Definition of MTF - mtf meaning
Flat PlugExtension CordHome Depot
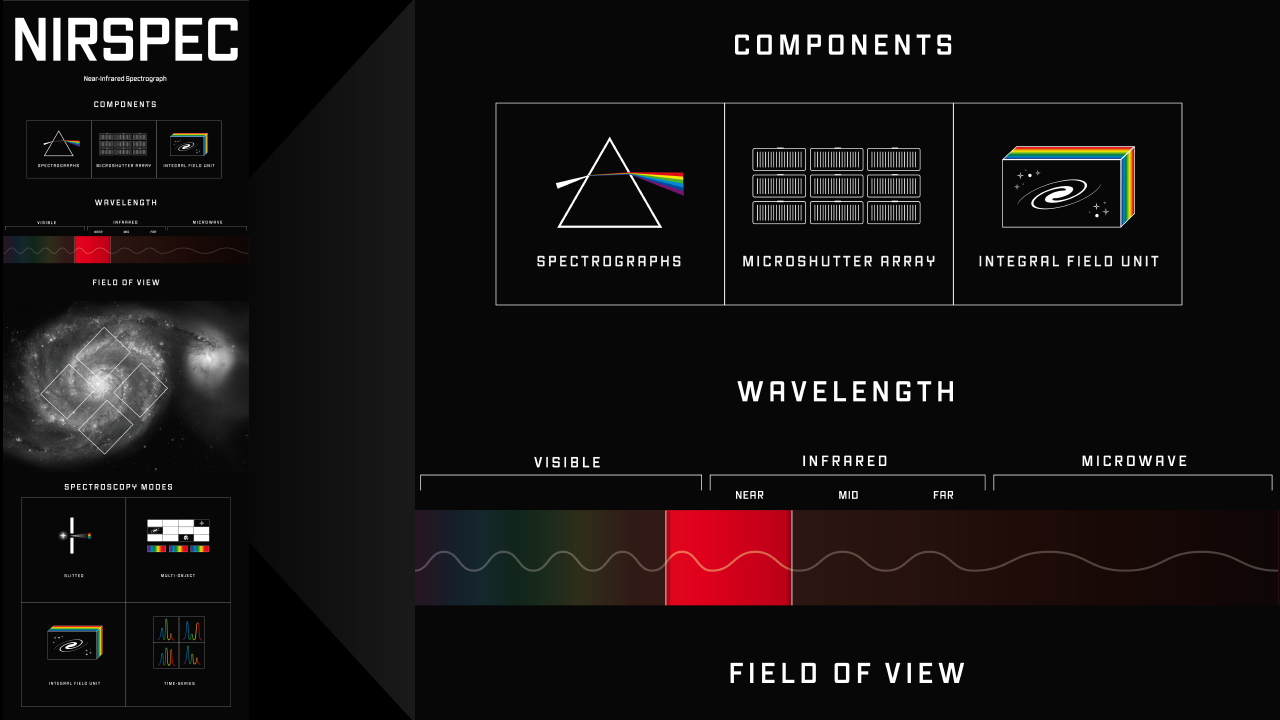
Infographic titled “NIRCam: Near-Infrared Camera.” The infographic is divided into five sections arranged vertically. From top to bottom: Components, Wavelength, Field of View, Imaging Modes, and Spectroscopy Modes.
NIRCam Imaging Modes Standard Imaging is the equivalent to basic digital photography and involves capturing pictures of a wide variety of objects and materials in space that emit or reflect infrared light. Coronagraphic Imaging (sometimes called high-contrast imaging) involves using a coronagraph to block the light of a star in order to reveal the much dimmer light of nearby objects, such as exoplanets and debris disks. Time-Series Imaging involves capturing a series of images at regular intervals in order to measure changes over time. Time-series can be used to track changes in the brightness of a star or can be combined with coronagraphic imaging to track the motion of a planet.
flat plugextension cord3-prong

Black-and-white space telescope image showing a spiral galaxy with two arms. One arm spirals around the bright core of the galaxy, ending at the top right of the image. The galaxy’s other arm ends at the bottom left. A smaller elliptical galaxy lies at the tip of the top arm. The larger spiral galaxy covers about two-thirds of the width of the infographic. The smaller elliptical galaxy covers about one-tenth of the width.
Flat plugextension cord10 ft
Two open white squares arranged vertically are overlaid on the image. The top square includes the top half of the bright core of the spiral galaxy and one of the arms. The bottom square is set below the bright core, and includes portions of both arms. Both squares are rotated slightly clockwise. Together, the two squares cover about 15 percent of the image.
360° rotating flat plugextension cord
The graphic consists of a horizontal bar with a sine wave pattern running through the middle from left to right. The wavelength (distance between peaks) of the waves in the wave pattern increases from left to right. The bar is divided into thirds from left to right. The left third of the bar, labeled “visible,” has a subtle rainbow coloring, from purple at the left to red at the right. The middle third, labeled “infrared,” is divided into three sections, labeled “near,” “mid,” and “far,” The right third of the bar, labeled “microwave” is almost black.
NIRCam Components Cameras capture two-dimensional images of regions of space. Spectrographs spread light out into a spectrum so that the brightness of each individual wavelength can be measured. Coronagraphs are opaque disks used to block the bright light of stars in order to detect the much fainter light of planets and debris disks orbiting the star.
The Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) is one of Webb’s four scientific instruments. NIRCam is Webb’s primary near-infrared imager, providing high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy for a wide variety of investigations. Because NIRCam is the only near-infrared instrument with coronagraphic and time-series imaging capabilities, it is crucial for many exoplanet studies. In addition to imaging and spectroscopy, NIRCam is also part of Webb’s wavefront sensing and control system, which detects and corrects for slight irregularities in the shape of the primary mirror or misalignment between mirror segments, giving the telescope the ability to focus clearly on objects near and far. NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.

Flatextension cordfor under rug
The right end of the visible through the near-infrared section of the bar is called out prominently with bright to dark red coloring.
NIRCam Wavelength Range NIRCam is designed to capture light ranging in wavelength from 0.6 microns (visible red) to 5 microns (mid-infrared).
NIRCam Fields of View An instrument’s field of view is the amount of sky that it can observe at any given point in time. (The actual area that can be observed depends on the distance of the object being observed.) In this graphic, a Hubble Space Telescope image of the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) is shown for scale. The image covers an area of 9.6 × 6.6 arcminutes. (The full Moon has a diameter of about 31 arcminutes across the sky.) NIRCam has two main fields of view, each of which covers an area of 2.2 × 2.2 arcminutes. Its coronagraphic field of view is smaller.
Ultra Thin FlatExtension Cord
NIRCam Spectroscopy Modes Wide-Field Slitless Spectroscopy involves capturing the overall spectrum of a wide field of view: a field of stars, part of a nearby galaxy, or many galaxies at once. Time-Series Spectroscopy involves capturing the spectrum of an object or region of space at regular intervals in order to observe how the spectrum changes over time. Time-series spectroscopy is used to study planets as they transit their stars.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500