Calibrated Photodiodes - silicon photodiode
Given that the first two satellites were launched together from the same launch vehicle, the initial phase angles are very small. Over time, the two satellites in the given plane will separate further within their respective orbital planes and eventually be separated by 180°.
• August 23, 2023: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) has revealed early insights from its GHOSt™ constellation, comprising GHOSt 1, 2, and 3, launched via the Transporter 7 and 8 missions. These satellites, featuring advanced hyperspectral sensors with an 8-meter ground sampling distance, provide the highest resolution hyperspectral monitoring available. This capability allows OSK to monitor Earth, focusing initially on oil and gas pipeline infrastructure, and detect methane plumes with high precision. OSK has developed sophisticated tools to analyze hyperspectral imagery, enabling the identification of specific risks to energy infrastructure, such as pipeline threats from suspicious vehicles or construction activities. In 2023, OSK's hyperspectral sensors scanned 12,000 miles of pipeline, identifying 100 methane leaks, 200 hydrocarbon leaks, and over 300 construction-related threats, while building a proprietary spectral library to enhance their chemical analysis capabilities. 10)
The high gain Ka-band antennas employed by the GHOSt satellites will use six band channels, allowing for six wideband emissions to share three frequency channels using polarisation diversity, thereby enabling the GHOSt satellites to utilise the spectrum at its highest efficiency.
What is diffraction gratingclass 12
4) ”Orbital Sidekick Awarded $16M U.S. Air Force STRATFI Contract,” Orbital Sidekick, 15 October 2020, URL: https://orbitalsidekick.com/news-blog/
GHOSt satellites are anticipated to operate at an average altitude of 525 km in a circular sun-synchronous orbit with an inclination of 97.5°.
Orbital Sidekick (OSK) Inc., a startup company of San Francisco, announced on 4 February 2021 that it has finalised plans to deploy its Global Hyperspectral Observation Satellite constellation known as GHOSt. The hyperspectral imaging (HSI) constellation consists of six 100 kg ESPA [EELV (Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle) Secondary Payload Adapter] class microsatellites, designed and manufactured by Astro Digital, with Maverick Space Systems providing mission integration & management services for the launches on SpaceX’s Falcon 9. The custom hyperspectral imaging payload is provided by OSK. 1)
When there is a need to separate light of different wavelengths with high resolution, then a diffraction grating is most often the tool of choice. This "super prism" aspect of the diffraction grating leads to application for measuring atomic spectra in both laboratory instruments and telescopes. A large number of parallel, closely spaced slits constitutes a diffraction grating. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for the double slit or multiple slits, but with a large number of slits the intensity maximum is very sharp and narrow, providing the high resolution for spectroscopic applications. The peak intensities are also much higher for the grating than for the double slit.
2) ”Orbital Sidekick to Monitor Pipeline Assets for Energy Transfer Using Satellite Technology,” OSK, 23 June 2022, URL: https://www.orbitalsidekick.com/news-blog/orbital-sidekick-to-monitor-pipeline-assets-for-energy-transfer-using-satellite-technology
3) Debra Werner, ”Orbital Sidekick notes growing demand for hyperspectral data,” SpaceNews, 24 February 2022, URL: https://spacenews.com/orbital-sidekick-aurora-in-q-tel/
We are looking at shooting a feature length project in the future on 8mm (likely 120 rolls over 4 weeks). I have shot a lot of 8mm, and ...
OSK plans to use a space-to-space L-band intersatellite link between its GHOSt satellites and the existing commercial Globalstar NGSO constellation. The GHOSt satellites will transmit to Globalstar satellites, pursuant to an agreement with Globalstar, but will not have the capability to receive communications from the Globalstar satellites.
GHOSt will capture more than 400 spectral bands in the visible to shortwave infrared range of 400 - 2500 nm to feed OSK's Spectral Intelligence Global Monitoring Application (SIGMA™) platform.
The Ophir Orion is a microprocessor-based Laser. Power/Energy Meter for measuring laser power or energy with Ophir measuring heads. It uses smart connector.
GHOSt-3 was launched on 12 June 2023 at 2:35 PDT (21:35 UTC) on SpaceX’s Transporter 8 rideshare mission, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California. The Falcon 9 rocket carried 72 payloads of varying sizes. 7)
"Persistent, hyperspectral imaging is a critical new capability in remote sensing," said Chris Biddy, Co-founder and CEO of Astro Digital. "We are very pleased to be supporting Orbital Sidekick's mission with our proven satellite technology and capabilities."
6) GeoSpatial World, "Orbital Sidekick Successfully Launches First Satellites in GHOSt Constellation", April 18, 2023, URL: https://www.geospatialworld.net/news/orbital-sidekick-successfully-launches-first-satellites-in-ghost-constellation-2/
GHOSt-1 has 498.6 km perigee, 514.7 km apogee, 97.4 ° inclination, a period of 94.6 minutes and a semi-major axis of 6877 km
Diffraction gratingpattern
The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double slit. However, angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating.
15) SpaceNews, “Orbital Sidekick shares first-light imagery”, April 3, 2024, URL: https://spacenews.com/orbital-sidekick-shares-first-light-imagery/
9) Geospatial World, “Orbital Sidekick Successfully Launches Third GHOSt Satellite”, June 14, 2023, URL: https://www.geospatialworld.net/news/orbital-sidekick-third-ghost-satellite/
• March 4, 2024: GHOSt-4 and 5 were launched at 6:54 PM EST, on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. 13) 14)
Analytically, the focal length is described by the lens maker's equation: 1/f = (n - 1)(1/R1 + 1/R2), where R1 and R2 are the radii of curvature, f is the focal ...
GHOSt-2 has 497.1 km perigee, 514.5 km apogee, 97.4 ° inclination, a period of 94.6 minutes and a semi-major axis of 6876 km
The tracks of a compact disc act as a diffraction grating, producing a separation of the colors of white light. The nominal track separation on a CD is 1.6 micrometers, corresponding to about 625 tracks per millimeter. This is in the range of ordinary laboratory diffraction gratings. For red light of wavelength 600 nm, this would give a first order diffraction maximum at about 22° .
Toric contact lenses for astigmatism ... Many glasses-wearers have astigmatism – when the lens of the eye is slightly oval-shaped. It causes blurry vision, but ...
Maverick Space Systems will provide mission integration hardware and services to launch GHOSt on SpaceX's Falcon 9 at the end of this year and continuing into 2022. "Taking advantage of frequent low-cost launch opportunities is critical to achieve Orbital Sidekick's constellation. We are excited to partner with them and further reduce their per-satellite launch costs by aggregating two GHOSt satellites per ESPA port," said Roland Coelho, CEO of Maverick Space.
Olympus unique UV-corrected apochromatic objective allows superior confocal imaging of UV excited fluorochromes. The objective is corrected from 350-650nm to ...
Diffraction gratingexperiment
• October 15, 2020: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) has secured a $16 million multi-year contract from the Department of the Air Force's AFVentures, alongside the Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) and the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), under the Strategic Financing (STRATFI) program. This funding, matched by private investment, will expedite the launch of six advanced hyperspectral imaging satellites with edge processing capabilities and integrate OSK’s SIGMA™ platform with the USAF's Advanced Battle Management System (ABMS). The SIGMA™ platform offers persistent global monitoring services, utilizing OSK’s high-fidelity hyperspectral data across more than 400 spectral bands. The first satellites are set to launch in December 2021, aiming for a daily revisit rate. This advancement supports both defense and commercial sectors, enhancing analytical insights for remote sensing challenges. 4)
The spacecraft bus is based on Astro Digital’s flight-proven Corvus-XL smallsat platform and utilises Astro Digital’s heritage flight computer, attitude determination and control system, power, and communications subsystems. The payload for each satellite consists of a proprietary hyperspectral imager manufactured by OSK. Each satellite has external dimensions of 57.8 cm x 57.8 cm x 111.4 cm and a total mass of 91.4 kg. Each satellite is equipped with state-of-the-art hardware and software solutions to ensure safe and efficient mission operations. Each GHOSt satellite will be capable of making orbital adjustments and performing collision avoidance manoeuvres by utilising differential drag, but will not carry propulsive systems.
GHOSt is a planned hyperspectral constellation by Orbital Sidekick Inc. (OSK), with the spacecraft to be built by Astro Digital.
Each GHOSt satellite features a proprietary hyperspectral imager manufactured by OSK. The sensor is developed to capture 512 spectral bands across the visible (VIS) to shortwave infrared (SWIR) region. The enhanced monitoring provided by these imagers will enable GHOSt to produce the highest resolution commercial hyperspectral imagery launched to-date. Some key applications include capturing critical environmental and situational awareness information for defence, detecting minute real-time changes in physical infrastructure, monitoring energy infrastructure and regulatory compliance, detecting environmental erosion and degradation, and monitoring crop yield and agriculture.
1) ”Orbital Sidekick Announces Upcoming Launch of its Newest Global Hyperspectral Earth Observation Constellation: GHOSt,” PR Newswire, 4 February 2021, URL: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/orbital-sidekick-announces-upcoming-launch-of-its-newest-global-hyperspectral-earth-observation-constellation-ghost-301222258.html
What is diffraction gratingin physics
Developed by Astro Digital, each of the GHOSt satellites have a mass of 91.4 kg and a planned total in-orbit lifetime of just over 5 years. The spacecraft are based on the flight-proven Corvus-XL smallsat platform and utilise Astro Digital’s heritage flight computer, attitude determination and control subsystem (AOCS), power and communications subsystems. Payload data downlink is to be conducted via Ka-band, in addition to S-band for high speed data (HSD) transmissions.
GHOSt will enable enhanced hyperspectral monitoring capabilities for commercial, scientific, and government applications. Upon deployment, the GHOSt constellation satellites will produce the highest resolution commercial hyperspectral imagery launched to-date. The market-leading sensing capabilities provided by OSK enable customers in the energy, extraction, infrastructure, agriculture, and forestry industries to make vital decisions with better information, thereby improving safety and potentially saving lives.
13) De la Cruz, Lia, “List of SpaceX Starlink launches for March 2024”, EarthSky. March 1, 2024, URL: https://earthsky.org/spaceflight/spacex-starlink-launches-march-2024/
GHOSt-4 and 5 were launched on 4 March 2024 at 6:54 PM EST, on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket, from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. 13)
In addition OSK is looking to utilise the 2025-2110 MHz S-band for Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C), as well as modulation and coding of the high speed data (HSD) link for payload transmissions. Specifically, OSK plans to use the 2045.0-2050.0 MHz band for the HSD control uplink. This technique adjusts the satellite’s modulation and coding to optimise payload downlink conditions, ensure proper link performance and efficiency, and advise the spacecraft to retransmit any lost data frames. A second link, operating within the 2054.85-2055.15 MHz band, will provide the traditional TT&C uplink operations for the GHOSt satellites.
Differentiate between diffraction and refraction of waves. Diffraction involves the bending and spreading of waves around obstacles, while refraction is the ...
GHOSt aims to provide enhanced hyperspectral imagery for use in industrial, government, agriculture, environmental and defence sectors. Specific key applications of its use include capturing critical environmental and situational awareness information for defence, detecting minute real-time changes in physical infrastructure, monitoring energy infrastructure and regulatory compliance, detecting environmental erosion and degradation, and monitoring crop yield and agriculture.
Diffraction gratingformula
GHOSt-1 and GHOSt-2, the first two satellites of Orbital Sidekick’s planned GHOSt constellation, were successfully launched on 15 April 2023 at 06:48 am UTC onboard the Transporter 7 rideshare mission on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
OSK seeks to utilise the 25.5-27.0 GHz Ka-Band for payload downlink operations under the co-primary EESS (space-to-Earth) allocation. All data transmitted in the requested band will be limited to payload sensor data or metadata directly pertaining to the operation of the payload.
10) Orbital Sidekick (OSK), “OSK Debuts Initial Hyperspectral Insights from GHOSt Constellation”, Aug 23, 2023, URL: https://www.orbitalsidekick.com/news-blog/osk-debuts-initial-hyperspectral-insights-from-ghost?utm_source=substack&utm_medium=email
Jun 29, 2024 — Steps to use Displacement Calculator · Input the velocity, time, and the unknown value "x" into their respective fields. · Click on the " ...
• April 15, 2023: Orbital Sidekick have announced the successful launch of GHOSt 1 and 2, the first satellites in its planned GHOSt™ (Global Hyperspectral Observation Satellite) constellation, aboard the Transporter 7 rideshare mission on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. 6)
What is gratingelement
The following are just some of the key industry sectors that will benefit from capabilities unlocked by the GHOSt constellation:
With the first satellites launched on 15 April 2023, Global Hyperspectral Observation Satellite (GHOSt) is a constellation of six technically identical hyperspectral imaging microsatellites by Orbital Sidekick Inc. (OSK). GHOSt aims to build on its predecessor Aurora to provide enhanced commercial data sets used in industrial, government, agriculture, environmental and defence sectors.
What is gratingconstant
The Mission Operations Center for GHOSt will be located at OSK’s headquarters in San Francisco, California and at Astro Digital’s facility in Santa Clara, California. Consistent with OSK’s National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) licence, the GHOSt constellation will be monitored at all times via automated and human systems, facilitating rapid response to any technical or regulatory concerns. OSK will conduct its mission operations through a network of ground stations that will initially consist of facilities in (i) Santa Clara, California; (ii) Tromso, Norway, (iii) Svalbard, Norway, and (iv) Troll, Antarctica. OSK may expand its ground station network over the course of the operational lifetime of the GHOSt constellation to include additional commercial stations either within or outside the United States and will seek to modify its authorization as conditions arise. OSK has initiated coordination efforts with Federal operators in its requested bands and will operate in accordance with the terms of any agreements.
The GHOSt system plans to operate in the radiofrequency bands outlined in Table 1 below. Satellite downlink transmissions can be turned on and off by ground telecommand. Although the GHOSt satellites are capable of transmitting throughout the entire orbit, they only transmit when visible to one of their Earth stations.
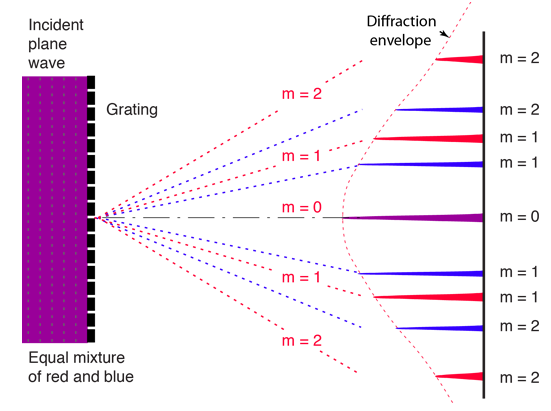
This illustration is qualitative and intended mainly to show the clear separation of the wavelengths of light. There are multiple orders of the peaks associated with the interference of light through the multiple slits. The intensities of these peaks are affected by the diffraction envelope which is determined by the width of the single slits making up the grating. The overall grating intensity is given by the product of the intensity expressions for interference and diffraction. The relative widths of the interference and diffraction patterns depends upon the slit separation and the width of the individual slits, so the pattern will vary based upon those values. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double slit. However, angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating. The diffraction grating is an immensely useful tool for the separation of the spectral lines associated with atomic transitions. It acts as a "super prism", separating the different colors of light much more than the dispersion effect in a prism. The illustration shows the hydrogen spectrum. The hydrogen gas in a thin glass tube is excited by an electrical discharge and the spectrum can be viewed through the grating. The tracks of a compact disc act as a diffraction grating, producing a separation of the colors of white light. The nominal track separation on a CD is 1.6 micrometers, corresponding to about 625 tracks per millimeter. This is in the range of ordinary laboratory diffraction gratings. For red light of wavelength 600 nm, this would give a first order diffraction maximum at about 22° . DiscussionCalculation
• April 3, 2024: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) released first-light imagery from the two hyperspectral satellites launched on March 4, 2024 (Figures 1 and 2). Both satellites, part of OSK's constellation which now includes five satellites, are in good health and undergoing commissioning. These satellites collect data across 468 spectral bands from 400 to 2,500 nanometers with 8-meter resolution. A sixth satellite is expected to launch within the year, and OSK aims to expand to a constellation of 14 to 20 satellites for weekly global monitoring. The hyperspectral data allows for detailed chemical analysis, particularly useful in detecting methane and hydrocarbon leaks, and monitoring potential threats to pipelines. This enables proactive measures to prevent leaks and ensure pipeline safety. 15)
OSK provides innovative remote sensing solutions for a diverse set of industrial and governmental customers, including end users across the energy, surveying and extraction, agriculture, environmental monitoring, and defence sectors. Examples of the kinds of data sets OSK provides its customers include protein content and evapotranspiration levels for crops, corrosion identification and leak detection for monitoring pipelines, accurate mineral surveying, environmental monitoring for various applications, and real-time road/rail infrastructure conditions. The GHOSt constellation represents the next evolution of OSK’s sensing capabilities and will allow OSK to scale its commercial product with larger coverage, reduced revisit times, better spatial resolution, and more spectral capability.
What is gratingin Physics
Jun 12, 2017 — An eye stroke, also known as retinal artery occlusion, is caused by a clot, or narrowing of the retina's blood vessels. The retina's blood flow ...
With a revisit rate of up to daily for certain locations the hyperspectral sensors onboard the constellation will provide a spatial resolution of 8.3 m for multispectral band and 3 m for panchromatic bands.
All you need to do is sort by 'orders' and you'll find the bestselling hologear holographic glowing reflective basketball on AliExpress! It's so easy and takes ...
7) Lentz Danny, "SpaceX Transporter-8 launches 72 payloads marking 200th booster landing", NSF (Nasa Space Flight), June 12, 2023, URL: https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2023/06/spacex-transporter-8/
"We're excited to partner with Astro Digital and Maverick Space for this initial constellation. Both companies bring a high degree of agility with proven execution to our mission, allowing OSK to focus on the payload and extracting information from our unique hyperspectral data," said Pete Friedhoff, Director of Space Systems for Orbital Sidekick.
GHOSt leverages OSK's previous experience collecting and analysing hyperspectral data with its ISS-HEIST (Hyperspectral Earth Imaging System Trial) mission on the International Space Station in 2019. The custom payload will produce the highest resolution commercial hyperspectral imagery launched to-date with a GSD (Ground Sample Distance) of approximately 8 metres. The payload will be integrated into Astro Digital's Corvus-XL satellite platform and will take advantage of its industry leading Ka-band data downlink capability.
The GHOSt mission will involve deploying a remote sensing constellation of small satellites with both radiofrequency and optical payloads. The satellite constellation will consist of six technically identical satellites launched into a sun-synchronous orbital inclination in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Each satellite is planned to have a total in-orbit lifetime of 5.2 years.
5) “Orbital Sidekick secures UGSG Technical Assistance Agreement”, News Desk, 3 October 2022, URL: https://www.geospatialworld.net/news/orbital-sidekick-secures-usgs-technical-assistance-agreement/
• June 12, 2023: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) announced the successful launch of GHOSt 3, the third satellite in its planned GHOSt (Global Hyperspectral Observation Satellite) constellation aboard the Transporter 8 rideshare mission. 9)
• October 3, 2022: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) has signed a technical assistance agreement with the U.S. Geological Survey’s (USGS) Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center as part of the Joint Agency Commercial Imaging Evaluation (JACIE) partnership. This agreement enables remote sensing experts from various government agencies, including USGS, NASA, NGA, NOAA, USDA, and NRO, to assess the quality and scientific utility of OSK's satellite imagery. Ensuring reliable product quality is crucial for supporting diverse remote sensing applications across government, NGOs, industry, and academia. Collaborating with USGS also allows OSK to expand its market reach in the ESG sector, enhancing objective and consistent environmental monitoring services. 5)
• June 23, 2022: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) has been selected by Energy Transfer, a North American energy infrastructure company, to monitor its assets in the Permian Basin using OSK’s advanced hyperspectral satellite technology. This partnership enhances Energy Transfer's pipeline integrity programs, surpassing regulatory requirements to ensure the safety and efficiency of its extensive pipeline network. OSK's technology allows for early detection and prevention of leaks, improving community safety, environmental performance, and operational efficiency. With the deployment of OSK’s GHOSt constellation starting in late 2022, OSK will provide frequent monitoring services to the global oil and gas industry via its SIGMA Platform, aiding in compliance, regulatory obligations, and promoting sustainable operations. 2)
When light of a single wavelength , like the 632.8nm red light from a helium-neon laser at left, strikes a diffraction grating it is diffracted to each side in multiple orders. Orders 1 and 2 are shown to each side of the direct beam. Different wavelengths are diffracted at different angles, according to the grating relationship.
GHOSt will capture more than 400 spectral bands in the visible to shortwave infrared range of 400 – 2500 nm to feed OSK’s Spectral Intelligence Global Monitoring Application (SIGMA TM) platform.
T-R1DS1P - Positive 1951 USAF Test Target, Ø1" Ø1" (Ø25.4 mm) Targets for Alignment in Ø1" Lens Tubes Determine Resolution of an Optical System Conforms to ...
The GHOSt constellation will use the 400.15-401.0 MHz band for TT&C downlink telemetry operations consistent with the secondary allocation for the Space Operation service
• February 24, 2022: Orbital Sidekick (OSK) is facing capacity constraints as it acquires data from Aurora, its first satellite launched in June 2021. Aurora, a precursor to the upcoming GHOSt constellation, launched via SpaceX’s Transporter-2 mission, has outperformed NASA’s Hyperion sensor. The GHOSt constellation, set to launch later this year, will offer significantly improved resolution of 8 meters per pixel. OSK is ramping up production and hiring to meet high demand for its dual-use satellite technology, with substantial backing from In-Q-Tel and AFVentures. This support aligns with the intelligence community's hybrid approach to Earth observation, utilizing both government and commercial satellite data. 3)




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500