LENSES BY EDMUND OPTICS - Sensors Incorporated - edmund optics lens
Working distancemicroscope
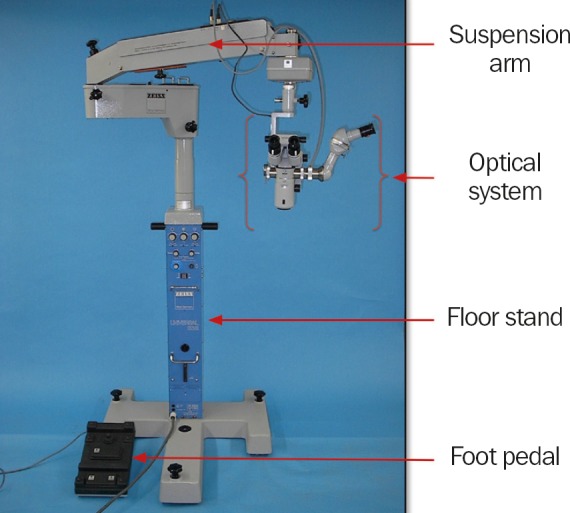
The optical system is attached to the suspension arm of the floor stand (Figure 3). The suspension arm makes it possible to position the optics exactly and to fix them in place. The floor stand has wheels and can be moved around the floor and fixed into place using the brakes.
To protect it from dust when not in use, drape a cover over the microscope. Vinyl coverings are preferred because they do not shed lint (like cloth coverings do). However, their use should be avoided in humid environments since they can trap moisture, which increases the risk of fungal growth.
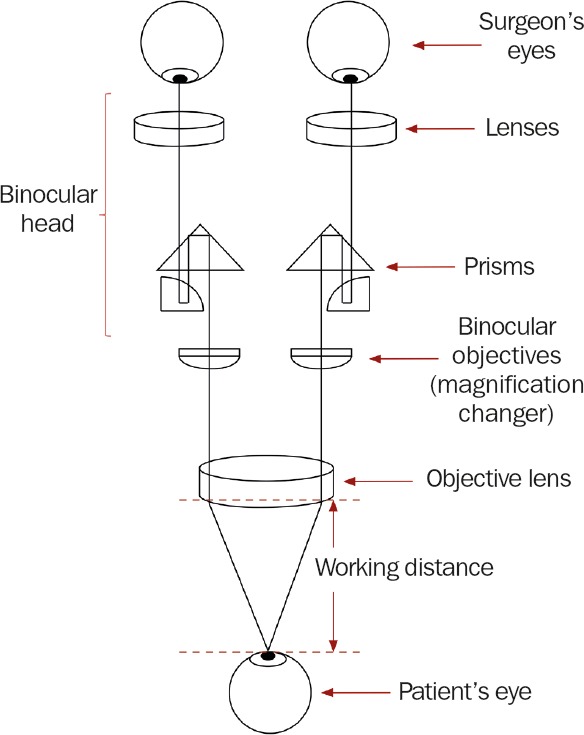
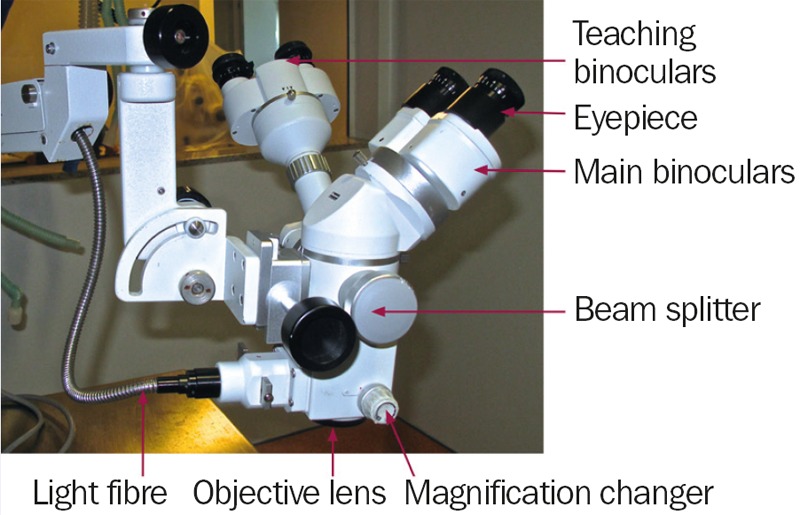
The optical components of a basic stereo microscope consist of the binocular head, a magnification changer, the objective lens and an illuminator which beams light through the objective lens and onto the operating field (Figures 1 and 2). The binocular head consists of two telescopes with adjustable eyepieces for users with refractive error. The magnification can be changed by turning a knob (which selects different magnification lenses) or by using a motorised zoom controlled by a foot pedal.
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Field of view microscope
The illumination system is usually housed in the floor stand in order to keep the bulb heat away from the operating field. In this case, the light is transmitted to the operating field by means of a fibre optic cable. The light in ophthalmic micro scopes is usually coaxial, meaning that it follows the same path as the image in order to avoid shadows.
Use a voltage stabiliser with the microscope. This will prevent sudden increases in voltage from destroying the bulbs and will ensure that the illumination provided remains constant.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
It is essential that all eye units develop protocols for performing microscope checks. Microscope optics should be inspected and cleaned on a weekly basis, or earlier if dirty. The entire microscope should be checked by a biomedical equipment technician at least once every six months.
When replacing the bulbs, avoid touching them with your fingers. The oil left as fingerprints on the bulb can shorten its life.
Parfocal length
A foot pedal connected to the floor stand allows the surgeon to control the focus, the zoom, the position of the optics over the eye (the x,y position on the horizontal plane) and to turn the illumination on and off.
Cover the foot pedal with a clear plastic bag to prevent surgical and cleaning fluids from entering and damaging the electronics.
An operating or surgical microscope is an optical instrument that provides the surgeon with a stereoscopic, high quality magnified and illuminated image of the small structures in the surgical area.
The optical system often includes a beam splitter and a second set of teaching binoculars (Figure 2) so that two people can view the operation simultaneously.
The working distance (Figure 1) is the distance from the microscope objective lens to the point of focus of the optical system. This value is fixed and is dependent on the chosen focal length of the objective lens. The choice of working distance depends on the type of surgery. For modern ophthalmic surgery that involves delicate work in the posterior chamber, objective focal lengths of 150 mm, 175 mm and 200 mm are commonly used.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500