The basics of polarization | Animated Guides - light and polarization
However, UV light in particular is increasingly popular as a way to disinfect surfaces, liquids, and air in a way that’s safe and fast.

Processes – and solely those processes – characterised by the use or manipulation of apparatus classifiable in this subclass, in particular
Cameras with paired lenses, one of which forms image on photographic material and the other forms a corresponding image on a focusing screen
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a focusing lens or other optical elements in photographic devices.
Control of exposure in accordance with both the intensity of the flash source and the distance of the flash source from object, e.g. in accordance with "guide number" of flash bulb and the focusing of the camera
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
... beams, the basic properties of laser light, the three ranges of laser light wavelengths, the two types of laser light reflection, and the laser classifications.
Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source
The difference between Near-UV and Far-UV is simply a matter of wavelength. The wavelength determines what happens when the light comes into contact with human skin as well as with dangerous pathogens.
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras as long as the focusing signal is not generated in the main electronic image sensor
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras based on image signal provided by the main electronic image sensor
Therefore, when the following subject matter is classified in this subclass, it is desirable to also classify it in subclass H04N, when some aspects are considered of interest for search purposes:
In particular, the introduction of products that feature UV-FORCE® technology has made far-UV disinfection that much more attractive as an option. But what is far-UV? And how does it differ from other types of UV light? Keep reading to find out.
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes
To learn more about how UV-FORCE® technology which utilizes Far-UVC light can be an effective disinfection tool in many scenarios, click below.
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves; Visualisation of the interior of objects by transmitting ultrasonic or sonic waves through the object
Safety glasses should be used at all times when operating the UV-C lamp. These glasses are ANSI Z87.1 approved, which means this eye wear meets the safety ...
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a power operated focusing lens or other optical elements for focusing
The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance does not always measure only absorption; it may measure attenuation (of ...
Controlling or varying light intensity in photographic printing apparatus by transforming the picture information intermediately into electrical signals
12VDC 3W/FT 5 m (16.4') Top-Emitting Neoloop, 2700K $323.80 NEW 12VDC 3W/FT 5 m (16.4') Top-Emitting Neoloop,
Investigating or analysing materials using electromagnetic radiation, other than infrared, visible or ultraviolet radiation, e.g. microwaves, or particles
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
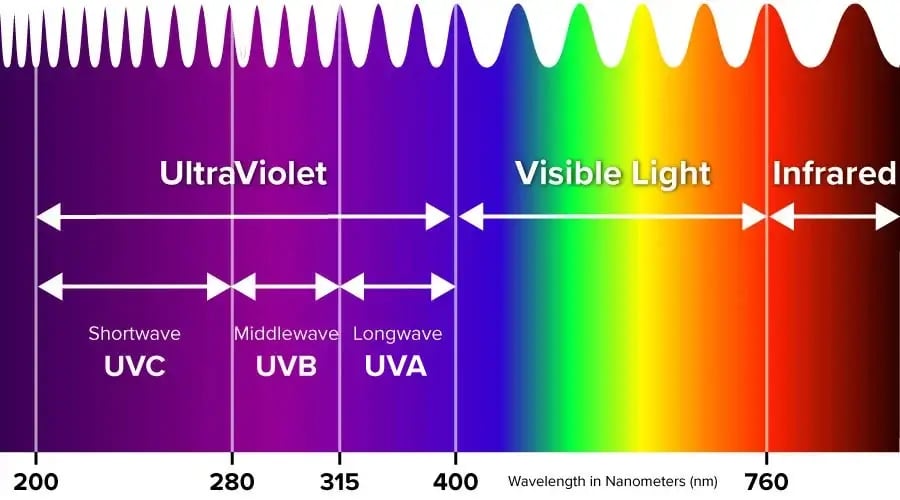
UV light has a wavelength between 100 and 400 nanometers, shorter than that of any visible light. The term “ultraviolet” refers to the fact that this light has a shorter wavelength than violet light, which has the shortest wavelength of any color light that is visible to the naked eye.
Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source
Buy LX-1010B Digital Light Lux Meter 0 - 50000 Lux Camera Photo for only $23.90 at Gain Express!
You probably already have some understanding of ultraviolet light. UV rays are what we’re protecting ourselves against when we wear sunscreen and avoid sunburns. But how does UV differ from other types of light? The difference is in the wavelength.
Thus, in G03B aspects of apparatus or methods for taking photographs using an electronic image sensor [EIS] for image capture are classified insofar as they correspond to those of said apparatus or methods for taking photographs using light sensitive film, i.e. insofar not peculiar to the presence or use of the EIS, e.g. mounting of optical elements or flashes, and their related controls insofar they are not peculiar to the presence of the EIS, e.g. exposure, focus, (opto-) mechanical motion blur (anti-shake);
In G03B, aspects of apparatus or methods for projecting or viewing images using an electronic spatial light modulator [ESLM] are classified insofar as they correspond to those of said apparatus or methods for projecting or viewing images using film stock, photographic film or slides, i.e. insofar as not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, e.g. mounting of optical elements not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, and their related controls not peculiar to the presence of the ESLM, e.g. cooling, beam shaping, optical keystone correction.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
If the intensity of light varies between maximum and minimum for every rotation of 90∘ of the analyser, the light is said to be partially polarised light.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Measuring linear or angular speed using photographic means; Measuring differences of linear or angular speeds using photographic means
Record carriers characterised by the selection of the material and comprising cinematographic film or slide with integral magnetic track
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a power operated focusing lens or other optical elements for focusing .
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras based on image signal provided by the main electronic image sensor
The printing of a record obtained via the processes or apparatus of subclass H04N is classified in class B41 if the only chemical processing involved consists in the after-treatment of ink applied to the recording surface but is classified in subclass G03B if a latent image is produced.
Device displaying image information by projection of light patterns, usually through an optical lens, wherein the light patterns are generated by illuminating an image, e.g. film or slide, or by converting an electric image signal into an optical signal using an electronic spatial light modulator
References · Lamonica, Martin. "A Cheaper Route to Making Chemicals from CO2". · Retka Schill, Susanne. "NJ company unveils low-cost CO2-to-chemical process".
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Process of recording pictures by means of capturing light on a light-sensitive medium, e.g. silver halide based chemical or an electronic image sensor. Light patterns reflected or emitted from objects expose such a light sensitive medium during a timed exposure, usually through a photographic lens in a device known as a camera
Holders for containing light sensitive material and adapted to be inserted within the camera, e.g. cassettes specially adapted for motion picture film
UV light in different forms is frequently used for disinfection in healthcare facilities, for food manufacturing, and in agricultural settings. Its shorter wavelength makes Far-UV the effective choice for disinfection. A Far-UV light can cause the physical destruction of viruses, bacteria, and fungi so that they will no longer cause infection or harm. Further, Far-UV light can cause this destruction quickly, without the use of potentially harmful solvents, making it an attractive choice for infection control tools.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Processing or use of electrical image signals from the EIS for the generation of camera control signals. e.g. focusing, exposure control, electronic blur correction, display in electronic viewfinder
Photographs or any other kind of latent, directly-visible or permanent storage of pictorial information, which consist of an imagewise distribution of a quantity, e.g. an electric charge pattern, recorded on a carrier member
Dozens of twinkling LED lights are arranged in geometric shapes at the end of fine rods which give this light, airy chandelier the appearance of floating ...
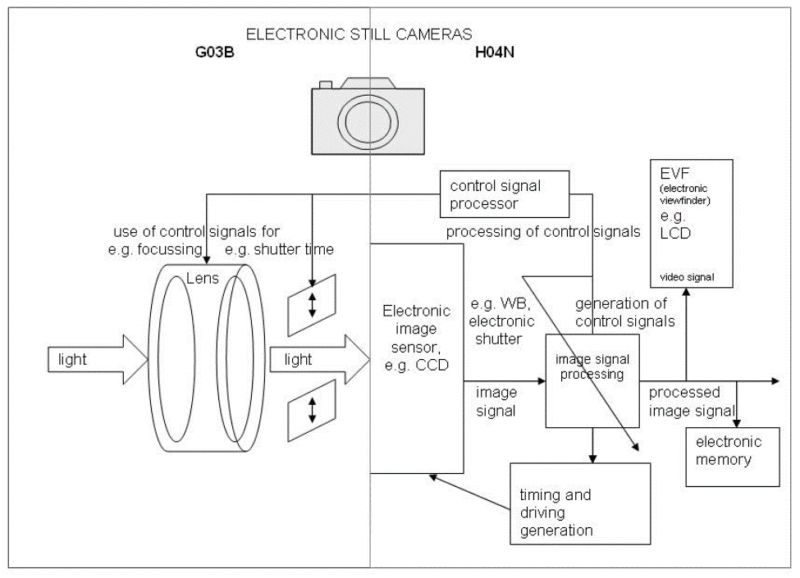
In the above image, elements on the left side correspond to G03B (e.g. light, use of control signals for focusing and shutter time). Elements on the right side correspond to H04N (e.g. control signal processor, processing of control signals, electronic image sensor, electronic shutter, generation of control signals, image signal processing, timing and driving generation, EVF, LCD, processed signal memory, and electronic memory).
Photographic processes are covered by subclass G03B when the process relates to the exposure of the photosensitive medium, in order to generate the latent image, whereas subclass G03C covers the photographic processes that involve a chemical transformation of the photosensitive medium, such that the latent image is transformed into a visible and permanent record.
G03B 29/00 covers constructional details of the combination of cameras with other non-optical apparatus. On the other hand, G03B 30/00 covers the camera modules themselves, which are to be embedded in other devices.
Dec 5, 2024 — The 'Babylon Berlin' director's first film since 2016's 'A Hologram for a King' stars Tala al Deen, Lars Eidinger and Nicolette Krebitz.
Electronic spatial light modulator: optoelectronic transducer converting electric signals representing image information into optical image information
Registration or positioning of originals, masks, frames, photographic sheets or textured or patterned surfaces in photo-mechanical production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. of integrated circuits
Photographic arrangements structurally combined with discharge tubes with provision for introducing objects or material to be exposed to the discharge
... small aperture, or a shallow depth of filed with a ... With the exposure meter uncovered by the lumisphere, the light meter can measure reflected light.
Mechanical and electromechanical details of driving and guiding a power operated focusing lens or other optical elements for focusing
Algorithms, control systems and user interfaces for performing autofocusing and for generating focusing signals in photographic cameras as long as the focusing signal is not generated in the main electronic image sensor.
Within the category of ultraviolet, there are subtypes also divided by the difference in wavelengths. Most commonly, you will see UV light divided into A, B, and C subtypes with A having the longest wavelength (320nm to 400nm) and C having the shortest (100nm to 290nm). UV-A light is also referred to as “blacklight,” UV-B light (290nm to 320nm) is what causes sunburns in humans upon exposure and UV-C light mostly absorbed by the atmosphere so we have little contact with this type of light.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Functional features or details of lighting devices or systems thereof; Structural combinations of lighting devices with other articles, not otherwise provided for
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by photographical inspection
Subclass H04N covers the electronic image projection apparatus or processes where an electronic image modulator converts electrical signals into an optical image, e.g. by controlling the electronic image modulator or by processing the electrical signals.
Panoramic or wide-screen photography;Photographing extended surfaces, e.g. for surveying;Photographing internal surfaces, e.g. of pipe
Electronic image sensor: optoelectronic transducer, converting optical image information into an electrical signal susceptible of being processed, stored, transmitted or displayed
When it comes to scientific use, different categories are used to distinguish one type of UV light from another. For these purposes, UV subtypes are Near, Middle, and Far, with Near-UV matching up closest to UV-A, Middle-UV matching with UV-B and Far-UV matching with UV-C in terms of wavelength.
Besides learning the colors of the visible light spectrum with a catchy acronym in middle school, most of us don’t spend much time thinking about ultraviolet radiation or UV rays.
Subclass H04N covers the electronic image capturing apparatus or processes where an electronic image sensor converts an optical image into electrical signals, e.g. by controlling the electronic image sensor or by processing the electrical signals.
As far as processes are concerned, only processes characterised by the use or manipulation of apparatus classified in G03B.
Structural combination of reactor core or moderator structure with viewing means, e.g. with television camera, periscope, window
Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500