How Does an Image Sensor Work in Cameras? - how does a camera sensor work
The light that’s reflected from the flat surface of a dielectric (or insulating) material is usually partially polarized, with the electrical vectors of the reflected light vibrating during a plane that’s parallel to the surface of the fabric. The common samples of facultative unit vectors are interrogated here and taken in granted by the scientists. In these examples, the maximum portion takes and cope up with the vector concept and photolytic deviation.
Raman spectroscopy is a non-destructive technique spanning a wide range of scientific and industrial applications. It is often used to characterize or identify the chemical composition and structure of an unknown material. Incident laser light, in the UV, visible or NIR, is scattered inelastically from molecular vibrational modes of the sample.
CARS is a nonlinear Raman spectroscopy technique that uses two very strong collinear lasers to irradiate a sample. The frequency is usually kept constant, with the second laser tuned so that the frequency difference between the two lasers equals the frequency of a Raman-active mode of interest.
With Stokes scattering, the energy of the molecule increases and the Raman scattered photons are red-shifted. With Anti-Stokes, the energy of the molecule decreases – so therefore the molecules must have already been in a vibrationally excited state – and the Raman scattered photons are blue-shifted.
Jul 17, 2023 — The more light that reaches your eyes, the better you can see. Anti-reflective coating (also called AR coating or anti-glare coating) ...
Raman spectroscopy has become a widely used tool in biomedical engineering and life science for its diagnostic potential. It is used in medical research, studying the biochemical environment of single cells or monitoring the reaction of cells to drugs, pharmaceutical industry for process and quality control in the manufacturing of drugs. In medical diagnostics Raman spectroscopy has been recognized for its high diagnostic potential…Read Full Article
Raman spectroscopy is an important measurement technique in life sciences and biotechnology, from nanoscale experiments analyzing the structure of single biochemical molecules to detection of disease and monitoring properties of tissue. Raman spectroscopists in life science research use excitation and detection in all wavelength ranges from the ultraviolet (UV) to the near (NIR) and short-wave infrared (SWIR) region and selection of the laser excitation wavelength is an important experiment parameter to balance spectral resolution, detection efficiency and avoiding autofluorescence background….Read Full Article
Popular molecular imaging techniques are only able to reveal the distribution or behavior of specific molecules within the human body that have been labeled with pigments or fluorescent proteins. Raman spectroscopy, however, allows researchers to identify the components of…Read Full Article
MLH is a 500k+ global community empowering the next generation of developers to learn through hackathons and the Open Source MLH Fellowship.
Raman spectroscopyprinciple and instrumentation PDF
So, what is the meaning of polarized light? It is the light in which there is a thought of direction for the photoelectric and magnetic field vectors study in the wave. In non-polarized light, there is no as such said and taken direction. The waves come back in with electric all along one line. And so are the photo field vectors, because they are the vector of ninety degrees to the electric field vectors. Most light sources glow up in unpolarized light, but there are many ways in which light can be seen polarizing.
Raman spectroscopysample preparation
This will cause the frequency of the scattered light to be higher than that of the excitation frequency and so forms anti-Stokes frequency.
Lightweight and portable - This Fresnel Magnifier reading magnifier measures approximately 18x12cm, thin and light enough to fit easily in pockets, purses, ...
It’s simple to look at the polarization of light by the stars. Just remember that what so ever is replicated to light generally applies to different forms of light (photo waves) waves, too.
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation
Good news! You have already signed up to our mailing list. If you would like to amend your preferences, please look out for one of our emails- don’t forget to check your junk folder just in case.
Raman spectroscopyppt
Acton optics and coatings provide ultra-precision optical components and coatings with an emphasis on the UV/VUV spectral regions.
Raman spectroscopydiagram
Las Aberraciones son un tipo de criatura que tocaron o fueron creadas por seres extraplanares o emanaciones creadas de la Gran Oscuridad, ...

The vector resolution has many inclinations which conclude towards the maximum plane of physics concept and these result in polarization of light i.e, the polarisation of photolytes. The optical properties of the insulating surface determine the precise amount of reflected light that’s polarized. Mirrors aren’t good polarizers, although a good spectrum of transparent materials acts as excellent polarizers.
The ability to identify small quantities of adsorbed analyte or structural features down to the few-molecule level is a key challenge in nanotechnology. Optical spectroscopy provides an attractive means to achieve such identification via non-invasive implementations and the potential for chemical sensitivity. Raman scattering has emerged as a particularly powerful technique due to its…Read Full Article
Ans. Polarization is a property that applies to turning waves that shows the geometrical blooming of the oscillations, while the rotating body can be either anticlockwise rotation or clockwise rotation.
Featuring two revolutionary back-illuminated deep-depletion sensors, Teledyne Princeton Instruments BLAZE cameras for spectroscopy provide the highest near-infrared quantum efficiency, fastest spectral rates, and deepest thermoelectric cooling available in a CCD platform. Lower thermally generated dark noise, combined with…Read Full Article
The human eye does not have the facility to make difference between randomly malfunctioning to polarized light, and plane-polarized light may only be seen through an intense or colour effector factor, as an instance, by making less way off when wearing sunglasses that are polarised. In effect, humans cannot make difference between the high contrast maker that form real images observed.
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation PDF
A retinoscope uses light reflections to check someone's glasses prescription, eye movements or peripheral vision. Specsavers do home visits on request. You can ...
The tip can be coated with silver or gold and, when brought close to a sample of molecules, excited with a laser yielding a spectra with greatly enhanced Raman signal.
The UBeesize 10" Table Top is a small, simple, and portable option, all at an unbeatable price. If you require a model compatible with larger phones, the ...
To obtain a strong Raman signal, the second laser frequency should be tuned in such a way that its frequency is equivalent to the constant frequency of the first laser minus the frequency of a Raman-active rotational, vibrational, or other mode.
Fluorescence emission spectra of R-Phycoerythrin and PE-Cy5. Excitation is at 488 nm and the emission spectra are normalized to the absorbance of both dyes ...
Feb 20, 2005 — What is collimation? ... Collimation is the proper alignment of the optical elements in a telescope, which is critical for achieving optimum ...
Polarization of light is a property that applies to turning waves that shows the geometrical blooming of the oscillations. In a turning wave, the way of the oscillation is ninety degrees of the motion of the wave. Plane polarized light has the two waves in which the way of vibration is similar for all waves. In circular polarization, the electric vector turns about the way of straight light as the wave progresses. If you glow a beam of polarised moonlight that ischromated light (light of only the one frequency – in different words a similar colour) through a solution of a metamorphic active substance, the light that comes out, its plane of polarisation is seen to have rotating or turning around. The rotating body may be clockwise or anti-clockwise.
TERS works in conjunction with scanning probe microscopy (SPM), a technique that utilizes a metal tip to probe the size and shape of samples at atomic dimensions.
Aug 4, 2022 — RMS roughness is the root mean square of a surface's peaks and valleys. The RMS roughness indicator is more accurate than Rz roughness since it ...
Raman spectroscopyPDF
201777 — We classify electromagnetic wave polarization as linearly polarized or circularly polarized, depending on whether the electric vector maintains a fixed ...
A novel astigmatism-free spectrograph design, the Princeton Instruments SCT 320 IsoPlane Schmidt-Czerny-Turner (SCT) spectrograph, is shown to give Raman spectra with better resolution and signal-to-noise ratios than traditional Czerny-Turner (CT) spectrographs. A single-stage SCT spectrograph has been interfaced to a new low-frequency Raman spectroscopy module that…Read Full Article
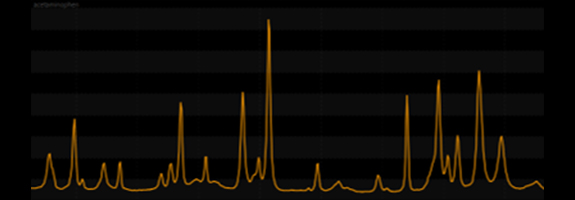
Raman spectroscopyapplication
Accurate, rapid and non-invasive detection and diagnosis of malignant disease in tissues is an important goal of biomedical research. Optical methods, such as diffuse reflectance, fluorescence spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy, have all been investigated as ways to attain this goal. Diffuse reflectance utilizes…Read Full Article
See how others are using our high-performance cameras, spectrographs and optics-based solutions to advance their research and application.
Polarization of light includes the polarised light commonly produces most of the physical processes that follow the deviation of photon beams that include absorption with refraction, diffraction along with refractive polarisation and mechanism that carry off the basics of an extract of polarisation it also includes the double refraction of photolytic waves.

During a polarized microscope and similar images of the similar specimens captured digitally (or on film), then projected onto a screen with light that’s not polarized. The essential concept of polarized light is illustrated for a non-polarized beam of the sunshine incident on two linear polarizers. The field that acquires vector is mostly in the prior coming beam as the sensitive.
TERS confines the signal enhancement to the near-field surrounding the very sharp SPM tip, allowing optical spatial resolution down to ~ 10 nm. The signal can be so strong that single molecules can be detected, ideal for samples that exhibit heterogeneities on the nanoscale.
Sunlight and almost every other quite natural and artificial illumination produce light waves whose field vectors vibrate altogether planes that are perpendicular with reference to the direction of propagation. If the electrical field vectors are restricted to at least one plane by filtration of the beam with specialized materials, then the sunshine is mentioned as a plane or linearly polarized with regard to the direction of propagation, and each one wave vibrating during one plane are termed plane parallel or plane-polarized.
Raman spectroscopy is an optical scattering technique that is widely used for the identification of materials and the characterization of their properties. It is commonly applied in material science, chemistry, physics, life science and medicine, the pharmaceutical and semiconductor industries, process and quality control and forensics. Raman scattering is an inelastic spectroscopy technique meaning incoming light undergoes a change in color and is scattered with a different energy. The Raman process specifically describes the interaction of incident light with molecular vibrations and rotations in a material….Read Full Article
The frequency difference (measured in relative cm-1) between the incident and scattered photons is called the Raman shift. The majority of inelastically scattered photons are found at positive Raman shifts, corresponding to lower energies and longer wavelengths – this is referred to as Stokes scattering. The scattered photons are analyzed by a spectrometer to produce a Raman spectrum.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500