C-CS-Mount-2-S-Mount (M12x0.5) Adapter for Board Lens ... - adapter c cs mount
Alright, let’s keep going. If we know that FPS rate is 18, and a foot of film has around 92 frames in it, that means a foot of film contains around 5.1 seconds of footage. So what happens when we break out those film lengths from the earlier table and convert it to viewing time? Let’s see!
Field of viewcalculator
Where D is the full display image dimensions (either horizontal or vertical), and d is the target dimensions (either horizontal or vertical).
There are many subcategories of UV light, each which need different sensor requirements. These include both physical and chemical sensor changes.

Field of view vs focal lengthcamera
It turns out there’s no universal length for 8mm film, because it comes in different reel sizes. That also means different film lengths. Let’s take a look at those different reel sizes in this handy dandy chart.
Acton optics and coatings provide ultra-precision optical components and coatings with an emphasis on the UV/VUV spectral regions.
Field of viewhuman eye
FOV tofocal lengthcalculator
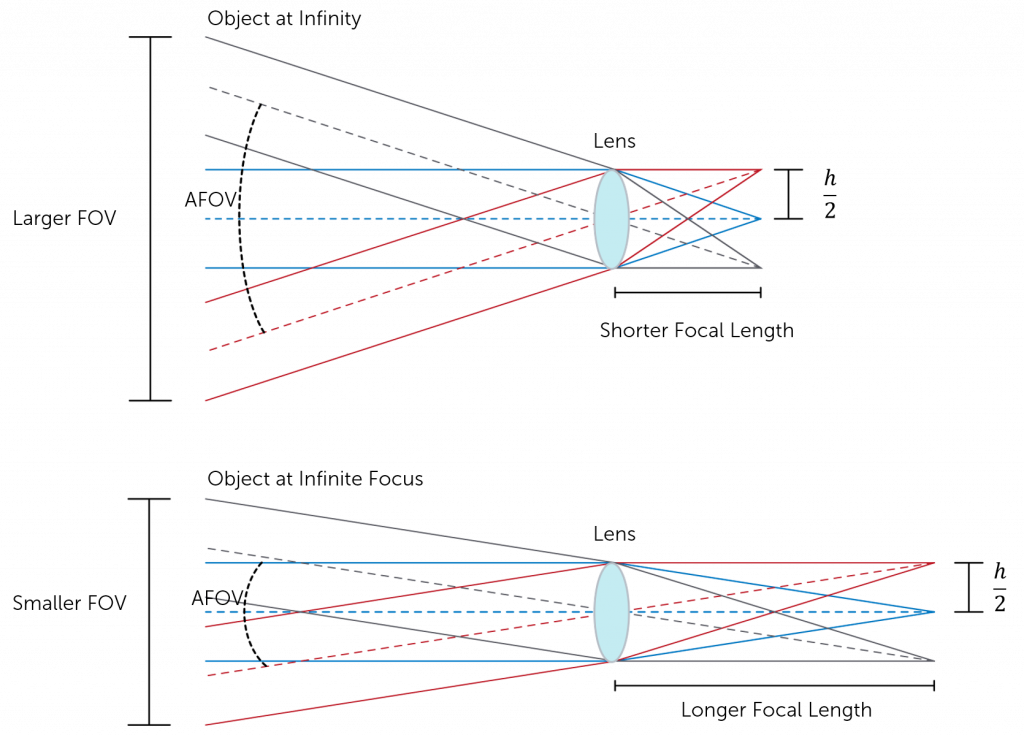
Field of view (FOV) is the maximum area of a sample that a camera can image. It is related to two things, the focal length of the lens and the sensor size. Figure 1 shows a comparison between the field of view and the size of the sensor. Assuming that the focal length of the lens is the same, the larger the sensor the larger the field of view.
This means that the distance of the focal length is determined by how strongly the light is converged by the lens in order to focus the subject being imaged. This, in turn, influences the angle from the horizonal of light that can be captured by the lens. This is known as the angular field of view (AFOV) and is required to determine the overall FOV. The AFOV is the angle between any light captured at the horizonal, and any light captured at the edge (as shown in Figure 2). If you have a fixed sensor size, altering the focal length will alter the AFOV and therefore the overall FOV. A shorter focal length provides a larger AFOV view, and therefore a larger FOV. The same is true but vice versa for longer focal lengths, as indicated in Figure 2.
The focal length of a lens converges light so that the image of an object is focused onto the sensor. This determines the angular field of view, a parameter of the overall field of view. This is defined as the angle between any light captured at the horizontal and any light captured at the edge of the of the object. All of these parameters play a role in determining the FOV of a camera and can be measured using either trigonometry and the angular field of view, or via an optical test, in which a black body is utilized to create a virtual image
Sensor size is determined by both the size of the pixels and number of pixels on the sensor. This can be optimized for each application, with larger sensors optimal for sensitivity limited applications, and smaller sensors optimal for resolution limited applications.
Field of view defines the maximum area of a sample that a camera can image, determined by the focal length of the lens and the sensor size.
Field of view vs focal lengthreddit
Most of our blog posts are centered on pretty easy to answer questions. We usually tell you things like “How wide is 8mm film?” The answer is easy: 8mm! Blog post over. Wrap it up. We’re done.
Field of viewcamera
Figure 3 shows a simplified version of how these assumptions allow for AFOV calculation. By using trigonometry, the AFOV can be expressed as:
See how others are using our high-performance cameras, spectrographs and optics-based solutions to advance their research and application.
What isfocal length oflens
Looking at the list, it’s pretty neat to see how long some of those film reels are! Even though the film is less than half an inch wide, the fact that it’s 50 feet long is quite the accomplishment! But how does that translate into viewing time? Let’s do some math.
There you have it! If you’ve ever wondered how long 8mm film is and what that means for viewing time, now you know! We figured out that a foot of 8mm film contains around 92 frames and about 5 seconds of viewing time. Using some math, we figured out that you had to use a LOT of film to get a pretty short video -- about 2 giraffes worth of film would only give you around 4 minutes of run time.
The gain relates the number of photoelectrons released to the gray levels displayed, and can be used to enhance contrast for low-light imaging.
There are two processes which can be used to enhance UV sensitivity for wavelengths >200 nm: UV photon conversion, and anti-reflection coatings.
To measure the FOV of UV, visible and infrared cameras, optical tests are commonly used. During the test, light is focused from a black body (an object that absorbs all light that falls on it) onto a test target at the focal place. By using a set of mirrors, a virtual image can be created that is at an infinitely far distance.

The sensor size is determined by both the number of pixels on the sensor, and the size of the pixels. Different sized pixels are used for different applications, with larger pixels used for higher sensitivity, and smaller pixels used for higher spatial resolution (find out more on Pixel Size and Camera Resolution).
First, we’ll figure out how many frames are each foot of film. A standard frame size for 8mm film is 4.8mm wide by 3.5mm tall. Doing a little metric to standard conversion leaves us with a frame height of .13 inches per frame. More math gets us to 7.69 frames per inch, which means 92.28 frames per foot.
Field of view vs focal lengthcanon
But this blog post won’t be so straightforward. Today, we’re turning the film the other direction and asking the same question: how long is the typical 8mm film reel? That’s a question that’s a little bit harder to answer, but we have the technology. But first, we’ll answer the question in a really annoying way. How big is a typical 8mm reel?
The focal length of the lens describes the distance between the lens and the focused image on the sensor. As light passes through the lens it will either converge (positive focal length) or diverge (negative focal length), however within cameras the focal length is predominately positive. Shorter focal lengths converge the light more strongly (i.e. at a sharper angle) to focus the subject being imaged. Longer focal lengths, in comparison, converge the light less strongly (i.e. at a shallower angle) in order to focus the image.
This allows the FOV dimensions (i.e. vertical and horizontal distances) to be measured without knowing lens focal length or sensor size. The image created, including the target, is then displayed on a monitor, with the target image being a subset of the full image display. This allows the FOV to be approximated as:
Next, we need to figure out how fast the film plays. For most regular recordings, frame speed is around 18, and we use a scale called frames per second (FPS). That means each second of recording uses 18 separate pictures -- or frames.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500