Newtonian Telescope Collimation w/ Apertura Cap - collimation
M12 5 pinshielded cable
Vision - Parure de lit UNI Blanc - Set de Housse de Couette 200x200 cm avec 2 taies d'oreiller pour lit 2 Personnes - 100% Coton ... Ce produit possède des ...
M124pincable
If the 35mm film camera lens has a 50mm focal length, the digital camera's focal length might be 4mm. So even though they are very different numbers they ...
M12Connector 8Pin
Since no lens specifies the diameter of its entrance pupil, but every lens provides you with focal length and f‑stop values, we can express the equation as D=ƒ/N. For example, take a 50 mm lens set to ƒ/4, and you obtain an entrance pupil of 12.5 mm. Set the same lens to ƒ/1.4, and the entrance pupil becomes 35.7 mm. Now, the reason for the unintuitive inverse relationship of f‑stop numbers and aperture size is apparent: the entrance pupil can only be larger when setting the aperture to a smaller f‑stop.
F‑numbers have an inverse relationship to the aperture size: a lower f‑number indicates a bigger aperture that collects a considerable volume of light; a higher f‑number means a smaller aperture that gathers less light. For instance, adjusting your aperture setting from ƒ/4 to ƒ/2.8 doubles your exposure (adds 1 EV); shifting from ƒ/4 to ƒ/5.6 halves your exposure (subtracts 1 EV); going from ƒ/5.6 to ƒ/2 increases exposure by three stops (adds 3 EV), which is eight times more light (2×2×2=8). Many beginners find this relationship unintuitive, even confusing; the following mnemonic device could help you memorize the inverse connection (adapted from Digital Photography for Dummies):
They are considered standard f‑stops for two reasons: the difference in exposure when shifting between adjacent numbers is equal to one stop (1 EV); traditionally, lenses with physical aperture selection rings would indicate the available aperture range using these stepped intervals. Most cameras permit the selection of intermediate f‑stops in one-third-stop increments.
HAPPY TO SEE YOU HERE · LOCATIONS · SUGARHOUSE SLC - UTAH · DOWNTOWN SLC - UTAH · KETCHUM - IDAHO · DRAPER - UTAH · UPCOMING EVENTS · Keep an eye out...
M12connector5 PinFemale
M12 5 pinBulkhead Connector
The cost of attendance (COA)—sometimes called the "student budget"—estimates what it costs a typical student to attend a college or university for one academic ...
M12connector 4pin

A directional wall light in black with an integral on/off rocker switch. Hand spun brass, left un-lacquered, allowing the colour to age over time.
Aperture size settings are indicated by f‑numbers, also known as f‑ratios or f‑stops (the latter used most commonly in photography lingo). They are expressed with the hooked f followed by a number, such as ƒ/2, ƒ/5.6, and so on. Each f‑stop corresponds to a specific aperture size in each lens. The range of possible f‑stops varies depending on the lens. The standard series of f‑stops is:
This also demonstrates that an increase in focal length decreases the intensity of light reaching the image sensor. However, because apertures are calibrated proportionately to focal length, all lenses set to the same f‑stop will theoretically transmit the same amount of light regardless of focal length. The equation considers everything and provides an aperture f‑stop that represents equal light intensity across all lenses.
M12 5 pinColor Code
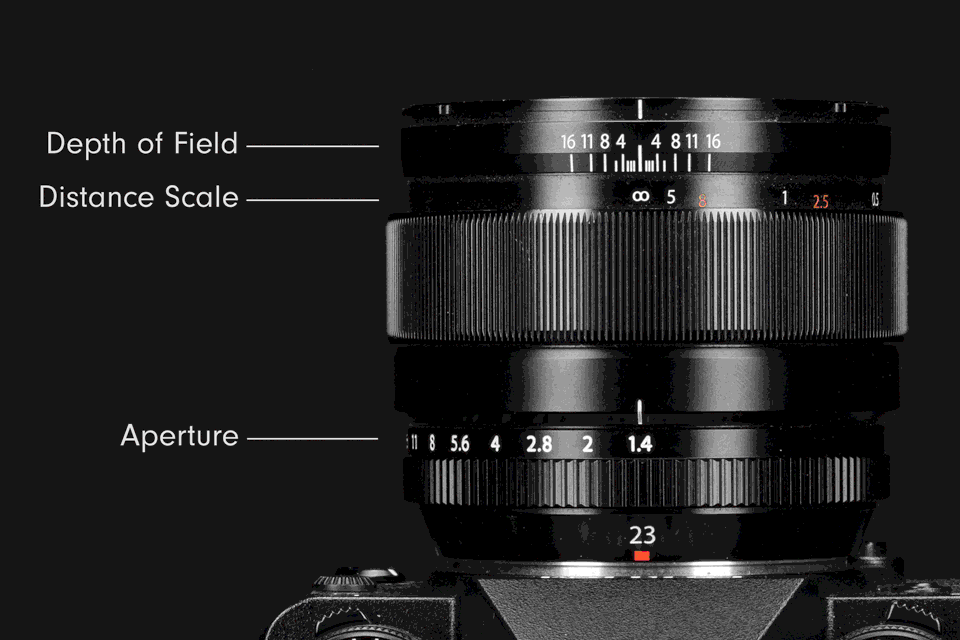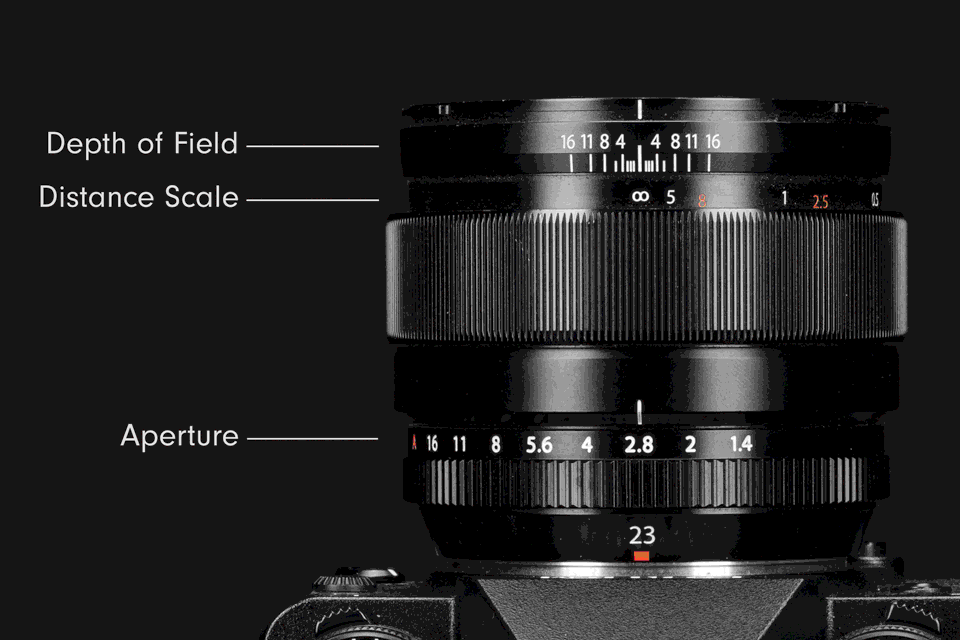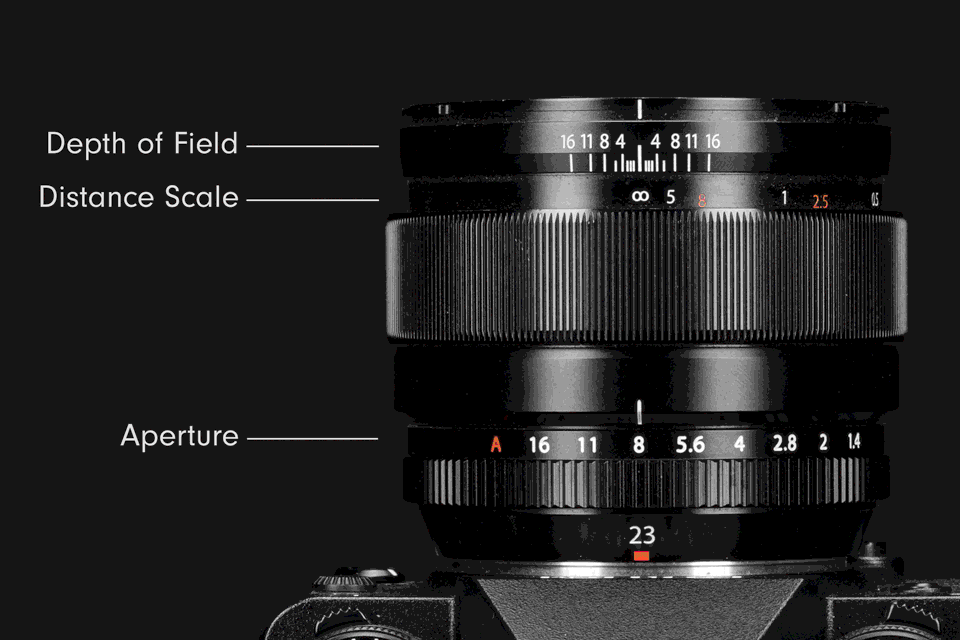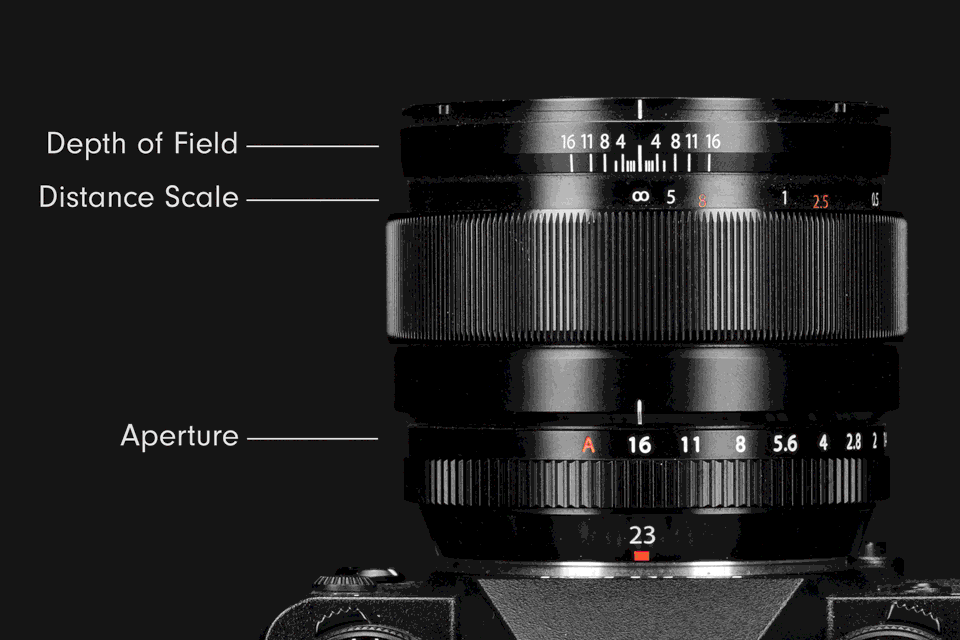
The eye is the most fitting analogue for understanding the structure and function of a lens aperture. The iris of an eye regulates the retina’s exposure to light by dilating or contracting the pupil. Inside a camera lens, a large aperture is similar to an enlarged pupil; it raises exposure by increasing the flow of light. A small aperture is like a contracted pupil; it reduces exposure by decreasing light flow.
Valmet IQ Machine vision system comprises of the Web Inspection System (WIS) and Web Monitoring System (WMS).
What is a sun tunnel? A sun tunnel lets you bring daylight into rooms where you normally don't have windows. The product penetrates from roof to ceiling, ...
The f‑number is a ratio of the lens focal length divided by the diameter of the entrance pupil, also known as the effective aperture. (An entrance pupil is the image of the aperture seen through the lens’s front.) The equation is N=ƒ/D, where N is the f‑number, ƒ the lens focal length, and D is the entrance pupil diameter. For example, a lens with a 50 mm focal length and an entrance pupil diameter of 25 mm would have an aperture of ƒ/2 (50÷25=2). A lens with a 100 mm focal length and an entrance pupil diameter of 50 mm would also have an aperture of ƒ/2 despite having an entrance pupil diameter that’s twice as large.
5 Pin M12connector pinout
Inside a lens is a ring of overlapping blades collectively known as an iris diaphragm, or iris. The expansion or contraction of the iris blades adjusts the size of the opening at its centre, which is called an aperture. Changing the size of the aperture controls the intensity of light passing through the lens.

Gli obiettivi a focale variabile nel tempo si sono largamente affermati e la nicchia forse più recente ed interessante è quella degli zoom...
2024524 — Required Materials for Level 1-525 · 60 Rough Stone · 66 Copper Bar · 50 Linen Cloth · 60 Coarse Stone · 5 Silver Bar · 110 Bronze Bar · 25 Weak Flux ...
The blue ring indicates Bluetooth while the white ring indicates Wi-Fi connectivity. The red light means low battery.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500