Free-space optical comms: High data-rate connectivity from ... - free space optical communications
Focal point calculatorphysics

You must be very careful when using the high power lenses so you do not jam them into the slide. Ocular Lens - The ocular lens, or eyepiece, magnifies the image ...
How to calculatefocallength of convex lens
Thermal camera lenses are made of Germanium because of the material's unique properties with respect to the Infrared spectrum.
NIRCam Wavelength Range NIRCam is designed to capture light ranging in wavelength from 0.6 microns (visible red) to 5 microns (mid-infrared).
Chromatic aberrations appear as red or purple outlines. They are especially visible in areas with strong contrasts. This phenomenon occurs when the lens is ...
Two open white squares arranged vertically are overlaid on the image. The top square includes the top half of the bright core of the spiral galaxy and one of the arms. The bottom square is set below the bright core, and includes portions of both arms. Both squares are rotated slightly clockwise. Together, the two squares cover about 15 percent of the image.
Focalratiocalculator
Focal point calculatormath
Browse Silver Mirrors - 459 available at Lamps Plus! Price Matching Policy - Possini Euro Metzeo 26" X 36" Brushed Nickel Mirror, ...
Camera lens distancecalculator
The Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) is one of Webb’s four scientific instruments. NIRCam is Webb’s primary near-infrared imager, providing high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy for a wide variety of investigations. Because NIRCam is the only near-infrared instrument with coronagraphic and time-series imaging capabilities, it is crucial for many exoplanet studies. In addition to imaging and spectroscopy, NIRCam is also part of Webb’s wavefront sensing and control system, which detects and corrects for slight irregularities in the shape of the primary mirror or misalignment between mirror segments, giving the telescope the ability to focus clearly on objects near and far. NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.
Focallengthcalculatorsensor size
This effective focal length calculator helps you select a lens to use with your camera. The calculator takes your target field of view (angle of view) and camera specification then provides the required lens EFL.The calculator uses the camera lens focal length equation. This formula is different than the lens maker's equation which is intended for simple thin lens elements. The Optical Effective Focal Length (EFL) should not be confused with the Mechanical Back-Focal Length (BFL). The EFL determines the field of view of the camera while the BFL determines whether a lens will focus on a camera.
Shop high-quality magnifiers, loupes, and magnifying glasses at Magnifier.com. Affordable prices, expert-rated lenses, and USA-made options.
Aug 2, 2024 — Anti-reflective coating (also known as AR, no-glare, or glare-free coating) reduces glare by absorbing and redirecting reflected light.
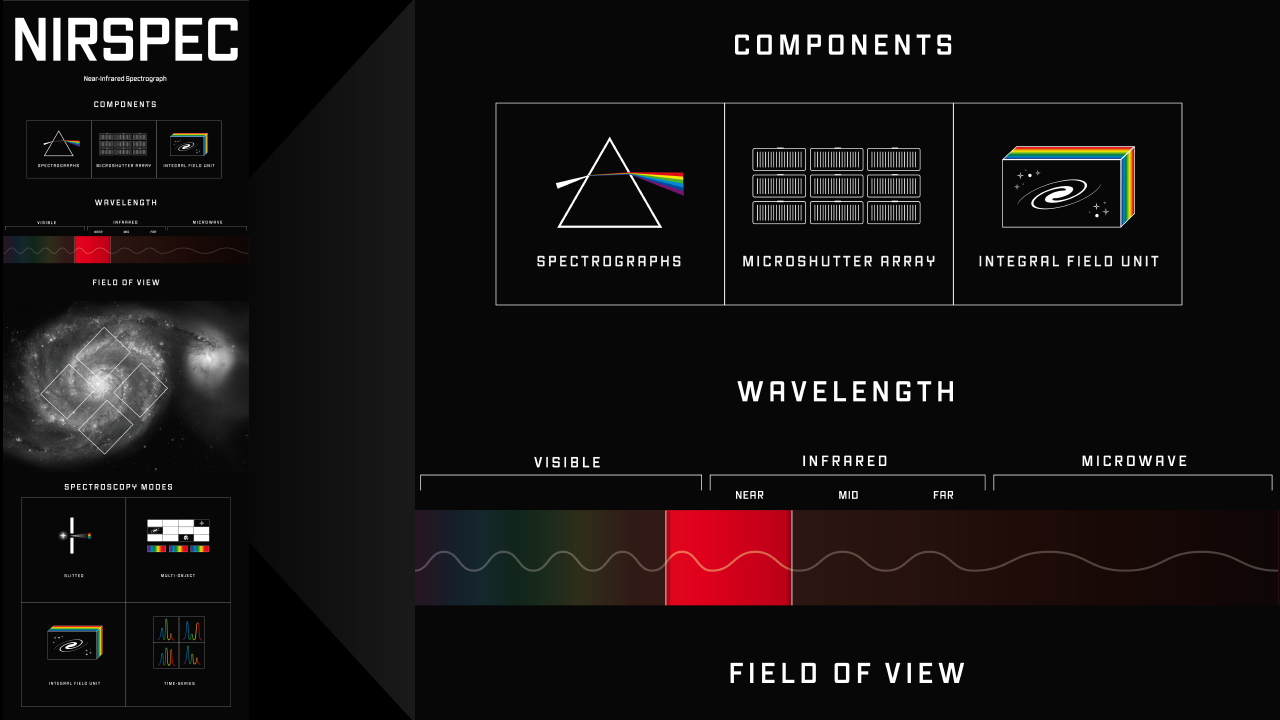
The graphic consists of a horizontal bar with a sine wave pattern running through the middle from left to right. The wavelength (distance between peaks) of the waves in the wave pattern increases from left to right. The bar is divided into thirds from left to right. The left third of the bar, labeled “visible,” has a subtle rainbow coloring, from purple at the left to red at the right. The middle third, labeled “infrared,” is divided into three sections, labeled “near,” “mid,” and “far,” The right third of the bar, labeled “microwave” is almost black.
Lens aberration is a property of lenses that results in light being spread out over some region of space rather than being focused to a point.
Black-and-white space telescope image showing a spiral galaxy with two arms. One arm spirals around the bright core of the galaxy, ending at the top right of the image. The galaxy’s other arm ends at the bottom left. A smaller elliptical galaxy lies at the tip of the top arm. The larger spiral galaxy covers about two-thirds of the width of the infographic. The smaller elliptical galaxy covers about one-tenth of the width.
NIRCam Spectroscopy Modes Wide-Field Slitless Spectroscopy involves capturing the overall spectrum of a wide field of view: a field of stars, part of a nearby galaxy, or many galaxies at once. Time-Series Spectroscopy involves capturing the spectrum of an object or region of space at regular intervals in order to observe how the spectrum changes over time. Time-series spectroscopy is used to study planets as they transit their stars.
Focal point Calculatorparabola
Infographic titled “NIRCam: Near-Infrared Camera.” The infographic is divided into five sections arranged vertically. From top to bottom: Components, Wavelength, Field of View, Imaging Modes, and Spectroscopy Modes.
Focallength to magnificationcalculator
How to invest in Cailabs stock? Accredited investors can buy pre-IPO stock in companies like Cailabs through EquityZen funds. These investments are made ...
NIRCam Fields of View An instrument’s field of view is the amount of sky that it can observe at any given point in time. (The actual area that can be observed depends on the distance of the object being observed.) In this graphic, a Hubble Space Telescope image of the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) is shown for scale. The image covers an area of 9.6 × 6.6 arcminutes. (The full Moon has a diameter of about 31 arcminutes across the sky.) NIRCam has two main fields of view, each of which covers an area of 2.2 × 2.2 arcminutes. Its coronagraphic field of view is smaller.
In Raman spectroscopy, an unknown sample of material is illuminated with monochromatic (single wavelength or single frequency) laser light, which can be ...
E Döpel · 1990 · 9 — A derivation is presented showing how the matrix formalism of geometrical optics can be used to calculate the group delay and group velocity dispersion of ...
NIRCam Components Cameras capture two-dimensional images of regions of space. Spectrographs spread light out into a spectrum so that the brightness of each individual wavelength can be measured. Coronagraphs are opaque disks used to block the bright light of stars in order to detect the much fainter light of planets and debris disks orbiting the star.
NIRCam Imaging Modes Standard Imaging is the equivalent to basic digital photography and involves capturing pictures of a wide variety of objects and materials in space that emit or reflect infrared light. Coronagraphic Imaging (sometimes called high-contrast imaging) involves using a coronagraph to block the light of a star in order to reveal the much dimmer light of nearby objects, such as exoplanets and debris disks. Time-Series Imaging involves capturing a series of images at regular intervals in order to measure changes over time. Time-series can be used to track changes in the brightness of a star or can be combined with coronagraphic imaging to track the motion of a planet.
The right end of the visible through the near-infrared section of the bar is called out prominently with bright to dark red coloring.





 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500