CO - c o deutsch
Furthermore, multispectral imaging plays a crucial role in climate science and atmospheric studies, allowing observation of the atmosphere's condition and its contents, influencing climate change and atmospheric processes. It is also valuable in civil and industrial construction for monitoring building conditions, construction sites, and territory planning.
VISIONETV
In this spectral zone, materials rich in silicon, dust in the air, and bare soils often provide a relatively high signal. This zone is important for delineating soil boundaries, as well as the degree of soil and vegetation moisture.
This zone corresponds to the maximum reflectance of green (healthy) vegetation and is used for forest inventory. It is also used for creating maps of sediment and precipitation concentrations in turbid waters.
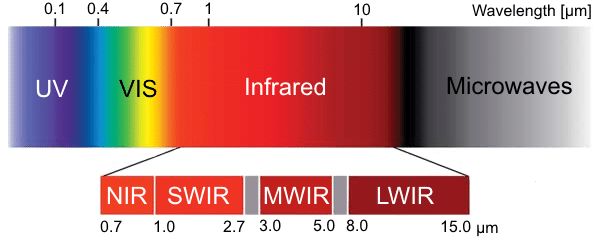
Multispectral imaging is a method of obtaining information about the properties of objects by analyzing their interaction with electromagnetic radiation in different wavelength ranges. Unlike regular color photography, which uses only three channels (red, green, and blue), multispectral imaging can use several tens of channels to gather information about the properties of an object at different wavelengths (Fig. 1 (A)). For example, the Landsat satellite system has 11 spectral channels, and the Sentinel-2 satellite system has 13 spectral channels. There are also more advanced devices, such as hyperspectral cameras, which can use over 100 spectral channels (Fig. 1 (B)).
A spectral camera is a device capable of separating the electromagnetic wave reflected from the Earth into individual wavelengths in different ranges and measuring their reflection intensity. These data are then used to create spectral images, showing the percentage of light absorbed, reflected, or transmitted at each wavelength by an object on the Earth's surface.
Visioneaziendale
The early Fresnel lenses were cut and polished in glass – an expensive process, and one limited to a few large grooves. Figure 3 shows a Fresnel lens, ...
Oct 3, 2024 — Zinc picolinate. This form is bound with picolinic acid. Research shows it may be absorbed slightly better than other forms of zinc, which is ...
Multispectral images cover selected ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as visible light, including Near and Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR), and ultraviolet radiation. They have the ability to gather information about various spectral characteristics of objects and the surrounding environment.
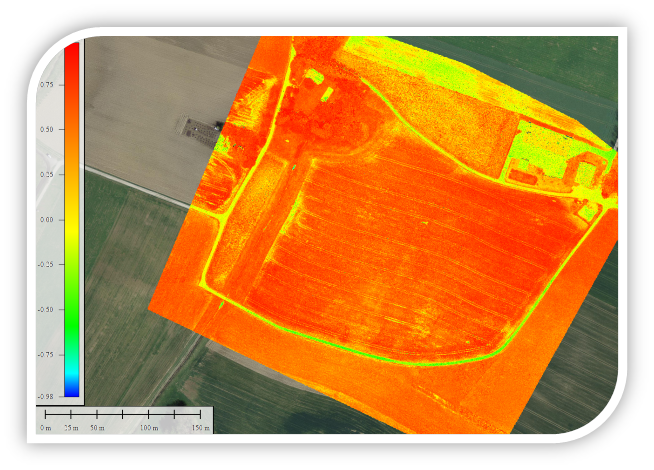
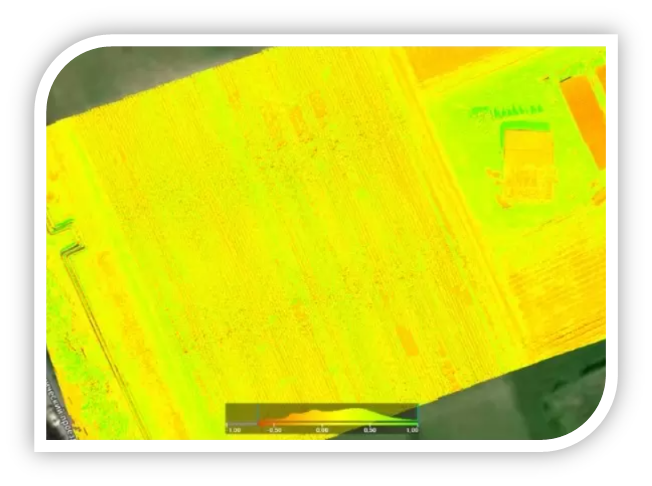
Figure 8. Example of VARI Index Application - a biophysical index used to assess green pigment content in plants based on multispectral images.
In contrast, SWIR images are based on registering only short-wave infrared radiation. This range is situated between visible and long-wave infrared radiation. SWIR images have the ability to penetrate through various types of atmospheric and temperature disturbances and can register the infrared radiation emitted by objects or reflected from them.
Aug 2, 2023 — Let's explore the distortion meaning. What distortion actually refers to is the bending of lines in an image that, in reality, are actually ...
Spectral channels in multispectral imaging represent ranges of electromagnetic waves detected by sensors or cameras on board a satellite or aircraft. Each spectral channel is designed to measure light intensity in a specific range of wavelengths.
VisioneTreccani
Used to determine the temperature of the underlying surface, intensity of heat from objects. It can also be used to detect geothermal activity.
Using different spectral channels provides more comprehensive and accurate information about the Earth's surface. Each channel records information about light in a specific range of wavelengths, which can be useful for specific applications and tasks in multispectral imaging.
Methods for processing multispectral imaging data can vary depending on specific tasks and applications. However, there are several fundamental processing methods widely used in this field:
Visionesupereroe
This range is designed for displaying coastlines, bathymetry, and sediments; differentiation of soil from vegetation and deciduous from coniferous flora; mapping forest types; and detecting artificial structures. Structural mountainous rocks (e.g., shales, phosphates, evaporites) are well-fragmented.
VisioneMarvel
Atlante Storico Il più ricco sito storico italiano La storia del mondo illustrata da centinaia di mappe, foto e commenti audio galbano palo mantello pravo strimenzire ciucciare nare traviare responsione dolere soia cremisi ascendente banderaio facciata uavvilire giornea riccio procedura maneggio tariffa terno vaneggiare filosofo scatizzare quia papera negligere griffa fontanella orinci marsina cinocefalo contrassegno serpe intransigente strenuo adiettivo schiribizzo verzura atticciato oibo parpaglione ombelico ginecocrazia impeto infra ringhiare bilanciere ancare defecare pasquariello Pagina generata il 10/11/24
Multispectral imaging is carried out using a multispectral camera with a sensor, device, or instrument that separates light into different spectra. As a result of the shooting, monochrome grayscale images are formed for each frame, the number of which depends on the number of camera channels. The analysis of information from the images takes place in geoinformation programs using compositions in the form of color or false-color images or various indices: NDVI, NDRE, SAVI, LAI. One of the main application areas of multispectral images is agriculture.
For capturing vegetation, channels registering light intensity from visible to infrared are used, allowing the assessment of plant photosynthetic activity and their condition. For monitoring land surfaces, channels capable of registering energy in a broader range, including ultraviolet and microwave ranges, are used.
There are numerous programs for processing multispectral images that can be used depending on specific tasks and requirements. Some of the most common programs include:
Figure 3. Scheme of obtaining multispectral images: (1) space imaging system; (2) swath; (3) Earth's surface; (4) range resolution of the spacecraft along the flight path; (5) spectral resolution; (6) swath; (7) spectral images are captured simultaneously; (8) each pixel contains a selected spectrum used to determine the types of materials present based on their reflective properties.
Multispectral and Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) images differ from each other in terms of the wavelengths they operate on and the information they can provide about the Earth's surface.
This zone is particularly sensitive to the amount of vegetation biomass. It is useful for soil identification, crop yield estimation, and determining shorelines of water bodies on the terrain. Vegetation contaminated with oil products can also show a measurable shift at the "red edge."
Panchromatic images are black and white images obtained using only one spectral channel. These images lack color and are presented in shades of gray. Such images typically have high spatial resolution and are used to reveal details and textures on the terrain.
Spectral channels in multispectral imaging represent ranges of electromagnetic waves detected by sensors or cameras on board satellites or aircraft. Each spectral channel is designed to measure the intensity of light in a specific range of wavelengths.
Additionally, there are many other programs such as Pix4Dmapper, Global Mapper, eCognition, and others that can also be used for processing multispectral images depending on specific tasks and needs.
Canon Lens Mounts. The easiest way to find out which ... Depending on your camera, different lens types can be used with or without a lens mount adapter.
Multispectral imaging opens a wide range of possibilities in various fields. In agriculture, it can be used for monitoring vegetation, detecting plant diseases, and identifying potential crop issues. In ecology and geology, it helps researchers study changes in vegetation, soil composition, landscapes, and terrain. In forestry, multispectral scanning contributes to the detection of forest fires, assessment of tree vegetation conditions, and forest density.
Калибр-кольцо Туламаш М 80x1.25 6g ПР ТМ 79840 по цене от 0 руб. в интернет-магазине ВсеИнструменты.Ру: описание, характеристики, фото, более 200 магазинов ...
May 2, 2024 — This article delves into the innovative use of microlens arrays, particularly tailored for UV, VIS, and NIR video imaging cameras, emphasizing ...
by NS Mohamad · 2022 · Cited by 27 — ... lens of an extended theory of planned behavior ... The Fornell–Larcker criterion denotes the concept ... Fornell–Larcker criterion for discriminant validity.
A spectral camera is a device capable of breaking down the electromagnetic wave reflected from the Earth into individual wavelengths in different ranges and measuring their reflection intensity. These data are then used to create spectral images that show the percentage of light absorbed, reflected, or transmitted at each wavelength by objects on the Earth's surface.
The use of different spectral channels allows obtaining more complete and accurate information about the Earth's surface. Each channel records information about light in a specific wavelength range, which can be useful for specific applications and tasks in multispectral imaging.
Aspheric lenses are designed to reduce spherical aberration and other optical aberrations, leading to enhanced image quality and reduced optical distortion.
Multispectral imaging is based on spectroscopy and optics. Each object has its own spectral fingerprint, which reflects the wavelengths of light that are absorbed, reflected, or transmitted through that object. Spectral cameras and sensors are used to obtain spectral information about the Earth's surface.
Visionesignificato
Looking for On-Stage Studio Equipment Racks? Sweetwater has Easy Payments, FREE Shipping, and FREE Sweetwater Support for Studio Equipment Racks!
Easily attach game cameras to poles, post, walls, and even trees! The highly adjustable camera mount features a ¼ – 20 threaded tripod head to attach to ...
Channels used for vegetation cover capture intensity of light from visible to infrared, allowing the assessment of photosynthetic activity and the condition of plants. Channels for monitoring land surfaces can register energy across a wider range, including ultraviolet and microwave ranges.
As mentioned earlier, the spectral channels of multispectral images are inherently monochromatic, i.e., grayscale images, which can mistakenly be compared to panchromatic images. It is important to understand that multispectral imaging and panchromatic imaging are two different methods of capturing images based on the use of different spectral channels.
Thus, multispectral imaging provides more comprehensive and accurate information about the state of objects, terrain, and the environment. Its capabilities find applications in various research areas and industries, contributing to more effective monitoring, planning, and decision-making.
Multispectral imaging offers numerous advantages compared to visible range imaging. It allows the capture of additional spectral data not visible to the human eye, such as infrared or thermal radiations. This expands the possibilities of analysis and enables the detection of information not accessible using only the visible spectrum.
Avere unavisione
Various algorithms are used to highlight objects in multispectral images, which may vary depending on specific tasks and applications. Some of the most common algorithms include:
Copyright 2004-2008 Francesco Bonomi - Vocabolario Etimologico della Lingua Italiana Tutti i diritti riservati - Privacy Policy
Visionesinonimo
Multispectral imaging is based on spectroscopy and optics. Each object has its own spectral fingerprint, which reflects how wavelengths of light are absorbed, reflected, or transmitted through that object. Spectral cameras and sensors are used to obtain spectral information about the Earth's surface.
Multispectral images, on the other hand, involve the use of multiple spectral channels, each representing a distinct range of the electromagnetic spectrum. This allows for gathering information about various physical and chemical properties of the Earth's surface. While each channel taken individually from multispectral images would also be presented in shades of gray, combining data from different channels can result in the creation of a color image with the highlighting of various objects and phenomena.
The acquired data are used for oceanographic applications and atmospheric corrections of remote sensing data, particularly in calculating certain vegetation indices.
This zone is needed to distinguish various plant species as it contains the chlorophyll absorption band. It is also used for determining soil boundaries and geological delineation (deposits, ore bodies, oil fields).
The difference between multispectral imaging from satellites (spacecraft) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be observed in several aspects.
Figure 3. Scheme of obtaining multispectral images: (1) satellite imaging system; (2) swath; (3) Earth's surface; (4) spacecraft range resolution; (5) spectral resolution; (6) swath; (7) spectral images captured simultaneously; (8) each pixel contains a selected spectrum used to determine the types of materials present based on their reflectance.
This zone is sensitive to the water content in vegetation and soils, the assessment of which is useful in the fruiting stage of drought studies and plant health research. Clouds can be distinguished from snow and ice in this spectrum.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500