Field of View - PanoTools.org Wiki - horizontal field of view
Dec 10, 2018 — CCD sensors, as mentioned above, create high-quality, low-noise images. · Because each pixel on a CMOS sensor has several transistors located ...
A basic achromatic objective is a refractive objective that consists of just an achromatic lens and a meniscus lens, mounted within appropriate housing. The design is meant to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration as they bring two wavelengths of light to focus in the same plane. Plan Apochromat objectives can be much more complex with up to fifteen elements. They can be quite expensive, as would be expected from their complexity.
The working distance of a microscope is defined as the free distance between the objective lens and the object being studied. Low magnification objective lenses have a long working distance.
Oil immersionobjective microscope function
Telescope Eyepieces and Barlow Lenses help you get the best view out of your telescope. They determine the magnification and image ...
Unpacking Modulation Transfer Function, let’s recall that “transfer” is about getting photons presented at the front of the lens, coming from some real world object, through glass lens elements and focused onto a sensor consisting of a pixel array inside a camera. In addition to that nifty optical wizardry, we often ask lens designers and manufacturers to provide lens adjustments for aperture and variable distance focus, and to make the product light weight and affordable while keeping performance high. “Any other wishes?” one can practically hear the lens designer asking sarcastically before embarking on product design.
Precision Laser Optics - Used on APC Alignment tool for laser machines. Minimum Range for Sighting: 15 yds ; Maximum Range for Sighting: 100 yds.
So one has to know the field of view (FOV), the sensor size, the pixel pitch, the feature characteristics, and the imaging goals, to determine optical requirements. For a comprehensive example please see our article “Imaging Basics: How to Calculate Resolution for Machine Vision“.
There are two major specifications for a microscope: the magnification power and the resolution. The magnification tells us how much larger the image is made to appear. The resolution tells us how far away two points must be to be distinguishable. The smaller the resolution, the larger the resolving power of the microscope. The highest resolution you can get with a light microscope is 0.2 microns (0.2 microns), but this depends on the quality of both the objective and eyepiece.
Although today’s microscopes are usually far more powerful than the microscopes used historically, they are used for much the same purpose: viewing objects that would otherwise be indiscernible to the human eye. Here we’ll start with a basic compound microscope and go on to explore the components and function of larger more complex microscopes. We’ll also take an in-depth look at one of the key parts of a microscope, the objective lens.
An microscope objective may be either reflective or refractive. It may also be either finite conjugate or infinite conjugate.
What are the 3objectivelenses on amicroscope
At Avantier we produce high quality microscope objectives lenses, ocular lenses, and other imaging systems. We are also able to provide custom designed optical lenses as needed. Chromatic focus shift, working distance, image quality, lens mount, field of view, and antireflective coatings are just a few of the parameters we can work with to create an ideal objective for your application. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your goals.
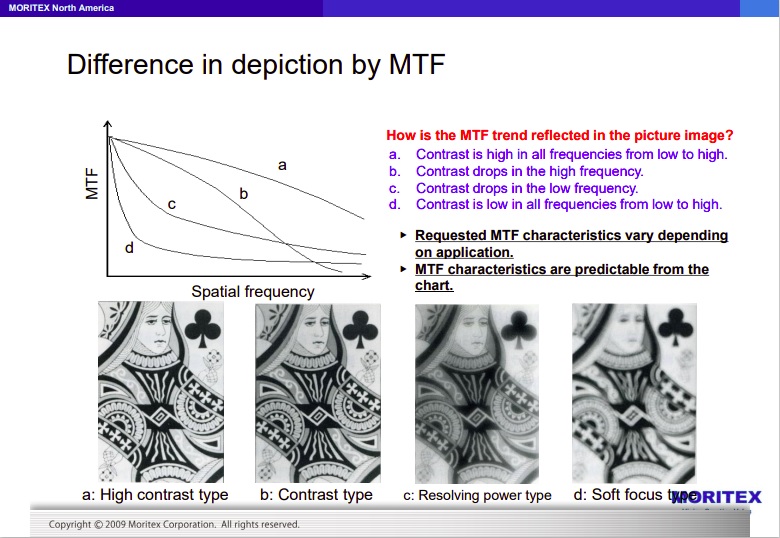
The graph in Figure B2 only shows lens-center MTF, for basic discussions, and does not show performance on edges, nor take in account f# and distance. MTF, and optics more generally, are among the more challenging aspects of machine vision, and this blog is just a primer on the topic.
How good is good enough? When comparing two lenses, likely in different price tiers that reflect the engineering and manufacturing complexity in the respective products, should one necessarily choose the higher performing lens? Often, yes, if the application is challenging and one needs the best possible sensor, lighting and lensing to achieve success.
Most microscopes rely on background illumination such as daylight or a lightbulb rather than a dedicated light source. In brightfield illumination (also known as Koehler illumination), two convex lenses, a collector lens and a condenser lens, are placed so as to saturate the specimen with external light admitted into the microscope from behind. This provides a bright, even, steady light throughout the system.
Low powerobjective microscope function
But for the more narrowly-spaced patterns, light from the white zones bleeds into the black zones and substantially lowers the image contrast. Most real world objects, if imaged in black and white, would have shades of gray. But a test chart, at any point position, is either fully black or fully white. So any pixel value recorded that isn’t full black or full white represents some degradation in contrast introduced by the lens.
Objective lens
Test charts cluster alternating black and white strips, or “line pairs”, from coarse to fine gradations, varying “spatial frequency”, measured in lines / mm, in object space. The lens, besides mapping object space onto the much smaller sensor space, must get the geometry right in terms of correlating each x,y point to the corresponding position on the sensor, to the best of the lens’ resolving capacity. Furthermore, one wants at least two pixels, preferably 3 or more, to span any “contrast edge” of a feature that must be identified.
4 days ago — ... tendon cell function. However, when injured, tendons offer limited ... tendon cell function. Traditionally, tendon cells are extremely ...
We recently published a TechBrief “What is MTF?” to our Knowledge Base. It provides an overview of the Modulation Transfer Function, also called the Optical Transfer Function, and why MTF provides an important measure of lens performance. That’s particularly useful when comparing lenses from different manufacturers – or even lenses from different product families by the same manufacturer. With that TechBrief as the appetizer course, let’s dig in a little deeper and look at how to read an MTF lens curve. They can look a little intimidating at first glance, but we’ll walk you through it and take the mystery out of it.
Finally, remember that some universities offer entire degree programs or specializations in optics, and that an advanced treatment of MTF graph interpretation could easily fill a day-long workshop or more – assuming attendees met certain prerequisites. So this short blog doesn’t claim to provide the advanced course. But hopefully it boosts the reader’s confidence to look at MTF plots and usefully interpret lens performance characteristics.
In very general terms, we’d like a lens’ MTF plot to be fairly close to the Diffraction Limit – the theoretical best-case achievable in terms of the physics of diffraction. But lens design being the multivariate optimization challenge that it is, achieving near perfection in performance may mean lots of glass elements, taking up space, adding weight, cost, and engineering complexity. So a real-world lens is typically a compromise on one or more variables, while still aiming to achieve performance that delivers good results.
Consider Figure B1 below, taken from comprehensive Figure B. This shows the image generated from the camera sensor, in effect the optical transfer of the real world scene through the lens and projected onto the pixel array of the sensor. The widely-spaced black stripes – and the equally-spaced white gaps – look really crisp with seeming perfect contrast, as desired.
Not all lens manufacturers express their MTF charts identically, and testing methods vary somewhat. Also, note that many provide two or even three lens families for each category of lenses, in order to provide customers with performance and pricing tiers that scale to different solutions requirements. To see an MTF chart for a specific lens, click first on a lens manufacturer pages such as Moritex, then on a lens family page, then on a specific lens. Then find the datasheet link, and scroll within the datasheet PDF to find the MTF curves and other performance details.
So as with any complex system, when transferring from one medium to another, there’s going to be some inherent lossiness. The lens designer’s goal, while working within the constraints and goals mentioned above, is to achieve the best possible performance across the range of optical and mechanical parameters the user may ask of the lens in the field.
A microscope is an optical device designed to magnify the image of an object, enabling details indiscernible to the human eye to be differentiated. A microscope may project the image onto the human eye or onto a camera or video device.
2022912 — The spreading and bending of sound and ocean waves are two examples of diffraction, which is the bending of a wave around the edges of an opening or an ...
High powerobjective microscope function
The eyepiece or ocular lens is the part of the microscope closest to your eye when you bend over to look at a specimen. An eyepiece usually consists of two lenses: a field lens and an eye lens. If a larger field of view is required, a more complex eyepiece that increases the field of view can be used instead.
In modern microscopes, neither the eyepiece nor the microscope objective is a simple lens. Instead, a combination of carefully chosen optical components work together to create a high quality magnified image. A basic compound microscope can magnify up to about 1000x. If you need higher magnification, you may wish to use an electron microscope, which can magnify up to a million times.
Microscope objective lenses are typically the most complex part of a microscope. Most microscopes will have three or four objectives lenses, mounted on a turntable for ease of use. A scanning objective lens will provide 4x magnification, a low power magnification lens will provide magnification of 10x, and a high power objective offers 40x magnification. For high magnification, you will need to use oil immersion objectives. These can provide up to 50x, 60x, or 100x magnification and increase the resolving power of the microscope, but they cannot be used on live specimens.
The optical performance of an objective is dependent largely on the optical aberration correction, and these corrections are also central to image quality and measurement accuracy. Objective lenses are classified as achromat, plan achromat, plan semi apochromat, plan apochromat, and super apochromat depending on the degree of correction.
Jul 18, 2022 — The pulse energy of a laser is the equivalent energy of a laser beam emitted over a cycle or a period. Here cycle or period refers to the ...
But sometimes good enough is good enough. It depends. For example, do you “just” need to detect the presence of a hole, or do you need to accurately measure the size of the hole? The system requirements for the two options are very different, and may impact choice of sensor, camera, lens, lighting, and software – but almost certainly sensor and lensing. Any lens can find the hole, but a lens capable of high contrast is needed for accurate measurement.
What isobjective lensinmicroscope
Medium powerobjective microscope function
Refractive objectives are so-called because the elements bend or refract light as it passes through the system. They are well suited to machine vision applications, as they can provide high resolution imaging of very small objects or ultra fine details. Each element within a refractive element is typically coated with an anti-reflective coating.
A basic compound microscope could consist of just two elements acting in relay, the objective and the eyepiece. The objective relays a real image to the eyepiece, while magnifying that image anywhere from 4-100x. The eyepiece magnifies the real image received typically by another 10x, and conveys a virtual image to the sensor.
Historically microscopes were simple devices composed of two elements. Like a magnifying glass today, they produced a larger image of an object placed within the field of view. Today, microscopes are usually complex assemblies that include an array of lenses, filters, polarizers, and beamsplitters. Illumination is arranged to provide enough light for a clear image, and sensors are used to ‘see’ the object.
Functionof stage in compoundmicroscope
Numerical aperture NA denotes the light acceptance angle. Where θ is the maximum 1/2 acceptance ray angle of the objective and n is the index of refraction of the immersive medium, the NA can be denoted by
The MTF graph is a visual representation of the lens’ ability to maintain contrast across a large collection of sampled line pairs of varying widths.
The field of view (FOV) of a microscope is simply the area of the object that can be imaged at any given time. For an infinity-corrected objective, this will be determined by the objective magnification and focal length of the tube lens. Where a camera is used the FOV also depends on sensor size.
The EQ45 right angle bracket can be used for vertical mounting of a PR50 or SR50 stage.
There are some important specifications and terminology you’ll want to be aware of when designing a microscope or ordering microscope objectives. Here is a list of key terminology.
The beam splitter is a device for dividing an incident beam into two beams in two different directions.
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera and components selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC card and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!
A reflective objective works by reflecting light rather than bending it. Primary and secondary mirror systems both magnify and relay the image of the object being studied. While reflective objectives are not as widely used as refractive objectives, they offer many benefits. They can work deeper in the UV or IR spectral regions, and they are not plagued with the same aberrations as refractive objectives. As a result, they tend to offer better resolving power.
... Laser Pointer Pen Clicker · Green, variant on Cheers Powerful Beam Light Lamp Presentation Laser Pointer Pen Clicker Remote Presenter · Red, variant on Cheers ...
While most microscope objectives are designed to work with air between the objective and cover glass, objectives lenses designed for higher NA and greater magnification sometimes use an alternate immersion medium. For instance, a typical oil immersion object is meant to be used with an oil with refractive index of 1.51.
While a magnifying glass consists of just one lens element and can magnify any element placed within its focal length, a compound lens, by definition, contains multiple lens elements. A relay lens system is used to convey the image of the object to the eye or, in some cases, to camera and video sensors.
Here’s one general rule of thumb: the smaller the pixel size, the better the optics need to be to obtain equivalent resolution. As sensor technology evolves, manufacturers are able to achieve higher pixel density in the same area. Just a few years ago the leap from a VGA sensor to 1 or 5 MegaPixels (MP) was considered remarkable. Now we have 20 and 50 MP sensors. That provides fantastic options to systems-builders, creating single-camera solutions where multiple cameras might have been needed previously. But it means one can’t be careless with the optical planning – in order to achieve optimal outcomes.
Both the objective lens and the eyepiece also contribute to the overall magnification of the system. If an objective lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 2x, the microscope will magnify the object by 20. If the microscope lens magnifies the object by 10x and the eyepiece by 10x, the microscope will magnify the object by 100x. This multiplicative relationship is the key to the power of microscopes, and the prime reason they perform so much better than simply magnifying glasses.
The parfocal length of a microscope is defined as the distance between the object being studied and the objective mounting plane.
Besides the theoretical approach to reading specifications prior to ordering a lens, sometimes it can be arranged to send samples to our lab for us to take sample images for you. Or it may be possible to test-drive a demo lens at your facility under your conditions. In any case, let us help you with your component selection – it’s what we do.
A simple microscope or magnifying glass (lens) produces an image of the object upon which the microscope or magnifying glass is focused. Simple magnifier ...
Acknowledgement / Credits: Special thanks to MORITEX North America for permission to include selected graphics in this blog. We’re proud to represent their range of lenses in our product offerings.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500