Laser safety eyewear - laser protection glasses
Magnification: Compound microscopes are designed for higher magnifications, typically used for observing microscopic details. Other microscopes may have lower magnification capabilities, suitable for larger specimens or samples.
Objective Lenses: Usually you will find 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope. They almost always consist of 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x powers. When coupled with a 10x (most common) eyepiece lens, total magnification is 40x (4x times 10x), 100x , 400x and 1000x. To have good resolution at 1000x, you will need a relatively sophisticated microscope with an Abbe condenser. An Abbe condenser is composed of two lenses that control the light that passes through the specimen before entering the objective lens on the microscope. The shortest lens is the lowest power, the longest one is the lens with the greatest power. Lenses are color coded and if built to DIN standards are interchangeable between microscopes. "DIN" is an abbreviation of "Deutsche Industrial Normen". This is a German standard that has been adopted internationally as an optical standard used in most quality microscopes. A typical DIN standard microscope objective lens has a 0.7965" (20.1mm) diameter threads, 36 TPI (threads per inch), and a 55º Whitworth. Many high power objective lenses are retractable (i.e. 40XR). This means that if they hit a slide, the end of the lens will push in (spring loaded) thereby protecting the lens and the slide. All good quality microscopes have achromatic, parcentered, parfocal lenses.
The “angle” is the symbol for surface roughness, and this symbol indicates that the surface should be no rougher than “32.” Prior to the release of the 2018 standards the symbol was written a little differently:
Ra, however, is blind to several critical aspects of surface texture, and relying solely on Ra to control surfaces can lead to quality issues. This happens all the time, in fact, as you’ll read in examples throughout this blog.
Ocularlens magnification
Average roughness is a good first-pass indicator of the overall height of the surface texture. For decades it has proven useful for tracking manufacturing processes in industries from automotive to medical devices. It can be measured quickly using only inexpensive gauges, making it an effective tool for shop floor quality control.
So, what does that mean, how should you measure it, what will this information tell us about the surface, and maybe most compelling: what won’t it tell us?
Rack Stop: This is an adjustment that determines how close the objective lens can get to the slide. It is set at the factory and keeps students from cranking the high power objective lens down into the slide and breaking things. You would only need to adjust this if you were using very thin slides and you weren't able to focus on the specimen at high power. (Tip: If you are using thin slides and can't focus, rather than adjust the rack stop, place a clear glass slide under the original slide to raise it a bit higher).
Vereinbaren Sie ein persönliches Informationsgespräch mit unserem Team. ... Unterscheidungsmerkmal bleiben. Mehr erfahren ... Unterscheidungsmerkmal bleiben.
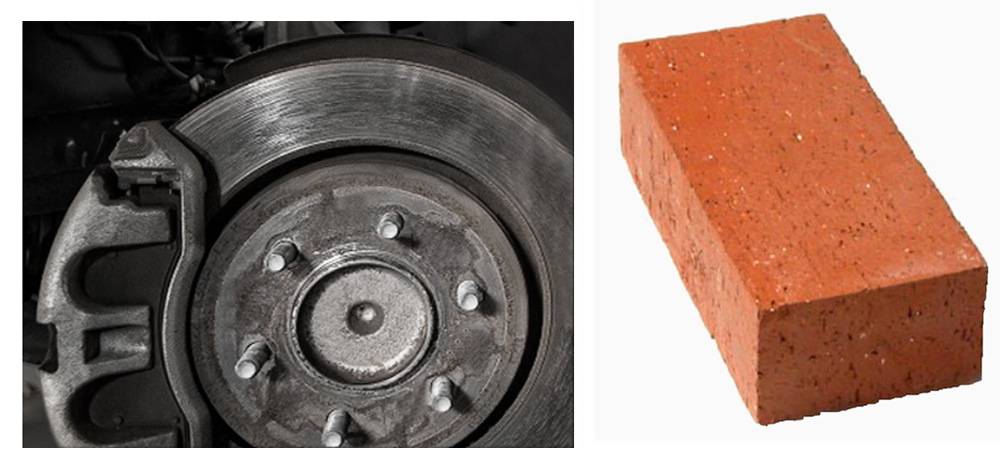
But the “32” is not arbitrary: it was determined from real average roughness measurements, with real units. So, what are the units of a “Ra 32” surface? An Ra of 32 µ-in would be typical of a machined surface, such as a brake rotor. An Ra of 32 microns, however, would be more like the surface of brick!
High Efficiency Anti-Reflection (HEAR) Coated Windows used to eliminate back reflections and reduce glare in optical systems are available at Edmund Optics.
1. Ocular eyepiece lens to look through. 2. Objective lens, closest to the object. Before purchasing or using a compound microscope, it is important to know the functions of each part. This information is presented below. Links will take you to additional information and images.
As we stressed earlier, a surface is a texture, not a number. A very fundamental aspect of surface texture (one which we discuss frequently in this blog and in our classes) is that surface texture consists of “spatial wavelengths,” ranging from short-wavelength roughness to longer wavelength waviness. The longest spatial wavelengths are called “form” and represent the general shape of the part.
Objective Lenses: Compound microscopes have multiple objective lenses mounted on a rotating nosepiece, typically with magnifications ranging from 4x to 100x or higher. Other microscopes, such as dissecting or stereo microscopes, usually have fixed magnification lenses.
Ra cannot distinguish the location of surface features across a profile. A surface with randomly scattered peaks will have the same Ra as a surface with those same peaks clustered at one end of the part. In a mating surface, a concentration of high peaks could lead to uneven loading, scratching, gouging, premature wear, etc. What’s more, a single profile measurement with a stylus instrument is quite likely to not even cross that peak material, leaving it entirely undetected.
Ocular objectivevs magnification
It's important to note that the term "other microscope parts" is quite broad and can include various microscope types with different designs and features. The above differences are generalized and may not apply to every microscope outside the category of compound microscopes.
High powerobjectivelens
Eyepiece/Ocular: Compound microscopes commonly have a pair of eyepieces that provide binocular vision. Other microscopes may have a single eyepiece or sometimes no eyepieces at all.
... Optics. "This made Rafaella® the perfect choice to partner with. The Rafaella Eyewear collection consists of the finest handmade acetate and stainless ...
Aug 1, 2020 — You have taken beam width 30 cm and depth 90 cm, which fulfils the criteria. Furthermore, the size of the beam depends on span and type of load ...
Average roughness (Ra) is the tip of the deep and complex world of surface texture analysis. As you’ll see throughout this blog and many excellent books, we have many tools today that we use to measure surface texture, and hundreds of ways to analyze the data. This information can be incredibly useful for solving production and quality problems.
A stylus instrument measures in two dimensions, recording the height at every point along a line. Other instruments, such as optical profilers, can measure in three dimensions, acquiring an entire area of data in just a few seconds. For 3D measurements we use “Sa” as the areal/3D equivalent to Ra (two-dimensional) average roughness.
Ocular objectiveexample
Ra (average roughness) measures the deviation of a surface from a mean height. The horizontal line through the profile represents the arithmetic mean height. The blue areas represent the deviations from that line. Ra, then, is the total blue area divided by the length of the profile.There is, of course, a bit more to it, but this is the basic gist.

Despite this level of complexity, though, by far the most typical encounter you will have with surface texture will be a callout on a print such as this one:
Shop Linear Polarizer Film Lcd/led Polarized Filter Polarizing Film Sheet For Polarization Photograph 5p (haoyi. One of many items available from our Audio ...
These crown glass biconvex lenses are suitable for almost all singlet lens applications.
Sa is the areal (3D) equivalent of two-dimensional Ra. Sa is the “areal average roughness,” the average height of all measured points in the areal measurement. The “S” parameters refer to measurements of a “surface,” as opposed to the “R” parameters which are calculated from the roughness profile.
Objectivelens microscope function
We're a precision optical company that has been ranked amongst the most respected brands. Our products continually set new standards in each of their respective ...
The application dictates which spatial wavelengths are important to measure and control. If a part needs to seal, say, we will need to be concerned about its roughness (too rough and its valleys may join up to form leak paths), but we will also need to be concerned about its waviness (too much overall curvature and a gasket may not be able to comply with its shape).
Ocular objectivemicroscope
Prisms - band, Princeton, New Jersey. 156 likes · 27 talking about this. Prisms / SE PA, Central NJ based rock and roll.
This calculator is designed to give the true field of view and magnification of a telescope. Enter the data for the scope's focal length; then either select an ...
Ra cannot discern short wavelength “roughness” from longer spatial wavelength “waviness.” These areal/3D measurements show two engine lifters with the same Ra. Yet, one ran smoothly while the other was noisy. The longer spatial wavelength texture was the issue…but Ra alone cannot tell you that.
Compound microscopes and other types of microscopes differ in their design and functionality. Here are the key differences between compound microscope parts and those of other microscopes:
Average roughness is typically measured in either microns (µm) or micro-inches (µ-in, µ”). One micron equals roughly 40 micro-inches (µ”). Also note that “micron” and “micrometer” are equivalent, and both terms are commonly used.
Applications: Compound microscopes are commonly used in fields such as biology, medicine, and research, where detailed examination of small structures is required. Other microscopes, such as stereo microscopes, are utilized for examining larger objects or conducting dissections. Electron microscopes are used for high-resolution imaging of nanoscale structures.
Key fact: Ra has units. You will hear people refer to a surface as a “32” or “64” as if it is a unitless standard. This practice dates from the use of “tactile gages” which were widely used to compare surface texture. A machine operator would drag a fingernail across the sample surface and then compare the “feel” to the samples on the tactile gage. Inexact, but quick and easy. The gages often listed the values without units, and thus several generation of machinists learned to feel a “32” surface, and to understand “roughness” as a number rather than a texture.
Historians credit the invention of the compound microscope to the Dutch spectacle maker, Zacharias Janssen, around the year 1590 (more history here). The compound microscope uses lenses and light to enlarge the image and is also called an optical or light microscope (versus an electron microscope). The simplest optical microscope is the magnifying glass and is good to about ten times (10x) magnification.
Objectivelens magnification
Sample Size and Depth of Field: Compound microscopes are designed to observe thin, transparent specimens placed on glass slides. They offer a narrow depth of field, allowing clear focus on one plane at a time. Other microscopes, like stereo or electron microscopes, can accommodate larger specimens or samples with more depth, providing a wider depth of field.
If not otherwise specified, the number in a callout such as the one shown at the beginning of this post is assumed to be stated in micro-inches. However, without specifying the units, the specification is open for potential misinterpretation.
These very different surfaces all have similar Ra values. Which will leak? Which will wear well? Ra cannot distinguish between them. Image courtesy Digital Metrology Solutions.
Stage with Stage Clips: The flat platform where you place your slides. Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down.
There is a great deal more to this topic and to specifying, measuring and analyzing surface texture. We invite you to read the rest of this blog to learn more about it. You may also want to learn more about our in-person classes. The Surface Texture and Tribology Short Course is also available on udemy.com if you are looking to take a deeper dive into surface texture analysis.
Diaphragm or Iris: Many microscopes have a rotating disk under the stage. This diaphragm has different sized holes and is used to vary the intensity and size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide. There is no set rule regarding which setting to use for a particular power. Rather, the setting is a function of the transparency of the specimen, the degree of contrast you desire and the particular objective lens in use.
Condenser Lens: The purpose of the condenser lens is to focus the light onto the specimen. Condenser lenses are most useful at the highest powers (400x and above). Microscopes with in-stage condenser lenses render a sharper image than those with no lens (at 400x). If your microscope has a maximum power of 400x, you will get the maximum benefit by using a condenser lenses rated at 0.65 NA or greater. 0.65 NA condenser lenses may be mounted in the stage and work quite well. A big advantage to a stage mounted lens is that there is one less focusing item to deal with. If you go to 1000x then you should have a condenser lens with an N.A. of 1.25 or greater. All of our 1000x microscopes use 1.25 Abbe condenser lens systems. The Abbe condenser lens can be moved up and down. It is set very close to the slide at 1000x and moved further away at the lower powers.
The difficulty with Ra is that it gives no indication of the spatial wavelengths that comprise the texture. In the image below, the engine lifter at the top ran smoothly and quietly. The lifter at the bottom, however, created engine noise because of the waviness in its surface. Both parts met the average roughness spec. If we only measure Ra, we cannot tell the difference!
Average Roughness, or Ra, is the most commonly specified surface texture parameter. It provides a general measure of the height of the texture across a surface. More exactly, Ra is the average of how far each point on the surface deviates in height from the mean height. Consider this profile, which is a cross-section through a typical surface:
Objectivelens
Feb 2, 2020 — Apply a bit of liquid to a cloth or paper to wipe the lens, and then wipe off the remaining liquid with a dry cloth. This will not damage lenses ...
Illumination: Compound microscopes often have built-in illumination systems, such as a substage light source, condenser, and diaphragm, to provide transmitted light through the specimen. Other microscopes, like dissecting or fluorescence microscopes, may utilize different lighting techniques or illumination configurations.

Ra measures absolute deviations from the mean height, treating peaks and valleys equivalently. As the image below shows, many very different surfaces—some uniform roughness, some with deep valleys or sharp peaks—may all have the exact same Ra value. Many of the quality and warranty issues that we see stem from this shortcoming of Ra: the parts all meet the Ra spec, yet some squeak, or leak, or wear prematurely. How can that be, when the Ra is within tolerance? The answer is often in those peaks and valleys…
Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
How to Focus Your Microscope: The proper way to focus a microscope is to start with the lowest power objective lens first and while looking from the side, crank the lens down as close to the specimen as possible without touching it. Now, look through the eyepiece lens and focus upward only until the image is sharp. If you can't get it in focus, repeat the process again. Once the image is sharp with the low power lens, you should be able to simply click in the next power lens and do minor adjustments with the focus knob. If your microscope has a fine focus adjustment, turning it a bit should be all that's necessary. Continue with subsequent objective lenses and fine focus each time.
Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: This is the part of the microscope that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change power.
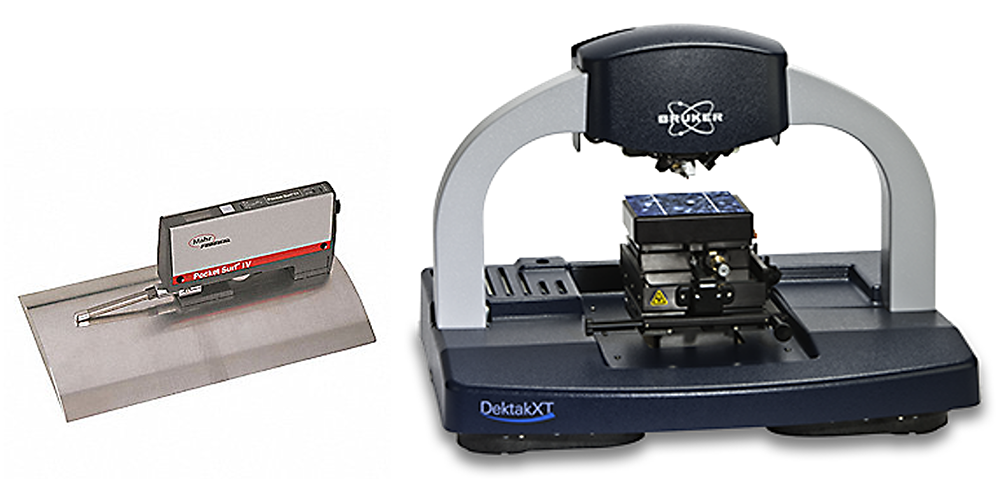
Stylus based measurement instruments are the most common tools for measuring surface texture. In these instruments a small tip is dragged across a surface while its deflection is recorded, providing a profile like the one we see in the image above.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500