Clear View Glasses Lens Cleaner Review 2022 - optical lens cleaner
GRIN lenstheory
Home Engineering Book Store Engineering Forum Applications and Design Beam Deflections and Stress Bearing Apps, Specs & Data Belt Design Data Calcs Civil Engineering Design & Manufacturability Electric Motor Alternators Engineering Calculators Excel App. Downloads Flat Plate Stress Calcs Fluids Flow Engineering Friction Engineering Gears Design Engineering General Design Engineering Hardware, Imperial, Inch Hardware, Metric, ISO Heat Transfer Hydraulics Pneumatics HVAC Systems Calcs Economics Engineering Electronics Instrumentation Engineering Mathematics Engineering Standards Finishing and Plating Friction Formulas Apps Lubrication Data Apps Machine Design Apps Manufacturing Processes Materials and Specifications Mechanical Tolerances Specs Plastics Synthetics Power Transmission Tech. Pressure Vessel Pumps Applications Re-Bar Shapes Apps Section Properties Apps Strength of Materials Spring Design Apps Structural Shapes Threads & Torque Calcs Thermodynamics Physics Vibration Engineering Videos Design Manufacture Volume of Solids Calculators Welding Stress Calculations Training Online Engineering
GRIN lensInscopix
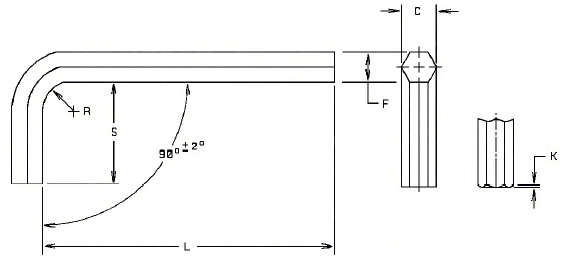
ANSI Hardware Design Guides ISO Metric Hardware Design Guides General Engineering and Design Resources Metric Allen Hexagon, Hex Key, Hexagon Keys Series Tools Metric Hexagon Keys per. ASME B18.3.2M Hardness: RC 45-53. Nominal Key Size F Hex Width Across Flats C Hex Width Across Corners S Length Of Short Arm L Length of Long Arm Short Series L Length of Long Arm Long Series R Radius of Bend Min. K Chamfer Max. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. 0.7 0.711 0.698 0.798 0.762 8 3 34 28 69 63 1.5 0.08 0.9 0.899 0.876 0.998 0.960 11 6 34 28 71 65 1.5 0.10 1.3 1.270 1.244 1.422 1.372 16 11 44 39 75 69 1.5 0.14 1.5 1.500 1.470 1.690 1.640 14 13 45 43 78 76 1.5 0.14 2 2.000 1.970 2.250 2.200 16 15 50 48 83 81 2.0 0.14 2.5 2.500 2.470 2.820 2.770 18 17 56 53 90 87 2.5 0.14 3 3.000 2.960 3.399 3.340 20 18 63 60 100 97 3.0 0.18 4 4.000 3.960 4.532 4.470 25 23 70 66 106 102 4.0 0.24 5 5.000 4.960 5.690 5.630 28 26 80 76 118 114 5.0 0.30 6 6.000 5.950 6.828 6.760 32 30 90 86 140 136 6.0 0.36 8 8.000 7.950 9.136 9.030 36 34 100 95 160 155 8.0 0.49 10 10.000 9.950 11.470 11.340 40 38 112 106 170 164 10.0 0.62 12 12.000 11.950 13.764 13.590 45 43 125 119 212 206 12.0 0.76 14 14.000 13.930 16.058 15.880 56 53 140 133 236 229 14.0 0.85 17 17.000 16.930 19.499 19.300 63 60 160 152 250 242 17.0 1.04 19 19.000 18.930 21.793 21.580 70 67 180 171 280 271 19.0 1.16 22 22.000 21.930 25.234 25.000 80 76 200 190 335 325 22.0 1.36 24 24.000 23.930 27.525 27.240 90 86 224 213 375 364 24.0 1.49 27 27.000 26.870 30.969 30.710 100 95 250 238 --- --- 27.0 1.68 32 32.000 31.840 36.704 36.430 125 119 315 300 --- --- 32.0 1.99 36 36.000 35.840 41.292 40.900 140 133 355 338 --- --- 36.0 2.25
GRIN lenspitch
Light doesnt always go straight! Lenses and mirrors bend light rays because glass has a higher refractive index (optical density) than air, so the rays bend due to the shape of the glass. But instead of having a constant refractive index and varying shape, you can equivalently have a constant shape and a varying refractive index.
© Copyright 2000 - 2024, by Engineers Edge, LLC www.engineersedge.com All rights reservedDisclaimer | Feedback Advertising | Contact
Adding sugar to water is an easy way to increase its density, and therefore its refractive index. Light bends towards areas of higher density, so if you can create a liquid that has a high density at the bottom and gradually gets lower as you go up, any rays entering it will bend downward!
Here, I poured a bag of sugar into the bottom of a fish tank, added a little water to make a super-concentrated solution, then freezed the whole thing, before pouring water on top. As the bottom melts, the sugar diffuses upward, creating a nice gradient refractive index. The index should drop off rapidly, meaning that near the top of the tank, the beam doesnt bend much:




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500