Prism Lens Fx Linear Prism Fx Filter 82Mm - linear prism filter
Optical densityformula
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
Reference surface is the base for the scale-limited surface, and represents the plane at the mean height of the evaluation area as per the ISO 25178 Surface Texture function.
Optical density definitionchemistry
Optical density is often defined without regard to the length of the sample; in this case it is a synonym for absorbance. Neutral density filters are typically quantified this way. Some filters, notably welding glass, are rated by shade number, which is 7/3 times the optical density. A shade number of 14 is regarded as safe for direct observation of the sun.
Although absorbance does not have true units, it is quite often reported in "Absorbance Units" or AU. Accordingly, optical density is measured in ODU, which are equivalent to AU cm−1.
Real surface indicates the surface constituted from measurement data in the XY plane direction. Generally, the height data is the subject of processing.
Optical density definitionin spectroscopy
Optical density definitionradiography
A region that is in contact with the boundary of the definition area at the material height c is called an "open area," while a region that is not is called a "closed area." Height c is given in areal material ratio and the default value is 50%.
The higher the optical density, the lower the transmittance. Optical density times 10 is equal to a transmission loss rate expressed in decibels per cm, e.g., an optical density of 0.3 corresponds to a transmission loss of 3 dB per cm.
Scale-limited surface means either the S-F surface or the S-L surface. It is the equivalent of the roughness profile or waviness profile in the profile method.
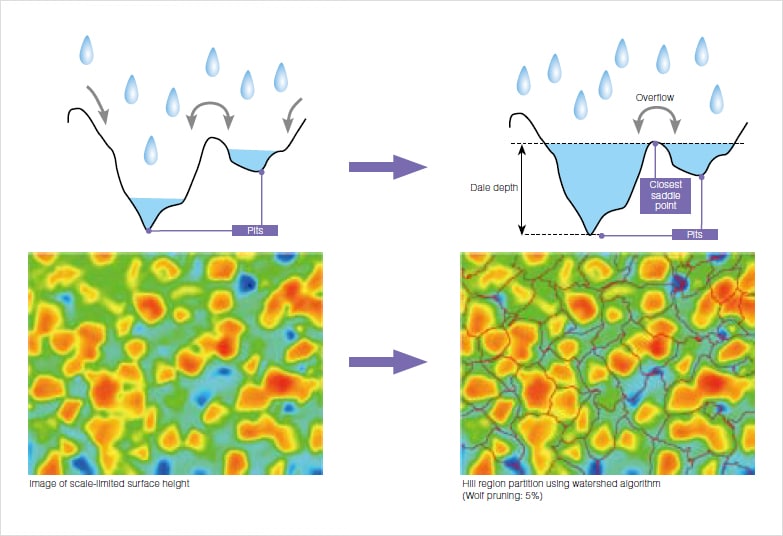
Peaks and pits merely need to be higher or lower that other points in their respective neighborhoods. For this reason, a surface with fine asperity can have a vast number of peaks and pits. Applying the watershed algorithm to such surfaces can result in meticulous segmentation into minute hill and dale regions. In order to suppress this over-segmentation, the Wolf pruning method is used to remove regions below a certain height/depth threshold. The threshold is provided as a percentage of the maximum height (Sz) of the surface. The default value is 5%.
The watershed algorithm is employed to partition regions, which are used in the calculation of feature parameters. Water is poured into the surface landscape, and it runs along the surface shape and reaches the pit. Upon continuing to pour water, the water surfaces of water filling different pits make contact with each other. The set of these contact points is the ridge line that partitions the dale region. The same approach can be applied to the hill region by vertically inverting the process.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500