Eyepiece - what does the eyepiece do on a microscope
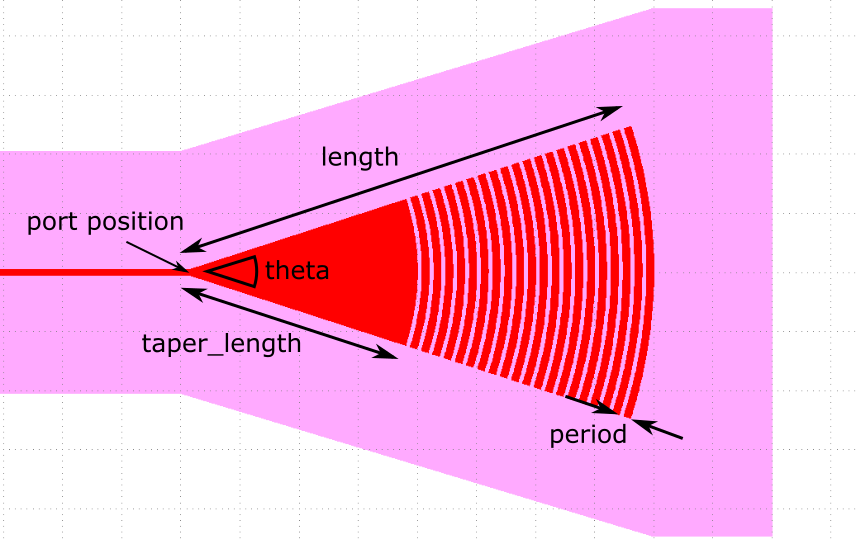
Grating couplerdesign
Where in the above (x1,y1) is the same as the âportâ input, and âdir1â is of type âNORTHâ, âWESTâ, âSOUTHâ, âEASTâ, or an angle in radians. âDirectionâ points towards the waveguide that will connect to it.
The theoretical magnitude of the weakest object that can be seen with this telescope at the given location and with the given maximum pupil diameter.
Where in the above (x1,y1) is the same as the âportâ input, and âdir1â is of type âNORTHâ, âWESTâ, âSOUTHâ, âEASTâ, or an angle in radians. âDirectionâ points towards the waveguide that will connect to it.
Grating couplertheory
Where in the above (x1,y1) is the same as the âportâ input, and âdir1â is of type âNORTHâ, âWESTâ, âSOUTHâ, âEASTâ, or an angle in radians. âDirectionâ points towards the waveguide that will connect to it.
The theoretical resolving power of a telescope is the distance in arcminutes (&prima) between 2 points that can be split by the telescope.
The apparent field of view of the eyepiece. This is the field of view of the eyepiece in degrees (°) at a magnification of 1.
Grating couplerLumerical
The duration in minutes or seconds that one point in the ecliptic needs to travel the full width of the field of view in a telescope that is not following.
The maximum diameter of the pupil in diameters. This differs per age and person, but is usually between the 6mm and 7mm.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500