How To Calculate Magnification On A Light Microscope - compound light microscope ocular lens magnification
Types of illumination PDF

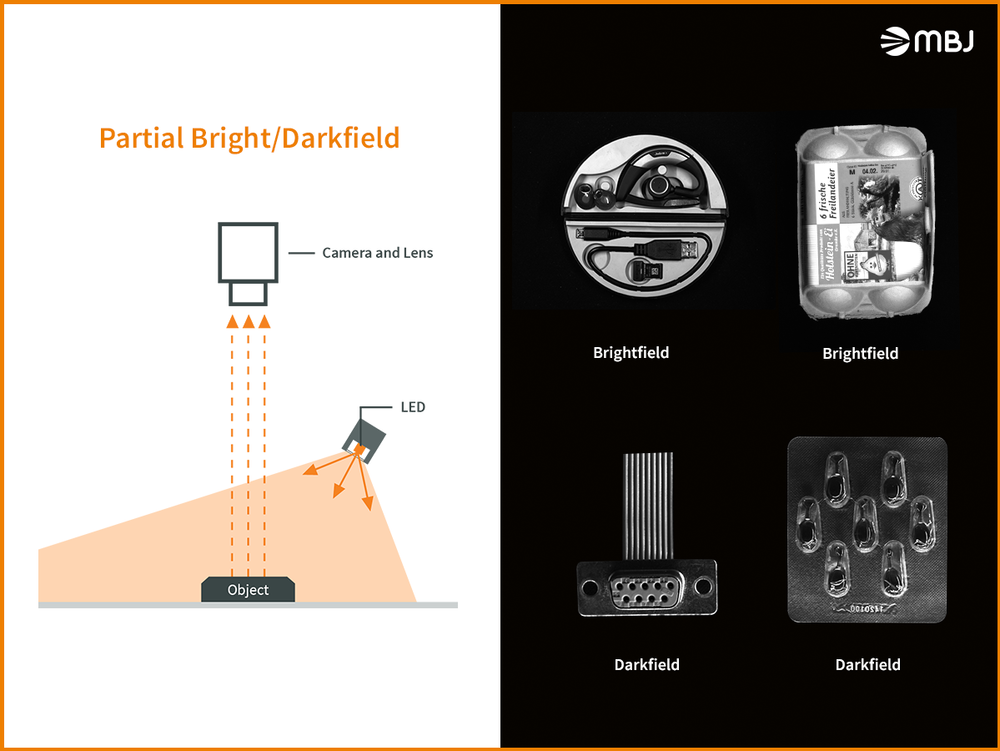
With this type of illumination, the camera looks directly at the illuminating surface of the light, hence the image background is bright. The object, between the illumination and the camera, creates a partial or even a complete shadowing of the light in the camera. It appears very dark in the image.
General illumination
Most light sources are unpolarized. The electric field is vibrating in many directions; all perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Polarized light is unique in that it vibrates mostly in one direction. Any direction is possible as long as it's perpendicular to the propagation, be itâ¦
Organic compounds that exist in both left and right handed forms are called stereoisomers. Those that are perfect mirror images of one another are called enantiomers. They demonstrate equal amounts, but opposite directions of optical rotation. In all other respects, their physical and chemical properties are identical. Their physiological actions may differ, because enzymes and other biological receptors can readily discriminate between many enantiomeric pairs. The other isomers may be indigestible or even toxic. Some are just interesting.
Chirality is the property of some objects that makes them distinguishable from their mirror images. Objects that exhibit chirality are said to be chiral. Human hands are the most easily accessible examples of chiral objects, which is why chirality is also often described as handedness. Chirality is just a painfully clever scientific word derived from the Greek word for hand â ÏεÏι (kheri).
Thus, the object and the background appear dark in the image. Only areas of the object that are at a certain angle to the camera reflect light back to the camera. They are displayed brightly and highlighted, e.g. raised edges, surface scratches.
Illumination lighting design
Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave that can be seen by a typical human. Wherever light goes, the electric and magnetic fields are disturbed perpendicular to the direction of propagation. This propagating disturbance is what makes light a wave. The fact that the electric and magnetic fields are disturbed makes light an electromagnetic wave. The fact that it disturbs these fields at right angles to the direction of propagation makes light a transverse wave. In this section we will explore what it means to be transverse.
Part of the light passes the camera lens and is only reflected back to the camera when the surface of the object changes it. At the same time, however, the special characteristics achieved by the strict application of bright or dark field are weakened.
spectroscopy, polarimetry, defectoscopy, astronomy, platography, material research, laser applications, light modulation, agricultural production, electric power generation, environmental control devices, molecular biology, biotechnology
Light illumination level
Illumination lighting meaning
All sugars produced by living things are right-handed molecules, but they may rotate the polarization of light in either direction. Glucose is the most abundant simple sugar (monosaccharide) and is the primary source of energy for all living things. Its name comes from the Greek word for sweet, Î³Î»Ï ÎºÎ¿Ï (glykos). Because it rotates plane polarized light clockwise it is also known as dextrose. Fructose is another simple sugar. Its name comes from the Latin word for fruit, fructus. Because it rotates plane polarized light counterclockwise it is also known as levulose.
For this setup, the light from a light source is positioned in a way that the light is not reflected back from the object into the camera's lens.
By changing the angle to a range between bright and dark field illumination, the light, via the object, is only partially reflected directly back to the camera.
Chemically bonding glucose and fructose produces sucrose â the stuff that most people today would call sugar (or maybe table sugar). Its name comes from the French word for sugar, sucre. The disaccharide sucrose is dextrorotatory but a mixture of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose is levorotatory. "Invert sugar" is made by heating a solution of sucrose and water. The two halves of the disaccharide separate (hydrolyze) and the rotation caused by the fructose dominates. The polarization of the solution has been "inverted" but the sugars themselves have not had their chirality inverted. Doing this would require the inversion of the molecule in three separate places, which is an extremely tricky thing to do.
Different illumination angles create varying images of the object in the camera and thus highlight different object properties. In this way, different inspection tasks can be covered with a variation in angles.
Illumination of light formula
Determining whether a particular compound is right- or left-handed is determined by a particularly complicated set of rules that I don't understand (and don't care to understand at this moment), but being able to do so is especially important in organic chemistry. Something possibly useful to know for physics students is that all naturally occurring sugars are right-handed and all naturally occurring amino acids are left-handed (except glycine, which is not chiral).
Optical rotation is the ability that all chiral molecules have to rotate plane polarized light. Think of a polarized light wave as a hand on an analog clock pointing to the 12. Shifting that hand a bit to the right rotates it clockwise, shifting it to the left rotates it counterclockwise. The Latin words for right and left are dexter and laevus, respectively. Chiral molecules that rotate the polarization clockwise are said to be dextrorotatory, while those that rotate it counterclockwise are said to be levorotatory.
What is illumination in the Bible
Carvone is a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids. Carvone has two enantiomers: a right-handed form which is found in the seed oils of caraway, dill, and anise; and a left-handed form which is found in spearmint oil. The difference in the two flavors is evidence that odor receptors have activation sites that are chiral. Your nose can smell the handedness of some molecules.
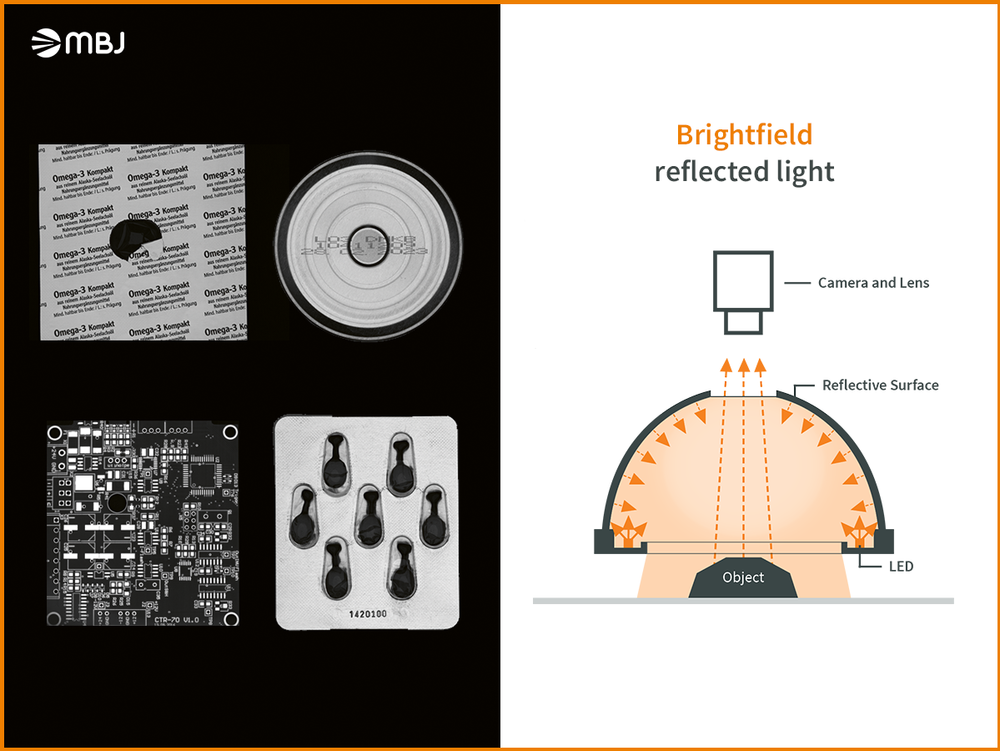
With this type of illumination, the light is reflected back directly into the camera via the object. This can be used for uniform illumination of an object space.
Types of illumination in slit lamp
We speak of toplighting when the illumination is above the object plane, in front of the object. We speak of backlighting when the illumination is below the object plane, behind or below the object.
A typical hand consists of four fingers, a thumb, and a palm. (In this context, a thumb is not considered a finger.) Using the two hands of one person, it is only ever possible to get two of these parts to point in the same direction at the same time.
Imagine a light wave traveling toward you, on its way to entering your eye. In what direction is the electric field vibrating? (Light is both electric and magnetic, but it is usually the electric field that we are interested in.) Up and down? Sure. Left and right? Sure, why not. Both alignments are perpendicular to the propagation of the wave.
Partial illumination at a wide variety of angles can be achieved very well with beams. In this case, four beam illuminators are usually mounted around the object.
If the object changes the light, e.g. by surfaces inclined away from the light, not all the light from these surfaces is reflected back into the camera. This is used to visualize changes caused by flaws in the object.
Polarized light carries information. Magnetic fields, chemical interactions, crystal structures, quality variations, and mechanical stresses can all affect the polarization of a beam of light.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500