Camera Field of View Calculator - how do you calculate the field of view
The ciliary body is critical for the lens to function correctly. While the ciliary muscles allow the lens to change shape to focus, the lens itself is kept in place by little fibers that are connected to the ciliary body — these are called zonular fibers, or zonules. The ciliary body also produces aqueous humor, which keeps the lens healthy and functioning.
The lens is made up almost entirely of proteins. In fact, proteins make up nearly 60% of the eye’s lens — a higher protein concentration than any other bodily tissue. The tissue is transparent, which allows light to easily enter the eye. It’s also flexible, so it can change shape and bend the light to focus properly on the retina.
Presbyopia is a natural, age-related vision change that affects a person’s ability to focus on close-up objects. The condition affects almost everyone, even if they’ve never had vision problems before.
For quantities such as the mass of a contaminant, heat or the amount of movement, the existence of a stirring material at microscopic scales is necessary for their diffusion. On the contrary, light can propagate in a vacuum. It is then not subject to any distribution. On the other hand, in a transparent medium, such as air or ice, whose composition is not uniform, diffusion may occur. In English, the distinction between this phenomenon and molecular diffusion is clear since this phenomenon is called scattering. The diffusion of light depends on the size of the diffusing objects, read The colours of the sky.
What do diffraction and refraction have in common inphysics
Having an eye doctor conduct a comprehensive eye exam gives them the opportunity to look inside the eye and make sure everything in it — including the lens — is healthy.
Sound waves are produced when something is caused to
Water droplets suspended in clouds and fogs can reach 100 microns, much larger than the wavelength of light. Diffusion is then reduced to multiple reflections on the droplet surface. It is therefore no longer selective, which explains the white colour of the clouds, with shades of grey depending on the amount of sunlight absorbed.
MOREAU René, Professor Emeritus in Grenoble-INP, SIMaP Laboratory (Science and Engineering of Materials and Processes), member of the Academy of Sciences and the Academy of Technologies. SOMMERIA Jöel, Joël Sommeria Author Encyclopedia Environment Research Director at the CNRS, Laboratory of Geophysical and Industrial Flows (LEGI).
For white light, the different components diffract at different angles, leading to the coloured patterns shown in Figure 3 (obtained in the case of a circular orifice). As the short wavelengths are more widely diffracted, it is conceivable that Mie’s diffusion is dominated by the blue color, in a way that depends on the size of the particles.
when sound is created, it travels to the ear through a compression. medium. rarefaction. surface.
The lens is a vital part of the eye and makes clear vision possible. Because it’s an internal structure, it can be difficult to know if something is amiss with the lens.
In its natural state, the lens looks like an elongated sphere — a shape known as ellipsoid — that resembles a deflated ball. The average lens size in adults is approximately 10 mm across and 4 mm from front to back.
Signs of presbyopia typically begin around the age of 40 and gradually progress until age 65 or 70, when presbyopia plateaus. Presbyopia is not harmful and can be corrected with glasses, contacts or vision surgery.
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum has
Cataracts occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy or hazy, resulting in blurred vision. Advanced age is the leading cause of cataract development, though it’s possible for children to be born with congenital cataracts.
Figure 1. Bluish colours in an ice cave due to Rayleigh scattering. [Source: pixabay]At the scales of air molecules, or water molecules constituting ice, objects much smaller (nanometers) than the wavelengths of light (between 0.4 and 0.8 μm), scattering is predominant for short wavelengths, thus selecting the color blue. It’s Rayleigh’s broadcast.
When light enters the eye, the lens will bend and focus incoming light directly on the retina, which is how the clearest possible image is produced.
As the eye ages, the proteins that make up the lens begin to clump together. This may occur in one or both eyes and likely will not affect vision in the beginning. Over time, eyesight can appear blurry, dull, hazy or dim, which can greatly affect one’s ability to see in low-light conditions (at night). If untreated, cataracts can lead to vision loss.
The crystalline lens projects a focused image on the retina. However, the initial image projected is inverted (either upside down or reversed). When the image is sent to the brain via the optic nerve, the brain will flip the image back to normal. [Read our article on how the visual process works.]
What do diffraction and refraction have in commonquizlet

Cover image. Blue sky due to Rayleigh’s diffusion with a white cloud that shows a non-selective diffusion by the droplets it contains. [Source: Pixabay, royalty-free]
how is an image formed by a plane mirror?
The lens relies on the aqueous humor for energy and cleansing rather than nerves or blood flow. Aqueous humor is the clear fluid located between the cornea and the lens that flows through the eye and then drains from the eye through the trabecular meshwork.
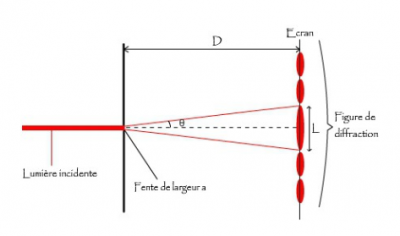
Figure 2. The diffraction of a red light through a thin slit leads to a pattern of red spots separated by dark areas. The central spot has the largest width L= 2Dθ, where the small angle θ is λ/a. [Source: Superprof, Article “All about diffraction”, available on : “https://www.superprof.fr/ressources/physique-chimie/terminale-s/optique/diffraction.html]These three types of diffusion correspond to different modes of interaction of light with the diffusing object. For objects that are large in relation to wavelength, it is possible to reason in terms of light rays, which corresponds to geometric optics. At the interface between two media, part of the light is reflected, and the other part passes through the interface with a modified propagation direction: this is called refraction. This process is observed in a prism like the one in the vignette of the focus Deviation of light by a prism (link). The different wavelengths of white light have different refractive angles, which leads to colour separation. Water drops or ice crystals can act as prisms, which leads to rainbows (Spectacular Rainbows) or other atmospheric halos phenomena (Atmospheric Halos). In clouds, reflections and refractions are multiple, which blurs the separation of colors, and restores the white color of sunlight.
Figure 3. Diffraction of polychromatic light through a circular orifice. The central spot is white due to the superposition of all wavelengths. Peripheral spots represent the entire spectrum of visible colours, with the shift in various wavelengths increasing as we move away from the centre. [Source: Superprof, Article “All about diffraction”, available on : “https://www.superprof.fr/ressources/physique-chimie/terminale-s/optique/diffraction.html]]For objects with dimensions close to the wavelength, the wave nature of light intervenes, which leads to the phenomenon of diffraction. Diffraction patterns are typically studied behind an orifice cut in a screen. The effect is similar to diffraction by a small object, but it is then easier to observe, thanks to the absorption of non-diffracted light. Figure 2 thus represents the diffraction pattern of monochromatic light of wavelength λ passing through a slit of width a. The diffracted light constitutes a main beam opening at an angle λ/a, surrounded by smaller side lobes. Thus within the limit of a wide slit (λ/a small), the beam remains parallel, in accordance with the geometric optics, while for λ~a, the diffracted beam opens very wide.
What do diffraction and refraction have in commonbrainly
The primary function of the lens is to bend and focus light to create a sharp image. To do that, the lens uses the help of ciliary muscles to stretch and thin out when focusing on distant objects, or to shrink and thicken when focusing on near objects.
On the other hand, at intermediate scales, close to the wavelengths of light, such as pollens, aerosols and fumes, Mie scattering imposes a slightly bluish greyish grey colour. Thus, this colour is typical of the blue line of the Vosges above coniferous forests emitting pollen and isoprene microbeads (originally a compound of natural rubber).
Green plants need lightinorder to survive
Accommodation relies on elasticity of the crystalline lens, which makes it easier to change focal distances. As we age, the crystalline lens loses its elasticity, which results in a condition called presbyopia.
For example, if you’re approaching a traffic light while driving, the lenses in your eyes will be focused distantly, because the light is relatively far away. As you get closer to the light, your lenses will make tiny changes in shape to accommodate the approaching object that used to be distant.
RELATED READING: Refractive lens exchange (replacing the natural lenses to correct a refractive error rather than to treat cataracts)
The lens of the eye, also called the crystalline lens, is an important part of the eye’s anatomy that allows the eye to focus on objects at varying distances. It is located behind the iris and in front of the vitreous body.
If you notice any sudden changes in your vision, or if it’s been longer than two years since your last eye exam, it’s time to schedule one. It’s a small but important step in keeping your vision clear and your eyes healthy.

The cause of presbyopia is related to alterations within the lenses’ composition. Aging triggers a change in the protein of the lenses, which causes them to thicken and become inflexible. The ciliary muscle fibers that keep the lens in place and help it change shape are also affected.
Cataract surgery can be performed to remove the clouded lens and replace it with an artificial one, known as an intraocular lens (IOL). There are many types of IOLs available for the surgery, including monofocal, multifocal and toric.
Accommodation refers to the lenses' ability to bounce between focusing on near objects and far objects with little interference.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500