Patterns and properties of polarized light in air and water - light and polarization
Adjust the brightness of the lighting and the shutter speed of the camera to clearly define the areas you want to emphasize and those you prefer not to.
UV radiation from the sun has always played important roles in our environment, and affects nearly all living organisms. Biological actions of many kinds have evolved to deal with it. Yet UV radiation at different wavelengths differs in its effects, and we have to live with the harmful effects as well as the helpful ones. Radiation at the longer UV wavelengths of 320-400 nm, called UV-A, plays a helpful and essential role in formation of Vitamin D by the skin, and plays a harmful role in that it causes sunburn on human skin and cataracts in our eyes. The incoming radiation at shorter wavelengths, 290-320 nm, falls within the UV-B part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (UV-B includes light with wavelengths down to 280 nm, but little to no radiation below 290 nm reaches the Earth’s surface). UV-B causes damage at the molecular level to the fundamental building block of life— deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
People and plants live with both helpful and harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. (Photograph courtesy Jeannie Allen)
Using this property, we can control whether an object is “brightened” or “darkened” by using monochromatic lighting on a colored object.“In fact, using a monochrome camera and lighting a red (R) green (G) and blue (B) object with each color of red (R), green (G), and blue (B) will produce the following image.
Among wavelengths invisible to the human eye, wavelengths shorter than visible light are called “ultraviolet light” and longer wavelengths are called “infrared light”.(See the figure on the previous page.)
In addition to highlighting defects, the same concept of lighting selection can be used to eliminate excess background or unnecessary objects.
Resolution is expressed by the above formula, but if the same lens (same NA) is used, the longer the wavelength, the greater the spatial resolution=less finely resolved.
The three most basic colors are Red, Green, and Blue and are represented by the acronym RGB.Mixing the three colors of light in equal proportions produces white light.Indoor lighting such as fluorescent lamps and sunlight appear white because the various colors of light are mixed in proportion to each other.In addition, almost any color can be produced by controlling the balance of RGB.
It is necessary to obtain completely different results for (1) and (2), which can be achieved by adjusting the “irradiation solid angle”
In addition to their own resiliency, living things and the cells they are made of are protected from excessive amounts of UV radiation by a chemical called ozone. A layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere absorbs UV radiation and prevents most of it from reaching the Earth. Yet since the mid-1970s, human activities have been changing the chemistry of the atmosphere in a way that reduces the amount of ozone in the stratosphere (the layer of atmosphere ranging from about 11 to 50 km in altitude). This means that more ultraviolet radiation can pass through the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, particularly at the poles and nearby regions during certain times of the year.
It can transmit through specific objects. This allows detection of substances within the object that are not visible with visible light.It can also darken and detect areas that contain more moisture than their surroundings, due to the absorption properties of moisture in a specific wavelength range of infrared light.
Exposure of certain objects, including phosphors, to ultraviolet light causes a fluorescence phenomenon (excitation) that absorbs the ultraviolet light and emits light with a longer wavelength.This allows the position of objects that are difficult to recognize with visible light to be captured more easily.
As described above, the color, type, size, and installation method of lighting can change the way an object is seen. The selection of the lighting is essential together with the camera and lens.VS Technology offers verification with actual objects, so please contact us for more information.
DNA readily absorbs UV-B radiation, which commonly changes the shape of the molecule in one of several ways. The illustration below illustrates one such change in shape due to exposure to UV-B radiation. Changes in the DNA molecule often mean that protein-building enzymes cannot “read” the DNA code at that point on the molecule. As a result, distorted proteins can be made, or cells can die.
Machine visionBacklight
Ultraviolet Radiation Introduction Effects on the Biosphere What Determines UV at the Surface? How Much Are We Getting? Predictions and Monitoring References
LEDillumination
AS manufacturing technology has advanced in recent years, various products can be mass-produced in a short period of time. As a result, “product inspections” are no longer able to keep up with visual inspections by humans due to the demand for higher accuracy, inspection speed, and difficulty in training new employees. Replacement of visual inspection is underway with machine vision (image processing equipment), which inspects products for defects based on image data captured by industrial cameras and lenses.Machine vision has many advantages, such as 24-hour operation, programmable operation, and reduced variation in inspection results. However, machine vision is not simply a matter of installing cameras. In fact, the human eye excels in its ability to constantly focus on a product depending on its distance and viewing angle, and it is able to recognize both bright and dark areas in a single glance. It can flexibly respond to any given situation. In contrast, machine vision often requires a single image of the product being delivered by a fixed camera, lens, and lighting, and unless the defective part is clearly visible in the image, it is impossible to correctly determine whether the product passed or failed.
What isilluminationof light
Electromagnetic radiation exists in a range of wavelengths, which are delineated into major divisions for our convenience. Ultraviolet B radiation, harmful to living organisms, represents a small portion of the spectrum, from 290 to 320 nanometer wavelengths. (Illustration by Robert Simmon)

(Example 1)If white light is shined on a red apple, it will appear red because it absorbs blue and green light and reflects only red.f green light is shined on a red apple, it absorbs green and reflects no color, making it appear black.
There is no difference under natural and visible light, but as we move to longer wavelengths, the water appears blacker and the difference becomes clearer.
The sun radiates energy in a wide range of wavelengths, most of which are invisible to human eyes. The shorter the wavelength, the more energetic the radiation, and the greater the potential for harm. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface is in wavelengths between 290 and 400 nm (nanometers, or billionths of a meter). This is shorter than wavelengths of visible light, which are 400 to 700 nm.
This site collects and uses access data using cookies for the convenience of browsing the site, as well as to understand the site operation and usage status.By pressing and closing the permission, you agree to the setting and use of cookies. See Privacy Policy for details on setting and using cookies.
Advancedillumination
If you want to image a small workpiece at high resolution, it is necessary to carefully select the wavelength of the lighting and the numerical aperture of the lens.
Lateralillumination
But living cells are “smart.” Over millions of years of evolving in the presence of UV-B radiation, cells have developed the ability to repair DNA. A special enzyme arrives at the damage site, removes the damaged section of DNA, and replaces it with the proper components (based on information elsewhere on the DNA molecule). This makes DNA somewhat resilient to damage by UV-B.
“Light” is a class of waves called electromagnetic waves.The range of this light that the human eye can perceive is called “visible light” and extends from about 380 nm to 780 nm (nanometers).The wavelength range used in imaging is even wider than visible light, ranging from ultraviolet to infrared.
The lighting is uneven on both sides and top and bottom, and the lighting is partly reflected in the image making it too bright.
Ultraviolet (UV) photons harm the DNA molecules of living organisms in different ways. In one common damage event, adjacent bases bond with each other, instead of across the “ladder.” This makes a bulge, and the distorted DNA molecule does not function properly. (Illustration by David Herring)
Dome LightMachine Vision
(Example 3)When detecting blue stains on a red object, red lighting can be used to capture the object brighter and the stain darker, resulting in a high-contrast image.
As shown above, when the light source color that includes the color of the object is irradiated, the object can be imaged brightly (white).Conversely, if the object is illuminated by a light source color that does not include the object’s color, the object can be imaged dark (black).
Illuminationtechniques in slit lamp
(Example 2)When white light is shined on a yellow banana, it absorbs blue light and retlects a mixture of red and green light, making it appear yellowish.“If you shine blue light on a yellow banana, it absorbs blue and appears blackish because it absorbs blue.
(1) When you want to make the unevenness stand out as a defect.(2) When you do not want the unevenness to stand for defects, but want to detect other stains, etc.

Dark field lighting
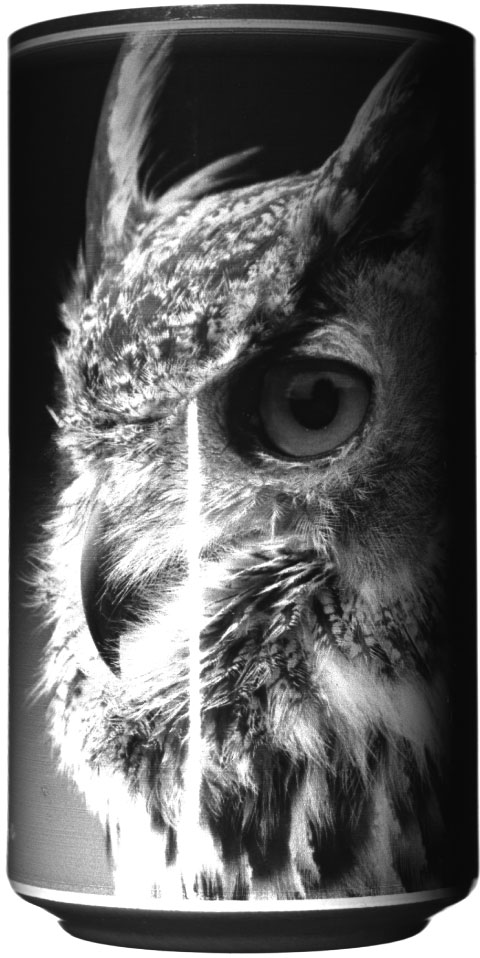
There is a cylindrical container with a picture of a bird printed on it.Let’s capture an image of this with a combination of lens + camera +lighting.What is the difference between a good image and a bad image?
The color of an object is determined by the color of the light that reaches the object from a light source, such as the sun, and is reflected without being absorbed by the object.
The irradiation solid angle is the angle of incident light to a point on an object, and the size of the irradiation solid angle controls the appearance of unevenness.
A rough, low-reflective workpiece such as paper or untreated wood will appear equally bright no matter where the light is projected.On the other hand, a workpiece that is shiny and highly reflective, such as a mirror, polished metal or glass, is captured in a completely different image depending on where the light is projected from.
Without the layer of ozone in the stratosphere to protect us from excessive amounts of UV-B radiation, life as we know it would not exist. Scientific concern over ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere has prompted extensive efforts to assess the potential damage to life on Earth due to increased levels of UV-B radiation. Some effects have been studied, but much remains to be learned.
The basic idea is to focus on the object by adjusting the depth of field with the aperture and brightness of the lighting.(In some cases, the image may be intentionally blurred.)




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500