Electric pallet jack - palet jack
Winnipeg is located in Treaty One Territory, the home and traditional lands of the Anishinaabe (Ojibwe), Ininew (Cree), and Dakota peoples, and in the National Homeland of the Red River Métis. Our drinking water comes from Shoal Lake 40 First Nation, in Treaty Three Territory.
As an atom-transferring substance – An oxidizing agent is a substance that transfers at least one electronegative atom to a chemical species in a chemical reaction. The transferred atom is typically an oxygen atom. Several combustion reactions and organic redox reactions involve the transfer of an electronegative atom between two reactants.
Types ofoxidising
V300 body camera. Designed to go further with a removable battery and connections to the Motorola Solutions technology ecosystem, the V300 is everything you ...
Strongoxidisingagent meaning
An oxidizing agent (often referred to as an oxidizer or an oxidant) is a chemical species that tends to oxidize other substances, i.e. cause an increase in the oxidation state of the substance by making it lose electrons. Common examples of oxidizing agents include halogens (such as chlorine and fluorine), oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
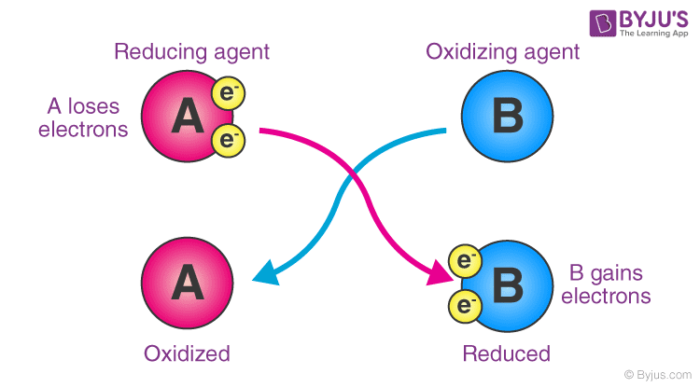
An oxidizing agent is a substance that causes oxidation by accepting electrons and thus becoming reduced. A reducing agent is a substance that causes reduction by losing electrons, causing it to be oxidized.
Searching for the ultimate sports bar? Twin Peaks never settles on made-from-scratch food, 29° draft beer & all the best sports. Find a location near you ...
In the example illustrated above, the Fe2O3 molecule acts as an oxidizer by transferring an electronegative oxygen atom to the carbon monoxide molecule.
Oxidizing agents normally exist in their highest possible oxidation states and, therefore, have a strong tendency to gain electrons and undergo reduction. Ions, Atoms, and molecules having a strong affinity towards electrons are considered to be good oxidizers. The stronger the electron affinity, the greater the oxidizing power.
As an electron acceptor – They are chemical substances whose atoms remove at least one electron from another atom in a chemical reaction. As per this definition, oxidizing agents are the reactants that undergo reduction in redox reactions. An illustration detailing the electron-accepting properties of oxidizing agents is provided below.
To learn more about oxidizing agents and the part they play in oxidation-reduction reactions, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
SPILL STATION ; Code: TSSIS40OF. $152.81 · 40 Litre Oil Fuel Spill Kit - AusSpill Quality Compliant ; Code: TSSIS40GP. $172.22 · 40 Litre General Purpose ...
Oxidisingprocess
Oxygen is the element corresponding to the atomic number 8 and is denoted by the symbol ‘O’. It belongs to the chalcogen group of the periodic table and is a highly reactive non- metal with good oxidizing properties. In general, metals tend to form metal oxides by reacting with atmospheric oxygen, due to the strong oxidizing power of oxygen. Oxygen is observed to be a part of a majority of combustion reactions.
The group 17 elements of the periodic table are collectively referred to as Halogens. They are said to have a strong ability to gain electrons, attributed to their high electronegativities when compared to elements from other groups. This implies that they have the ability to easily attract electrons towards their respective nuclei. Examples of the halogens that are good oxidizing agents include iodine, bromine, chlorine, and fluorine. Fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent due to its highest electronegativity, as discussed earlier.
Information collected will be used to improve our website. Do not use this form to submit a request for service or information because it will not be forwarded to departments for response. To submit a request for service or information, contact 311.
This document provides information on understanding oil spills in freshwater environments.
Oxidisingin chemistry
Many organisms make use of electron acceptors, or oxidizers, to collect energy from the redox reactions such as in the process of hydrolysis of glucose.
2023119 — In 1990, Rick and Tom Smith bought their mother a gun for her birthday, but they began to wonder if there was a better alternative than a deadly ...
All traffic signs (which include traffic signals and road markings) placed on a highway or on a road to which the public has access (right of passage in ...
This is called drive stun or dry TASERing, and is intended to cause pain without incapacitating the target.6. Although TASERs are acknowledged to be a safer ...
What isoxidisingagent
Hydrogen peroxide is the chemical compound having formula H2O2. It appears to the human eye as a colourless liquid which has a greater viscosity than water. Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest compound having a peroxide functional group with an oxygen-oxygen single bond. It finds its uses as a weak oxidizing agent, disinfectant, and bleaching agent.
Here, substance ‘A’ undergoes oxidation, resulting in an increase in its oxidation number. On the other hand, the oxidation state of substance ‘B’ becomes smaller (since it gains electrons by undergoing reduction).
Oxidisingsubstance symbol
Oxidisingexamples
Some compounds that exhibit large oxidation states can also be considered good oxidizing agents. Ionic examples include the permanganate ion, the chromate ion, and the dichromate ion. Acidic examples of good oxidizers include nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulphuric acid. The electronegativity of the molecules increases with the increase in the oxidation states of the atoms, increasing their ability to oxidize other substances.
By accepting electrons from other substances, oxidizing agents cause their oxidation states to become more positive. Oxidizing agents are reduced as well.
Elemental fluorine is said to be the strongest elemental oxidizing agent. This is perhaps due to the fact that fluorine is the most electronegative element in the modern periodic table, and therefore exerts the strongest attractive force on electrons amongst all the elements. In fact, the oxidizing power of diatomic fluorine (F2) is strong enough to cause metals such as asbestos and quartz (and even molecules, such as water) to burst into flames when exposed to it.
Both items consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion or cup at each end to usually cover both ears ...
An oxidizing agent is a compound or element that participates in a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction and accepts electrons from a different species. An oxidant is a chemical compound that easily transfers oxygen or another substance atoms in order to gain an electron.
This collection of your personal information is authorized by section 36(1)(b) of The Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy Act. Your information will be used to respond to you and to assure service quality. It is protected by the Act’s privacy provisions and will not be used or disclosed for any other purpose, except as authorized by law. Contact the Corporate Access and Privacy Officer by mail (City Clerk’s Department, 510 Main Street, Winnipeg MB, R3B 1B9) or by telephone (311), if you have questions about the collection or use or your personal information.
Oxidisingchemicals
Retail loss prevention includes operating environment and to deliver a delicate balance between maximizing sales and minimising loss.
The standard electrode potential of a half-reaction in a redox process provides insight into the oxidizing power of the chemical substance. An illustration ranking some oxidizers in terms of their oxidizing powers is provided below.
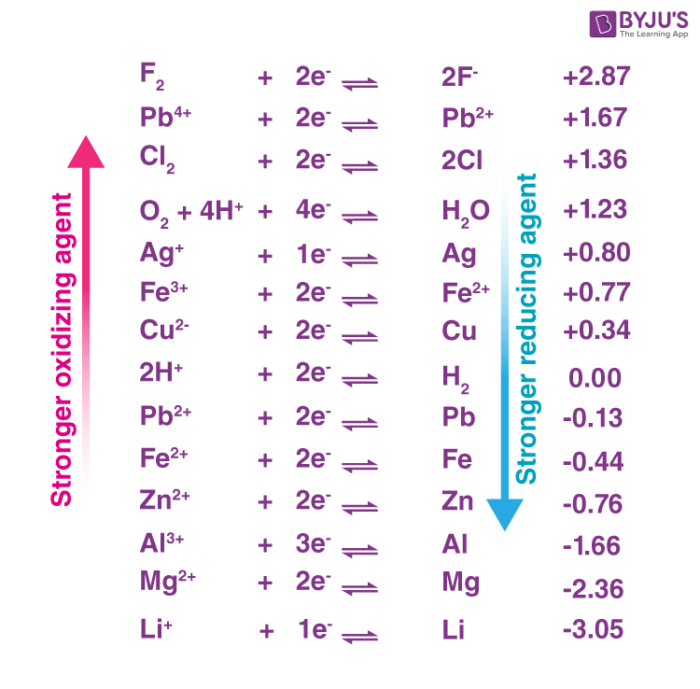
Many other oxidizing agents are commonly used industrially as well as in the day-to-day lives of humans. Examples include household bleach (NaClO), Potassium Nitrate (KNO3), and Sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
B-401 plastic signs from Brady® are ideal for use in light duty industrial, utility, commercial and institutional environments. Part: 103852.
A few other examples of elemental oxidizing agents include diatomic oxygen (O2), diatomic chlorine (Cl2), and ozone (O3). These oxidizers are the elemental forms of the second and the third most electronegative elements (oxygen and chlorine respectively), making them good electron acceptors.
When it comes to electron transfers, an oxidizing agent gains electrons while oxidation is the process of losing electrons. Reduction, on the other hand, means gaining electrons. As a result, the oxidizing agent gains electrons from the species being oxidized, implying that it undergoes reduction (as it gains electrons).




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500