All Outdoor LED Spotlights - green led spotlight

Absorption of lightin physics
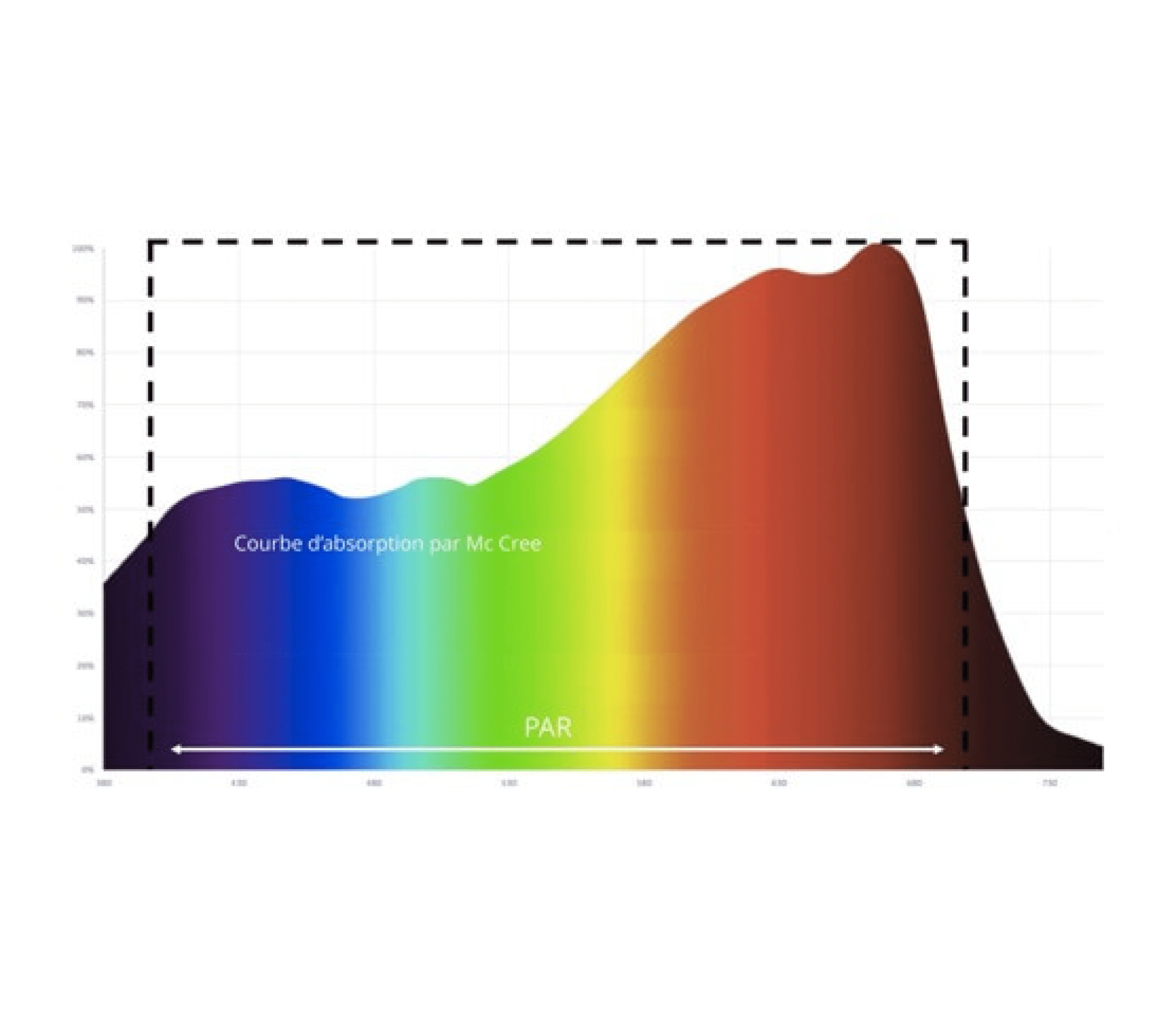
• Red light between 570 and 700 nm is the most absorbed, with a major absorption peak at 660 nm for chlorophyll A and 645 nm for chlorophyll B.
Absorption of lightExamples
In reality, not all wavelengths in the PAR spectrum are absorbed in the same way. This has been highlighted by Mc Cree’s work that characterizes photosynthetic activity as a function of each wavelength.
Absorption of lightin wavelength
We draw your attention to the fact that this Mc Cree absorption curve is only an indicator. In reality, light absorption varies according to the species and stage of development of the plant. In some cases, light intensity can even saturate certain photoreceptors and change this absorption spectrum.
If we take a closer look at this phenomenon, we notice that plants absorb light in two distinct forms: photosynthetic light and photosignaltic light.
CSI refers to a class of optical surface measurement methods wherein the localization of interference fringes during a scan of optical path length provides a means to determine surface characteristics such as topography, transparent film structure, and optical properties. See Wikipedia for more information about Coherence scanning interferometry.
Absorption of lightequation
The instrument works by scanning in Z and recording the Z position for each and every pixel on the detector for where zero optical path difference (ZOPD) occurred. The objectives are designed so the internal reference and the test path have zero optical path difference at the focal plan of the objective. So, as the scanner moves through Z, when the surface starts to come into focus for each pixel, the inference fringes will become measurable, and the Z position of the center fringe (highest intensity) is recorded as it passes through ZOPD. Our detector is a 1024x1024 camera, which means our scan results in 1,048,576 (x,y,z) coordinates that make up the image.
The John A. Dutton Institute for Teaching and Learning Excellence is the learning design unit of the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences at The Pennsylvania State University.
Absorption of lightin photosynthesis
Author: Mark Fedkin, John A. Dutton e-Education Institute, College of Earth and Mineral Sciences, Penn State University.
The College of Earth and Mineral Sciences is committed to making its websites accessible to all users, and welcomes comments or suggestions on access improvements. Please send comments or suggestions on accessibility to the site editor. The site editor may also be contacted with questions or comments about this course.
All plants absorb light radiation nearby to grow, with no differentiation between a natural source such as the sun or artificial sources such as LED lighting. Plants have evolved millions of years under sunlight and are able to absorb most of the wavelengths present. They derive most of their energy between 400 and 700 nm. This is called the PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) spectrum, which has become the standard measurement for horticulture. (Link to article 1)
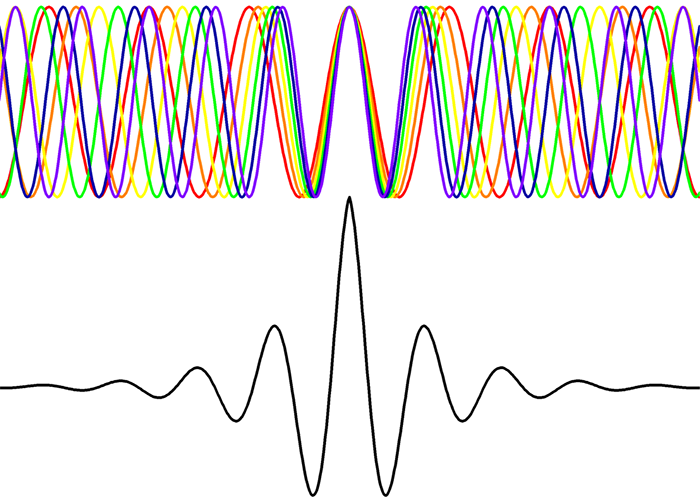
The image to the left depicts a white light source (top) and its distribution of component colors. The coherence length length is inversely proportional to the bandwidth, so the coherence length is very short. The "random" noise of white light produces an inference signal only when the optical path difference between reference and test paths is less than the coherence length of the beam. This can be seen in the resultant wave at the bottom. That center fringe of highest intensity is our point of zero optical path difference and essentially the probe of the interferometer.
The quality of the spectrum received by the plant affects its growth rate, appearance and hormonal reactions. A spectrum adapted to your crops will always allow you to optimize energy consumption as well as the yields and quality of your productions.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500