Laser Optics Technology - LEOT.AS | STCC - laser optics
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Discover Sony's wide ranges of Alpha lens from prime lens to zoom lens, and from ultra-wide angle lens, super telephoto lens, G Master to G lens.
Illuminator or light source: the light source is usually built into the base of the microscope, and directs light through the condenser to the specimen.Alternatively, the light source may be separate, and be directed toward the condenser with a mirror. The intensity of the light can be adjusted using the rheostat (light) control knob. The microscope you are using has a rheostat on the front of the base and a switch on the left of the base.
Attention ▶Silicon lens has metallic luster so that visible light is reflected and absorbed. Because of this, no transmittance occurs. ▶Silicon lens without an anti-reflection coating has a loss due to surface reflection and results in transmittance of about 50%.
Steel Specification : CRV Steel / Carbon steel / Selected Steel Drop Forged Seam less tube Finish : Nickel Plated / Satin finish / Zinc plated With or ...
Illuminator or light source: the light source can be built into the base of the microscope, transmitting light through the specimen and/or the light source may be above the specimen as incident light. The lights can be turned on using rheostat (light) control knob on the front of the base.
The resolving power of a microscope is dependent on the numerical apertures of the optical lenses and the wavelength of light used to examine the specimen. It is the smallest distance between two points (measured in microns) that can be seen with the microscope. If two small objects close together can be seen clearly as two distinct objects, a microscope is said to have high resolving power.
Iris diaphragm: a unit below the condenser that controls the amount of light directed to the specimen. The diameter of the diaphragm can be adjusted by turning it to increase or decrease the size of the hole that light passes through.
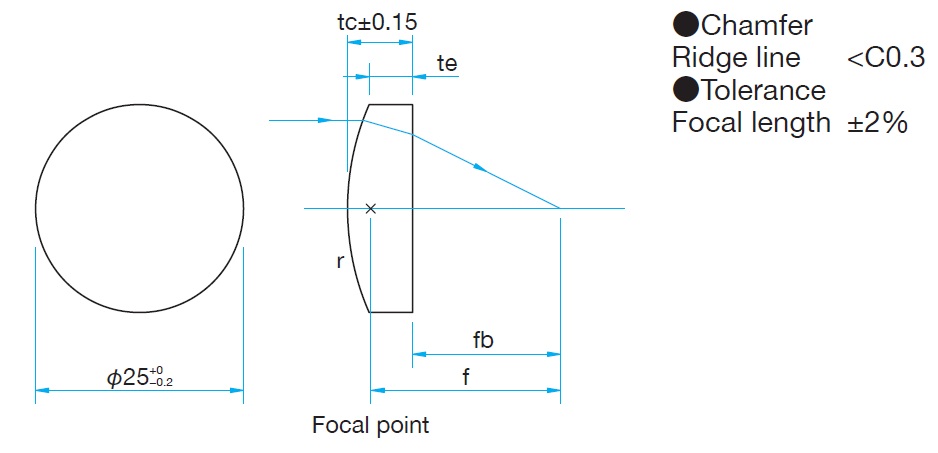
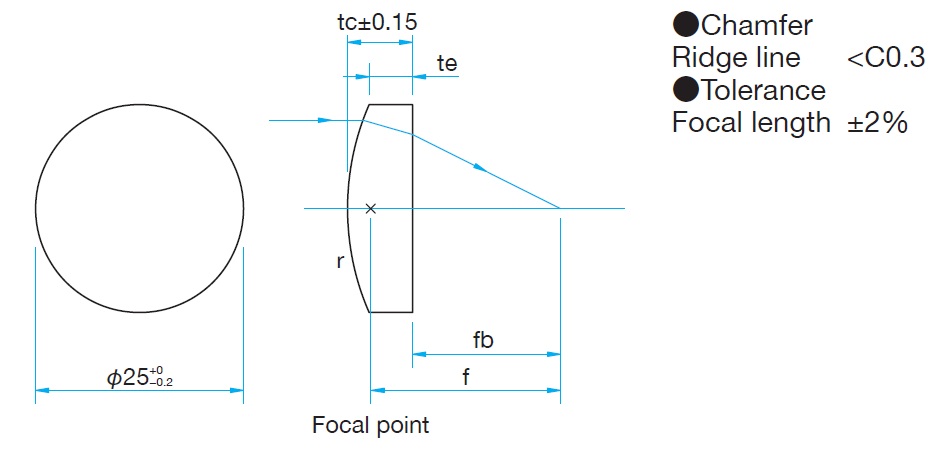
Plano-convexlens
Microscope are used by the students in many lab exercises. Instructors also need to learn to use the instructor microscope with the Leica camera and required LAS EZ & Leica AirLab Icon Guide software which will allow them to project the microscope images in real time.
UK Elliot Scientific Limited Unit 11 Sandridge Park, Porters Wood, St Albans, AL3 6PH TEL. +44 (0)1582 766 300 sales@elliotscientific.com United Kingdom
The 100X objective lens is called an oil immersion lens because oil is placed between the lens and the microscope slide to increase resolution (i.e., the level of detail that can be observed in an image). Light bends when it passes from the glass slide to air because of differing refractive indices. A drop of immersion oil between the slide and lens eliminates this problem because the oil has the same refractive index as the glass slide. Never use the 100X objective lens without oil and do not get oil on the 4X, 10X, or 40X lenses.
Sep 23, 2024 — Magnification = image size / actual size. Actual size = image size / magnification. Image size = magnification x actual size. Remember ...
USA OptoSigma Corporation 1540 Scenic Avenue, Suite 150, Costa Mesa, CA. 92626 TEL. +1-949-851-5881 sales@optosigma.com USA
Aspheric lenses
Focusing knob: the knob that allows you to focus on the object at each magnification by moving the stereo head up or down.
Stage: the flat surface upon which the slide with your specimen is placed. Most microscopes have a stage finger assembly to hold the slide on the stage. The entire mechanism including the slide moves horizontally across the stationary stage (left/right and forward/back) using two stage adjustment knobs situated under the stage (variably on the left or right side, in front of the focusing knobs).
Axial Resolution: point-to-point resolving power in the plane parallel to the optical axis. It is usually defined at the shortest distance between two longitudinal points on the specimen plane that can still be distinguished as separate entities.
1460-1600nm Near-Infrared Camera offers high speed electronic shutter and provides standard analog video output. Find out more at Edmund Optics.
Infraredlens
Köhler illumination is the alignment of the image-forming light path and the illumination light path of the microscope. In this process the con-denser is centered and focused, thereby providing an evenly illuminated field of view and more importantly maximum resolution of the specimen
SINGAPORE OptoSigma SEA 83 Science Park Drive, #02-01.The Curie, 118258 TEL. +65 6909 9318 sales@optosigma-sea.com SINGAPORE
Ocular lens or eyepiece: the secondary optical system that you look through. The ocular lens further magnifies (10x) the image and brings the light rays to a focal point. A binocular microscope has two ocular lenses and a monocular microscope has one ocular lens that sit on the adjustable binocular body. Binocular lenses can be adjusted to fit the distance between your eyes by gently pulling the oculars apart or by pushing them closer together.
Note: The microscope is now set to maximize resolution of the specimen. If you adjust the condenser height to gain contrast or adjust light intensity you will sacrifice the resolution capability. Use the aperture diaphragm and /or the illumination intensity to adjust contrast.
So now you know - FOV means "Field Of View" - don't thank us. YW! What does FOV mean? FOV is an acronym, abbreviation or slang word that is explained above ...
Compressed Air Duster for Electronics, 10 oz Can, 2/Pack. END11407. Buy Each $14.24/PK. Delivery: 1 - 2 business days.
Base: the bottom of the microscope, which supports the entire instrument. The stage plate is located directly on the base surface upon which a specimen is placed. The stage can have a removable black or white tile (that can be removed and cleaned) or it will have a light that will transmit light through the specimen.
A compound microscope is a high power microscope that uses a compound lens system. Higher magnification is achieved by using two lenses rather than just a single magnifying lens. While the eyepieces and the objective lenses create high magnification, a condenser beneath the stage focuses the light directly into the sample. A compound microscope has multiple lenses: the objective lens (typically 4x, 10x, 40x or 100x) is compounded (multiplied) by the eyepiece lens (typically 10x) to obtain a high magnification of 40x, 100x, 400x and 1000x. The objective lenses of a compound microscope causes the orientation of the image of the specimen to be inverted compared to the orientation of the actual specimen which means that a specimen viewed through a compound microscope will look upside down and backwards compared to how the specimen is mounted on the slide.
Lateral Resolution: point-to-point resolving power in the plane perpendicular to the optical axis. It is usually defined as the shortest distance between two lateral points on the specimen plane that can still be distinguished as separate entities.
Germanium IRLens
Coarse adjustment or coarse focusing knob: the large knob towards the back of the instrument that is used to significantly raise or lower the stage, when you first focus on a specimen at low power. It is never used when high power objectives are in place.
Microscopes must be calibrated so accurate measurements can be made. To calibrate a microscope both an ocular and a stage micrometer are used.
Knob moves the stage further in a turn than the Fine. Focus Knob does. Carefully try to turn each knob and remember what they do. Page 24 ...
Condenser: the lens located below the stage, which focuses light (from the illuminator) through the specimen being observed. Most microscopes have a movable condenser allowing its distance from the specimen to be adjusted using the condenser knob and condenser alignment screws.
Diopter: compensates for focusing differences between your eyes, it is very important this is set correctly, in order to prevent eye strain.
Silicone contactlens
Stereo microscopes have low magnifications that can range from 2 to 100x depending on the microscope, and are designed for viewing whole objects like rocks, plants, flowers, and invertebrate organisms by reflecting light off the specimen, producing a 3-dimensional image. Sometimes there is a light located in the base of the microscope that will allow transmitted light.
Fine adjustment or fine focusing knob: the smaller knob towards the back of the instrument that is used to make small adjustments in the height of the stage for final focusing on a specimen. It is the only focusing knob used with high power objectives.
Optical lenses
In your career at Waitrose, you'll be a champion for British produce and artisan foods. Apply today for our available jobs at over 350 Waitrose shops across ...
Depth of Field: is determined by the distance from the nearest specimen plane in focus to that of the farthest plane also simultaneously in focus. The thickness of the optical section along the optical axis within which objects in the specimen plane are in focus. High-magnification objectives have a decreased depth of field. The reverse is true of low-magnification objectives Field of View: the visible area seen through the microscope when the specimen is in focus. The greater the magnification the smaller the view. Focus: a specimen is in focus at the desired magnification when the image seen through the ocular lens is sharp and clear.
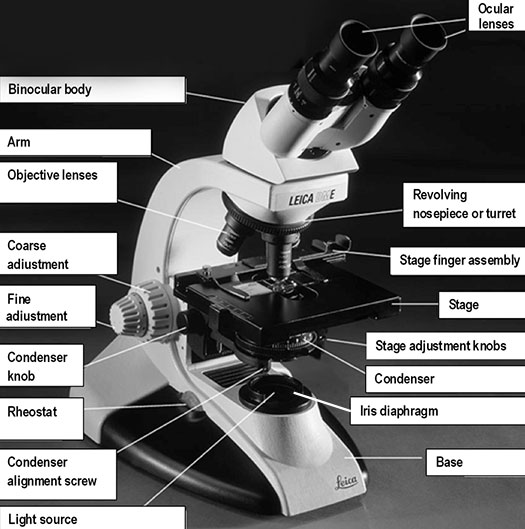
Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. In microscopy, it is the ratio between the size of an image produced by the microscope and its actual size. Microscopes magnify thin specimens mounted on microscope slides. They are ideal for observing unicellular or very small organisms, cells, and cell structures. We will use the compound and dissecting microscopes many times over the course of the semester. It is important to familiarize yourself with microscope use.
Jan 9, 2020 — The principal focus of a concave mirror is real while that of a convex mirror is.......................
Objective lenses: the primary optical system which produces a magnified image of the specimen. There are typically four objective lenses attached to the nosepiece with the magnification of each objective is engraved on its side.
These reflective microscope objective lenses eliminate chromatic aberration over a wide bandwidth from the UV to the MWIR. They are typically ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500