How does changing focal length affect depth of field? - lens focal length and depth of field
Choose from six flavors, from Spearmint to Wild Berry, and not only enjoy the good taste, but also effective cleaning and care. Simply in the application of how you are used to.
Wavefront errors always occur as soon as the surface of an optical component deviates from its respective ideal shape. To describe the wavefront error, one assumes a plane wavefront (surface with the same phase of the wave), which usually moves orthogonally to the propagation direction. This wavefront is deformed due to the non-ideal surface of optical components. Two types are distinguished:
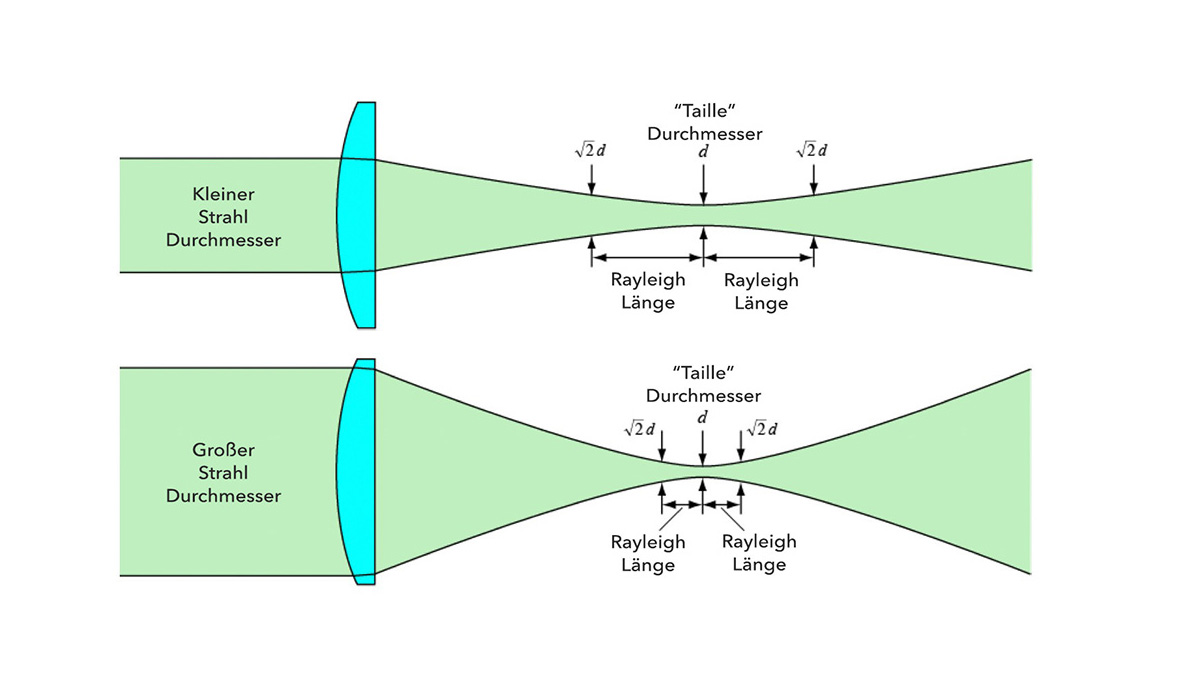
Non-imaging beams primarily contain the spectral information and the respective intensity (time could still be included, but is not often the case). The sample is rastered and the image is assembled afterwards in the computer using a lot of point information. This is e.g. the case in the confocal microscope (LSM) and in the STED microscope. The Rayleigh length criterion states that the focus offset must be less than one Rayleigh length due to the reflected wavefront error. Not to be confused with the Rayleigh criterion that separates two image points (see imaging beams). It should be noted that the Rayleigh length decreases with larger beam diameter (or NA).
ToothpasteTopper
Functional cookies are absolutely necessary for the functionality of the website. These cookies assign a unique random ID to your browser to ensure unhindered use of the website across multiple page views.
Transmitted wavefront error (TWE) considers the non-ideal wavefront after passing through an optical medium (lens, beam splitter, optical filter, etc.), where the error is the sum of the errors of both surfaces (front and back). The total wavefront error can be divided into a wedge error (non-parallel surfaces), a spherical, curved component (concave / convex lens) and a diffuse, non-regular component. As a rule, the wavefront error generated by transmission is relatively small and can be neglected.
STED stands for "Stimulated Emission Depletion" and is a method in fluorescence microscopy in which the diffraction limit is bypassed and thus an image resolution of less than 40 nm is possible. For imaging, the sample is scanned, as in a confocal microscope, and the image is subsequently stitched together from the pixels. The trick is that in addition to the scanning laser (to excite the fluorescent dye), a second laser is used, which has the shape of a "donut" (ring with a hole in the center) and is focused on the same spot. The "donut" with the fluorescence wavelength now ensures that the fluorophores in the sample are "excited" (returned to their ground state) and can no longer fluoresce. What remains are the fluorophores in the center of the "donut" ring, whose fluorescence intensity is measured and used for imaging.
In classical epi-fluorescence microscopy, the non-coherent excitation light is reflected onto the sample via the beam splitter and the fluorescence image is transmitted through the beam splitter. The resulting deviations from the beam splitter can usually be neglected, since the spot size and depth of excitation are not critical and the sample is excited over a wide area. The influence of the transmitted wavefront error on the fluorescence image is usually also marginal and not relevant.
These cookies are used to offer you further functions that make the use of the website more comfortable (e.g. a product wish or memo list).
Wavefront defects arise, on the one hand, from the stresses due to coating from the many layers of different material and thickness and, on the other hand, from coating irregularities or "passed on" substrate surface defects. The first defect creates a curvature like a kind of parabolic mirror ("salad bowl") and the other defect a kind of lunar surface.
Toothpaste tube- white with fluoride: Our white tooth cream in the aluminum tube is the power package for clean teeth. Simple, natural and good. Our white toothpaste cleans the teeth thoroughly. Sage boost an extra portion of vitamin A and antioxidants into the mouth. For a fresh and pleasant mouthfeel.
Due to the (reasonably symmetrical) curvature of the beam splitter, a focus is created so that a collimated beam has a focal point. The distance to the focal point corresponds to half the radius of curvature of the surface. (Approximation: spherical mirror, rays close to the axis).
RMS or rms means "Root Mean Square". In a simple form (only "positive" deviations, as in a "salad bowl"), the RMS value is approximately 70% of the "PV" value. For an irregular deviation, like a "potato chip," this value drops to about 30%. If the surface defect is more like a lunar surface, consider the many different irregularities separately, square them each, add them together, divide by the number of irregularities, and finally take the square root of them (the alternative representation expresses it a bit more elegantly, t equals x here):
With more and more high-resolution microscopy methods such as TIRF, STED, etc., the reduction of the wavefront error in the system plays a decisive role. Therefore, when selecting an optical filter or beam splitter, the flatness of the optical component should be specified and selected according to the application so as not to affect the performance of the system.
Optical beam splitters are optical components that divide a beam of light into two or more separate beams. They are often made of specially coated glass or other transparent materials. Beam splitters are used in various applications, such as laser technology, microscopy, and optical metrology, to direct light or filter specific wavelengths. There are different types, such as polarization-dependent and polarization-independent beam splitters, depending on the requirements for light polarization and angle of incidence. » Learn more about beamsplitters
Mathematically, the curvature (κ) indicates the local deviation from a straight line and is inversely proportional to the radius (R):
Yes, you can recycle the aluminum tubes. Aluminum is a very valuable raw material that can be recycled 100%.We recommend that you throw the tubes into the recycling container after use.
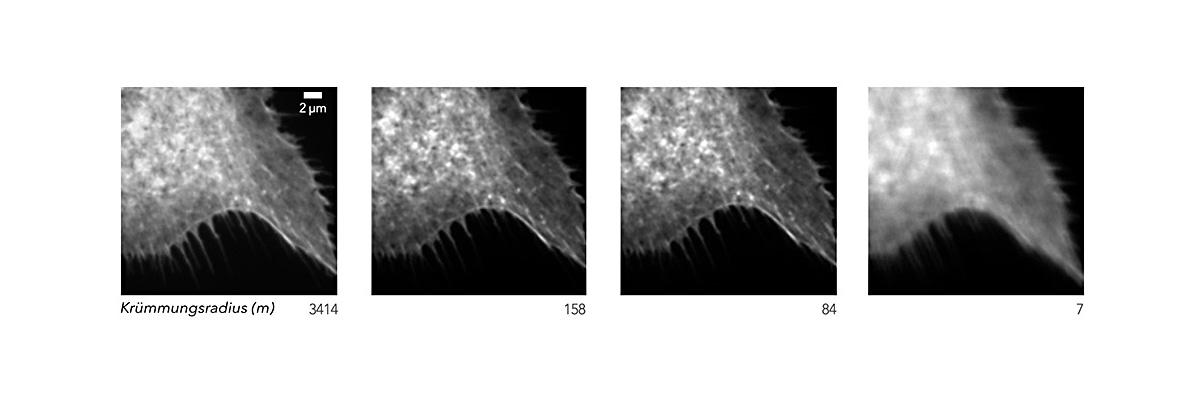
Conclusion: Since the shape of the excitation point and the "donut" are elementary, it is fundamentally important to use planar beam splitters.
Microscopes and optical setups in general consist of various optical components, and the performance of the system (resolution, contrast, etc.) can be negatively affected due to wavefront errors.
In practice, 5 or 6 mm thick beam splitters are used in STED microscopy. It is noticeable that the possible free aperture or maximum beam diameter for non-imaging beams is smaller than for imaging beams. This appears counterintuitive at first, since imaging beams additionally contain the location information of the sample, in contrast to non-imaging beams. The reason for this can be found in the different limiting criteria. The non-imaging beams are based on the Rayleigh length criterion (see below) and the imaging beams are based on the Airy Disk / Rayleigh criterion.
To show the relationships, we consider the stress generated by the coating that causes the curvature (δ in µm), the diameter (free aperture) of the surface under consideration (D in mm), the coating thickness (f in µm, where the difference is considered for double-sided coatings), the substrate thickness (s in mm), and a dimensionless constant C (depending on the glass type, coating material, etc.):
Flip toptoothpaste cap
With special coating equipment it is possible to reduce the surface tensions as far as possible and to produce very flat beam splitters with a standard thickness of 1 mm. However, with the framework condition of flatness, not any number of layers can be applied, so the spectral edge between reflection and transmission cannot be arbitrarily steep. This means that the beam splitters are not suitable for all applications, since in some cases the useful signal is spectrally very close to the excitation (e.g. Raman).
The Airy Disk / Rayleigh criterion states that the magnification of the beam diameter due to the reflected wavefront error must not be greater than 1.5 times the Airy Disk diameter. For a concave/convex curved beam splitter, the maximum imaging beam diameter depends on the wavefront error (PV/inch) or flatness. This results in the following diagram, from which the maximum wavefront error (PV/inch, and from this the flatness) can also be derived depending on the own beam diameter.
Toothpaste CapFunny
In the case of reflected wavefront error (RWE), the wavefront reflected from a surface and the resulting error are considered. The curvature (convex, concave) and the unevenness of the beam splitter primarily have a negative effect on the reflected wavefront. The beam reflected by 180° gets a deviation twice as large as the distance of the surface error (flatness) of the beam splitter due to the double path. For reflections not equal to 180°, the reflected wavefront error is multiplied by the cosine of the angle of incidence to the normal of the surface:
The use of aluminum tubes for toothpaste is sustainable because aluminum can be recycled infinitely.We use a high proportion of recycled aluminum for the production of our tubes.
Toothpaste tube- black with fluoride: Black and strong - the power package for bright white teeth! Activated carbon solves discoloration in no time - and that is very natural. For a fresh breath and healthy teeth that shine in every situation.
The advantage of the RMS value is: it tries to capture the unevenness as a whole. The disadvantage is: it is not so easy to determine and less descriptive or understandable.
This shows that the flatness is quadratically related to the substrate thickness and the area under consideration – and linearly related to the coating thickness. This means that it is first necessary to check whether the required flatness can be achieved by a smaller aperture or a thicker substrate. If not, the coating thickness can be effectively reduced by spreading the coating over the front and back surfaces, although this will drive up the cost due to the longer coating time. Alternatively, the coating thickness can be reduced by a simpler design – but at the cost of spectral performance (steepness of edges, blocking, etc.).
Now discover our new generation of toothpaste tube in a set for naturally healthy teeth and fresh breath! There is something for every taste in our toothpastes in the tube. From sweet to fruity to mint fresh. For dental care, as individual as you. We rely on natural sodium fluoride to strengthen the enamel and counteract the dismantling. Find your new favorite variety for naturally healthy teeth and fresh breath!
Toothpaste capthat minimizes waste and mess
Toothpaste capreplacement
Another common way to compensate for stresses is to split the coating in two and coat the beamsplitter front and back. This creates a counter stress and the beam splitter is flatter in total than if the whole coating was on one side. However, one has to be careful here, because due to the second coating on the back, spectral components are reflected on the back and can lead to a "ghost effect". In reality, this results in more or less intense double images. If it is used selectively and the two spectra from the front and back side are known, this technique can be used without any disadvantages.
If you would like to benefit from our many years of experience in this regard, we would be happy to take care of the filter assembly for you:
Discover more than just toothpaste - Our environmentally friendly aluminum packaging not only protects your mouth, but also the earth by infinite recycling.
Producing and measuring super-flat beam splitters is one thing – mounting them in such a way that the flatness is still guaranteed at the end is another. If unfavorable mounting stresses act on the beam splitter when it is installed in a filter cube due to bonding or clamping, this can deform the beam splitter and, in the worst case, make it unsuitable for the application. This is especially true for high-resolution microscopy techniques such as TIRF, STORM, PALM, GDSIM, STED, MINFLUX, etc.
Toothpaste tube - Coco Mania with fluoride: Our Coco Mania toothed cream in the aluminum tube is the power package to clean your teeth. Our tropical toothpaste with the miracle cure Cocos oil. It has strong antibacterial properties that the ability to slow caries is gently to the enamel and relieves inflammation. So a real miracle cure for your oral hygiene.
Toothpaste tube - Spearmint with fluoride: The powerful formula Our Spearmint toothpaste in the aluminum tube cleans your tooth and leaves an incomparably fresh breath. Spearmint is our freshest toothpaste. The natural mint has an invigorating effect and ensures the special kick. For an incomparably fresh breath.
Toothpaste capDispenser
Toothpaste aluminum - Black with fluoride: aqua (water), hydrated silica, glycerin, hydrogenated star, Lauryl glucoside, aloe barbadensis leeaf extract, erythritol, aroma (fragrance), xanthan gum, sodium fluoride, citric acid, salvia officinalis) Leaf Water, Mentha Arvensis (Peppermint) Leaf Oil, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Limonene, Benzyl Alcohol, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate. Toothpaste aluminum - cinnamon orange with fluoride: aqua (water), hydrated silica, glycerin, hydrogenated star hydrolyzate, aloe barbadensis Leaf extract, erythritol, lauryl glucoside, aroma (fragrance), alcohol, xanthan fluoride, citric acid, ocimum basil around (Basil) Leaf Extract, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Limonene, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate. ZAHNPASTA ALU - COCO MANIA MIT FLUORID: Aqua (Water), Hydrated Silica, Glycerin, Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, Aloe Barbadensis Leaf Extract, Erythritol, Lauryl Glucoside, Aroma (Fragrance), Alcohol, Xanthan Gum, Sodium Fluoride, Citric Acid, Cocos Nucifera (Coconut) Oil, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate. ZAHNPASTA ALU - SPEARMINT MIT FLUORID: Aqua (Water), Hydrated Silica, Glycerin, Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, Aloe Barbadensis Leaf Extract, Erythritol, Lauryl Glucoside, Aroma (Fragrance), Xanthan Gum, Citric Acid, Sodium Fluoride, Alcohol, Mentha Arvensis ( Peppermint) Leaf Oil, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Limonene, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate. Toothpaste aluminum - White with fluoride: aqua (water), hydrated silica, glycerin, hydrogenated star, lauryl glucoside, aloe barbadensis leeaf extract, erythritol, aroma (fragrance), xanthan gum, sodium fluoride, citric acid, salvia officinalis) Leaf Water, Mentha Arvensis (Peppermint) Leaf Oil, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Limonene, Benzyl Alcohol, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate. Toothpaste aluminum - Wild Berry with fluoride: aqua (water), hydrated silica, glycerin, hydrogenated star hydrolyzates, aloe barbadensis Leaf extract, erythritol, lauryl glucoside, aroma (fragrance), xanthan gum, alcohol, sodium fluoride, citric acid, ananas sativtus (Pineapple) Fruit Extract, Stevia Rebaudiana Extract, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate.
The table gives an orientation which flatness is required for a beam splitter depending on the application. Experience has shown that the use of beam splitters with a smaller PV or radius of curvature specification is advisable for STED microscopy and general confocal microscopy.
The next obvious step to reduce wavefront error is to use thicker substrates (as in making mirrors), e.g., 3 mm or even 5 mm thick substrates. This helps – but has the catch that the beamsplitters need special holders and have a larger offset of the transmitted beam that must be taken into account.
Toothpaste tube - cinnamon orange with fluoride: Fruity orange with the mild aromas of cinnamon. This toothpaste is the favorite for the whole family. Thanks to the power of the extracts from the leaves of the basil, your mouth is protected against germs and bacteria. This prevents and keeps your breath fresh.
These cookies are used to display advertisements on the website in a targeted and individualized manner across multiple page views and browser sessions.
The resolving power can also be colloquially compared to image sharpness. The following diagram shows the influence of the flatness of a beam splitter (radius of curvature m) on the image sharpness:
To illustrate the effect of a non-planar beam splitter, we consider the reflection of a laser from a curved (A) or flat (B) beam splitter and the image produced on the wall or ceiling.
A tube toothpaste should last about 4-6 weeks depending on the frequency of use.We recommend that you properly close the tube after use to ensure a long shelf life.
Toothpaste tube - Wild Berry with fluoride: Fruity with the mild flavors of wild berries. This toothpaste protects reliably and convinces with its unique taste. Natural pineapple extract not only gently cleans the teeth, but also loosens the dental pad. During this, the extract from the aloe vera gently maintains the gums.
If one now plots the beam diameter against the maximum wavefront error (or the minimum flatness, which is proportional to it), the following diagram results:
Yes, aluminum is safe for use in toothpaste tubes. It is an extremely durable and durable material that is also used for many other packaging such as beverage cans and food containers.
Yes, our toothpaste is also suitable for sensitive teeth.We use gentle ingredients that gently clean and protect your teeth.
In TIRF (Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence) microscopy, the evanescent field of a totally reflected excitation beam (usually laser) is used to excite the sample in a very limited (exponentially decreasing) region behind the boundary layer (100–200 nm). This strongly limits the area that can fluoresce and thus obtains selective image information. Deviations from the ideal beam path can lead to the excitation light no longer being totally reflected, but also penetrating the sample. Since the evanescent field decreases exponentially and the total reflection depends on the angle, the method is very error-prone (see picture: laser on the wall). For more information, see our article about » TIRF microscopy.
Imaging beams contain the information of non-imaging beams, plus the location information (x/y axis) of each point (image). The decisive factor here is the point at which two points can be perceived as separate (resolving power). The Rayleigh criterion considers two diffraction discs/images (airy discs) with the same color and brightness and their diffraction rings. The resolving power then corresponds to the distance of the two diffraction images of 0th order, which just do not overlap any more (Source: University of Vienna, "Light microscopy online")
The RMS value is more suitable if the surface defect is composed of different or very punctual unevennesses and is not uniform. For the roughness of a surface, the RMS is therefore more suitable. To describe the "deformation" of a non-flat (but possibly smooth) surface, the PV value or radius of curvature is more suitable.
Unfortunately, the specification of the flatness of beam splitters is not uniform, which is why you have to look carefully when comparing the flatness of different manufacturers. In general, however, the deviation or error is specified in units of a reference wavelength (632.8 nm in the ANSI standard and 546.07 nm in the ISO standard) over a defined area (usually a circular area with diameter 1 inch = 25.4 mm).
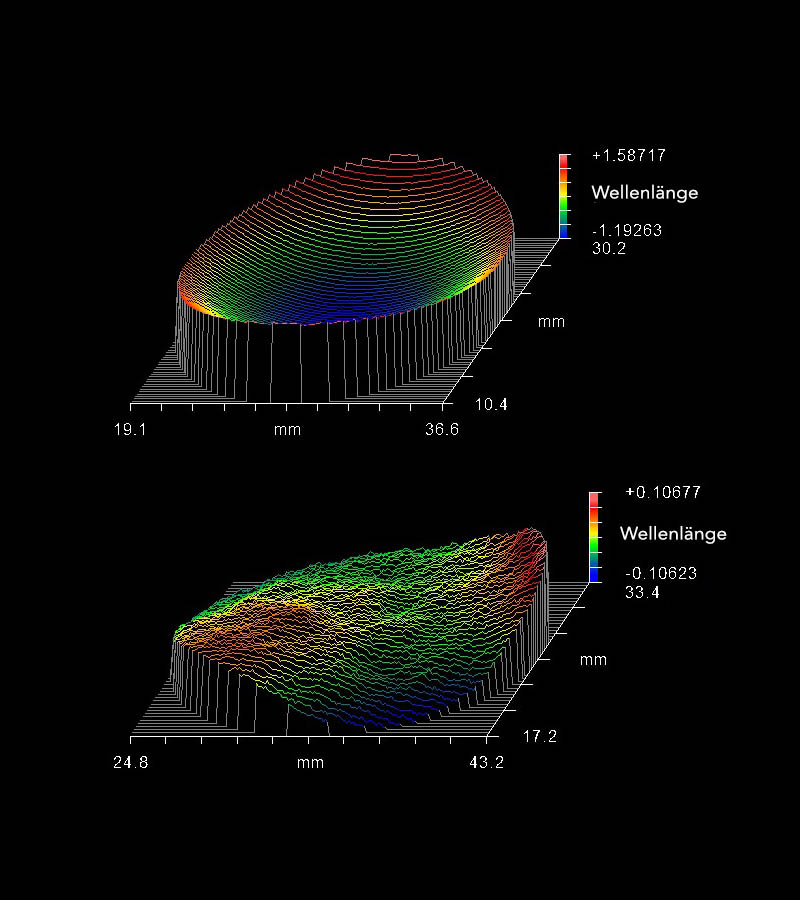
In peak-to-valley (PV, mountain to valley), the specification of unevenness refers to the difference of the highest to the lowest point within a defined area (1 inch or the free aperture). Consideration must also be given to what exactly is being specified: the unevenness of the object or the reflected/transmitted wavefront. The reflected wavefront error is up to twice the unevenness of the reflecting surface and depends on the angle of incidence. The transmitted wavefront error is made up of the front and back - where it can be smaller than the sum of the individual errors of a surface.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500