luminance (candela per square meter).

Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Light intensityunit
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
The second NIR window (NIR-II, 900 – 1700 nm) is of special interest as it is able to penetrate deeper into soft tissue with reduced scattering and less autofluorescence. This window also takes advantage of the water transparency window, a wavelength range in which water absorption is negligible (800 – 1400 nm).
lightintensity中文
The candela (cd) is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the luminous efficacy of monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz, Kcd, to be 683 when expressed in the unit lm W−1, which is equal to cd sr W−1, or cd sr kg−1 m−2 s3, where the kilogram, meter and second are defined in terms of h, c and ∆νCs.
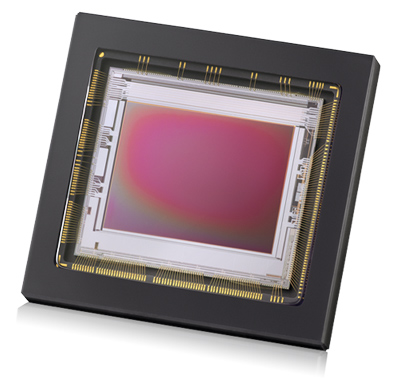
NIR-II imaging relies on NIR-II emitting fluorophores, which are undetected by traditional silicon based sensors. The band gap within silicon sensors means there is a minimum amount of energy required to absorb a photon. The energy of NIR-II photons (or any above 1100 nm) is too low to produce this energy. Therefore InGaAs sensors are required.
Near-infrared (NIR) and shortwave infrared (SWIR) fluorescence is rapidly being used within medical and biological research as wavelengths in the NIR can penetrate soft tissue producing high resolution images of in vivo structures.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500