Yaw Definition & Meaning - define yaw
Pinhole cameras and camera obscuras use a fixed aperture opening. However, most lenses we encounter today create this opening with an adjustable iris diaphragm mechanism. Similar to the iris in the human eye, the iris in a camera lens expands and contracts to control the amount of light that can pass through. This affects both the brightness of the image and its depth of field.
The light vs. driving current (L-I) curves measured for quantum and interband cascade Lasers (QCLs and ICLs) include a rollover region, which is enclosed by the red box in Figure 1.
For example, an f-number of f/2 tells us that the aperture is equal to our focal length divided by 2. If we are using a 50 mm lens at f/2, the iris diaphragm will open the aperture to a diameter of 50 mm/2, or 25 mm. From this, we can calculate the area of the aperture opening: 490.9 mm^2.
This is how a camera obscura, the precursor to our modern camera, can project a scene from outside onto the wall of a dark room. Likewise, the aperture of a pinhole camera is simply a tiny hole in the camera body, often literally punched with a pin in DIY camera projects.
Quantum Cascadelaser price
The back face of the C-mount package is machined flat to make proper thermal contact with a heat sink. Ideally, the heat sink will be actively regulated to ensure proper heat conduction. A Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) is well suited for this task and can easily be incorporated into any standard PID controller.
Of course, you can shoot great video without knowing anything about the iris diaphragm or its function. However, this knowledge does give you an appreciation for the mechanical feats and optical phenomena that make image capture possible. After all, we have the iris diaphragm to thank for our adjustable apertures and the creative control these mechanisms offer.
24″ X 50″ DIAMOND PANE WINDOW 1/1 — Product No. 3774 — Quantity:3 — Exterior Measurement: .640 X 1.240 — Fits Within: .550 X 1.150 — Additional Notes: ...
202439 — Base: The base provides stability to the microscope and also houses the illuminators. Arm: Connecting the base to the head and the eyepiece tube ...
The size of the aperture created by the iris diaphragm is measured in f-stops. Each full stop down reduces the amount of light coming through the aperture by half. The larger the f-number, the smaller the opening and the less light can enter the camera. This is because the f-number is actually a fraction representing the aperture’s diameter.
The IF3800CM2 Interband Cascade Laser used for this measurement emitted CW laser light with a center wavelength of 3.781 µm. Our LDMC20 temperature-stabilized mount held the laser's temperature at 25 °C. The output beam was collimated by a C037TME-E lens located immediately downstream of the laser face. This lens was selected because of its large NA of 0.85 (which helped maximize collection of the emitted light) and because of its AR coating (Ravg < 0.6% per surface from 3 µm to 5 µm). We measured 10 mW of output power after the lens.
Quantum cascadelaser applications
Laser OperationThese lasers operate by forcing electrons down a controlled series of energy steps, which are created by the laser's semiconductor layer structure and an applied bias voltage. The driving current supplies the electrons.
As shown by the graph above and to the right, we observed significant astigmatism in the collimated beam: the beam waist of the parallel direction occurred around z = 300 mm, while the beam waist of the perpendicular direction occurred around z = 600 mm. This astigmatism corresponds closely to what is expected for this laser, given that the IF3800CM2 laser is specified with a parallel FWHM beam divergence of 40° and a perpendicular FWHM beam divergence of 60°.
Laser Mount CompatibilityThorlabs' LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount ships with current and TEC cables for the LDC4005, ITC4001, ITC4002QCL, ITC4005, and ITC4005QCL controllers. To use the LDMC20 with our other controllers, custom cables will be required. If designing your own mounting solution, note that due to these lasers' heat loads, we recommend that they be secured in a thermally conductive housing to prevent heat buildup. Heat loads for Fabry-Perot QCLs can be up to 18 W.
Most lenses use between five and eleven blades in their iris construction. However, you’ll sometimes find vintage and higher-end lenses with higher blade counts. More blades mean that the aperture opening will be smoother and closer to a perfect circle. Fewer blades, on the other hand, produce a more angular polygonal shape. Thus, iris diaphragm mechanisms that use more blades are often considered more desirable since they offer a rounder, smoother bokeh shape.
Aperture refers to the opening through which light can enter the chamber of the camera body. The shutter controls the duration light is allowed to pass through that opening. When exposure is set properly, the shutter will briefly open to let the proper amount of light shine through the aperture to the image sensor. Then, usually in a fraction of a second later, the shutter will close before the image becomes overexposed.
When you adjust the aperture in your camera’s exposure settings, you are changing the size of the opening created by the iris diaphragm. The aperture ring on a lens mechanically adjusts the size of this opening. Turning it moves a lever that spins the iris diaphragm ring. This causes the blades of the iris to expand or contract, which opens or closes the aperture to control the amount of light entering the camera. If the lens doesn’t have an aperture ring, the camera moves the iris diaphragm ring internally according to your aperture settings.
Jan 1, 2024 — Euclid Vision Corporation (Euclid) provides specialty lenses for proactive myopia management, irregular corneas, and dry eye disease. The ...
Videomaker is always looking for talented, qualified writers. If you have a great idea you’d like to share with our readers, send it to editor@videomaker.com.
Thorlabs' Fabry-Perot Quantum Cascade Lasers (QCLs) exhibit broadband emission in a range spanning roughly 50 cm-1. Each QCL's specified output power is the sum over the full spectral bandwidth. Since these lasers have broadband emission, they are well suited for medical imaging, illumination, and microscopy applications. Thorlabs also manufactures Distributed Feedback QCLs, which emit at a well defined center wavelength and are tunable over a narrow frequency range.
Data AnalysisPresented to the right are the second-order moment (D4σ) beam widths for the parallel and perpendicular directions as a function of distance from the laser face (denoted as z). Along the parallel direction, we obtained a minimum beam width of 1.5 mm, while along the perpendicular direction, we obtained a minimum beam width of 1.3 mm. The spatial profiles we observed at the two minimum beam width positions, as obtained by the pyroelectric camera, are shown below.
The 0.85 NA of the collimating lens we used is the largest NA of any lens for this wavelength range that is offered in our catalog. Despite this large NA, we observed lobes in the far field (shown by the figure below) that are consistent with clipping of the laser-emitted light. An ideal measurement would not contain these artifacts.
This information allows the appropriate collimating lens to be selected. Thorlabs offers a large selection of black diamond aspheric lenses for the mid-IR spectral range. Since this laser emits at 3.80 µm, the best AR coating is our -E coating, which provides Ravg < 0.6% per surface from 3 to 5 µm. The lenses with focal lengths closest to the calculated value of 3.46 mm are our 390036-E (unmounted) or C036TME-E (mounted) Molded Aspheric Lenses, which have f = 4.00 mm. Plugging this focal length back into the equation shown above gives a final beam diameter of 4.62 mm along the major axis.
More details are available on the Custom & OEM Lasers tab. To inquire about pricing and availability, please contact us. A semiconductor specialist will contact you within 24 hours or the next business day.
Because quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) and interband cascade lasers (ICLs) have intrinsically large divergence angles, it is necessary to install collimating optics in front of the laser face, as shown in the Collimation tab. We are frequently asked what beam quality can be reasonably expected once the beam has been collimated. This tab presents an M2 measurement we performed using our previous generation 3.80 µm Interband Cascade Laser.
Avoid StaticSince these lasers are sensitive to electrostatic shock, they should always be handled using standard static avoidance practices.
The apparatus we used to determine M2 is shown schematically in the figure above. In order to ensure that our results were rigorous, all data acquisition and analysis were consistent with the ISO11146 standard.
A fan may serve to move the heat away from the TEC and prevent thermal runaway. However, the fan should not blow air on or at the laser itself. Water cooling methods may also be employed for temperature regulation. Do not use thermal grease with this package, as it can creep, eventually contaminating the laser facet. Pyrolytic graphite is an acceptable alternatives to thermal grease for these packages. Solder can also be used to thermally regulate two-tab C-mount lasers, although controlling the thermal resistance at the interface is important for best results.
Now, if we want to decrease the amount of light coming in by one stop, we would need to halve the area of our aperture. That makes the opening 245.45 mm^2. Retracing our steps, we can then find the diameter of our new aperture: 17.7 mm. To find the new f-number, we take our focal length, 50 mm, and divide by the new diameter. This gives us 2.8, the next number on the standard exposure scale.
Since NALens > NALaser, the 390036-E or C036TME-E lenses will give acceptable beam quality. However, by using the FWHM beam diameter, we have not accounted for a significant fraction of the beam power. A better practice is to use the 1/e2 beam diameter. For a Gaussian beam profile, the 1/e2 beam diameter is approximately equal to 1.7X the FWHM diameter. The 1/e2 beam diameter is therefore a more conservative estimate of the beam size, containing more of the laser's intensity. Using this value significantly reduces far-field diffraction (since less of the incident light is clipped) and increases the power delivered after the lens.A good rule of thumb is to pick a lens with an NA of twice the NA of the laser diode. For example, either the 390037-E or the C037TME-E could be used as these lenses each have an NA of 0.85, which a little less than twice that of our IF3800CM2 laser (NA 0.5). Compared to the first set of lenses we identified, these have a shorter focal length of 1.873 mm, resulting in a smaller final beam diameter of 2.16 mm.
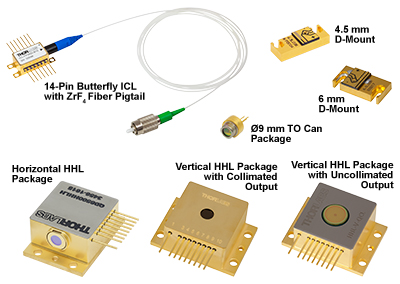
PackagesEach quantum cascade laser is mounted on a two-tab C-mount that provides high thermal conductivity and can be secured using a 2-56 or M2 screw with the counterbored Ø2.4 mm (Ø0.09") through hole. As measured from the bottom of the C-mount, the emission height of the QCLs is 7.15 mm or 7.39 mm, depending on the chosen QCL; the outer dimensions of the C-mounts are the same. Click on a laser's blue info icon () and view the Drawing tab to find the laser's emission height. All lasers sold on this page are electrically isolated from their C-mounts. Please see the Handling tab for more tips and information for handling these laser packages.
As the temperature of the lasing region increases, more electrons are scattered, and a smaller fraction of them produce light instead of heat. Rising temperatures can also result in changes to the laser's energy levels that make it harder for electrons to emit photons. These processes work together to increase the temperature of the lasing region and to decrease the efficiency with which the laser converts current to laser light.
BBB accredited since 3/27/2018. Optical Imaging in Barrington, NJ. See BBB rating, reviews, complaints, get a quote & more.
The typical operating voltages of our QCLs are 7 - 16 V. These lasers do not have built-in monitor photodiodes and therefore cannot be operated in constant power mode.
Carefully Make Electrical ConnectionsWhen making electrical connections, care must be taken. The flux fumes created by soldering can cause laser damage, so care must be taken to avoid this. Solder can be avoided entirely for two-tab C-mount lasers by using the LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount. If soldering to the tabs, solder with the C-mount already attached to a heat sink to avoid unnecessary heating of the laser chip.
Tunablequantum cascadelaser
To make the size of the opening adjustable, the iris in a camera lens uses a series of thin blades arranged in a fan formation. These blades are held in place by the diaphragm. When the diaphragm ring spins, these blades move, changing the size of the aperture and letting in more or less light.
The maximum drive current and the maximum optical output power of QCLs and ICLs depend on the operating conditions, since these determine the heat load of the lasing region.
AR coatings improve the efficiency of optical instruments, enhance contrast in imaging devices, and reduces scattered light that can interfere with the optical ...
Aperture size also affects the depth of field of your image. In other words, it changes how much of your image is in focus. A wider aperture gives you a shallower depth of field, meaning the plane of focus will be thinner and less of your image will be in focus. The opposite is true for a narrower aperture.
If designing your own mounting solution, note that due to these lasers' heat loads, we recommend that they be mounted in a thermally conductive housing to prevent heat buildup. Heat loads for Fabry-Perot QCLs can be up to 18 W (see the Handling tab for additional information).
Proper precautions must be taken when handling and using two-tab C-mount lasers. Otherwise, permanent damage to the device will occur. Members of our Tech Support staff are available to discuss possible operation issues.
An electron must give up some of its energy to drop down to a lower energy level. When an electron descends one of the laser's energy steps, the electron loses energy in the form of a photon. But, the electron can also lose energy by giving it to the semiconductor material as heat, instead of emitting a photon.
Interbandcascadelaser
At the same time, we do need to let some light into the camera. Otherwise, we can’t capture any image at all. Thus, we need a way to control how and when light is allowed into this enclosed space. We do this using the shutter and the aperture.
High-Power Fabry-Perot QCLsFor Fabry-Perot lasers, we can reach multi-watt output power on certain custom orders. The available power depends upon several factors, including the wavelength and the desired package.
Aug 7, 2024 — We repair and replace all parts of the IPL Hand Piece, including: ... TJS can provide Preventive Maintenance contracts, on-site emergency service, ...
The specifications for the IF3800CM2 indicate that the typical parallel and perpendicular FWHM divergences are 40° and 60°, respectively. Therefore, as the light propagates, an elliptical beam will result. To collect as much light as possible during the collimation process, consider the larger of these two divergence angles in your calculations (in this case, 60°).
A pyroelectric camera (Spiricon Pyrocam IV) with 80 µm square pixels was scanned along the beam propagation direction, and the beam width was measured along the parallel and perpendicular directions using the second-order moment (D4σ) definition. Hyperbolas were fit to the beam width to extract M2 for each direction. The camera's internal chopper was triggered at 50 Hz since the pyroelectric effect is sensitive to changes in temperature rather than absolute temperature differences. A ZnSe window was present in front of the detector array to help minimize visible light contributions to the signal.
Thermally Regulate the LaserTemperature regulation is required to operate the laser for any amount of time. The temperature regulation apparatus should be rated to dissipate the maximum heat load that can be drawn by the laser. For our quantum cascade lasers, it can be up to 18 W. The LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount, which is compatible with our two-tab C-mount lasers, is rated for >20 W of heat dissipation.
Since the output of our MIR lasers is highly divergent, collimating optics are necessary. Aspheric lenses, which are corrected for spherical aberration, are commonly chosen when the desired beam diameter is between 1 - 5 mm. The simple example below illustrates the key specifications to consider when choosing the correct lens for a given application.
The rollover region includes the peak output power of the laser, which corresponds to a driving current of just under 500 mA in this example. Applying higher drive currents risks damaging the laser.
Quantum cascadelaser spectroscopy
Laser welding requires a small beam spot capable of deep penetration, so a high-intensity laser beam with low diffusion is considered high quality. The quality ...
All camera systems — from the most advanced and the most primitive — rely on a few basic components. The most crucial component is the body of the camera. After all, “camera” literally translates to “chamber” in Latin.
A temperature controlled mount is typically necessary to help manage the temperature of the lasing region. But, since the thermal conductivity of the semiconductor material is not high, heat can still build up in the lasing region. As illustrated in Figure 2, the mount temperature affects the peak optical output power but does not prevent rollover.
An anti-reflection coating (AR coating) is a dielectric thin-film coating applied to an optical surface in order to reduce the reflectance (also often called ...
Thorlabs manufactures custom and OEM quantum cascade lasers in high volumes. We maintain chip inventory from 3 µm to 12 µm at our Jessup, Maryland, laser manufacturing facility and can reach multi-watt output on certain custom orders.
Quantum cascadelaser PDF
If you’re familiar with the exposure triangle, you’ve likely already experimented with different aperture settings on your camera. Apertures are important tools in any videographer’s arsenal, but what exactly is the aperture and how does it work? Let’s take a closer look at the mechanism that makes the aperture possible — the iris diaphragm.
Minimize Physical HandlingAs any interaction with the package carries the risk of contamination and damage, any movement of the laser should be planned in advance and carefully carried out. It is important to avoid mechanical shocks. Dropping the laser package from any height can cause the unit to permanently fail.
This chamber conceals a photosensitive surface: a film strip or, in digital cameras, an image sensor. For a camera to produce a legible image, this surface must be protected until it is intentionally exposed. If the camera’s body is not lightproof, we’ll get light leaks or, worse, a completely washed-out frame.
Before shipment, the output spectrum and L-I-V curve are measured for each serial-numbered device by an automated test station. These measurements are available below and are also included on a data sheet with the QCL. Each Fabry-Perot laser has an HR-coated back facet. As a custom option, our Fabry-Perot lasers can be ordered with an AR coating on the front facet; however, the custom item will operate as a gain chip and not as a CW laser. Though these QCLs are specified for CW output, they are compatible with pulsed applications. To order a Fabry-Perot QCL with a tested and specified pulsed optical power or other custom features, please contact Tech Support.
Quantum cascade laserswikipedia
In order to obtain the hyperbola coefficients a, b, and c for the parallel and perpendicular directions, we fit the discrete beam width measurements along each direction to hyperbolas, as shown in the graph to the right. These coefficients were substituted into Equation 2 (taking λ = 3.781 µm) to yield M2.
The aperture range of a lens determines what focus and exposure effects are possible. However, there is another factor to consider when comparing different lenses. That is iris blade count. This may not seem important, but blade count does influence how defocused points of light — also known as bokeh — appear in your image. Depending on the type of shots you hope to capture, bokeh shape may influence which lens you add to your kit.
Use the tables below to select a compatible controller for our MIR lasers. The first table lists the controllers with which a particular MIR laser is compatible, and the second table contains selected information on each controller. Complete information on each controller is available in its full web presentation. We particularly recommend our ITC4002QCL and ITC4005QCL controllers, which have high compliance voltages of 17 V and 20 V, respectively. Together, these drivers support the current and voltage requirements of our entire line of Mid-IR Lasers. To get L-I-V and spectral measurements of a specific, serial-numbered device, click "Choose Item" next to the part number below, then click on the Docs Icon next to the serial number of the device.
A larger opening means more light will be able to move through the lens to the camera’s sensor. This means the image will be brighter, but that is not the only impact aperture size has on your image.
Use a Current Source Specifically Designed for LasersThese lasers should always be used with a high-quality constant current driver specifically designed for use with lasers, such as any current controller listed in the Drivers tab. Lab-grade power supplies will not provide the low current noise required for stable operation, nor will they prevent current spikes that result in immediate and permanent damage.
DFB QCLs at Custom WavelengthsFor distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, we can deliver a wide range of center wavelengths with user-defined wavelength precision. Our semiconductor specialists will take your application requirements into account when discussing the options with you.
Field of view defines the maximum area of a sample that a camera can image, determined by the focal length of the lens and the sensor size. Sensor size is ...
While the shutter is an important way to control exposure value, cameras rely on an aperture to produce any image at all. Since light rays travel in a straight line, a small enough opening will admit only those light rays that traveled directly through it into a darkened chamber.
Mounts, Drivers, and Temperature ControlWe generally recommend the LDMC20 C-Mount Laser Mount and ITC4002QCL or ITC4005QCL Dual Current / Temperature Controller for use with these QCLs. This device combination includes all the necessary components to mount, drive, and thermally regulate a two-tab C-mount laser. Other compatible current and temperature controllers are listed in the Drivers tab.
Quantum cascadelaser working principle
The graphs below and photos to the right illustrate some of our custom capabilities. Please visit our semiconductor manufacturing capabilities presentation to learn more.
Avoid Dust and Other ParticulatesUnlike TO can and butterfly packages, the laser chip of a two-tab C-mount laser is exposed to air; hence, there is no protection for the delicate laser chip. Contamination of the laser facets must be avoided. Do not blow on the laser or expose it to smoke, dust, oils, or adhesive films. The laser facet is particularly sensitive to dust accumulation. During standard operation, dust can burn onto this facet, which will lead to premature degradation of the laser. If operating a two-tab C-mount laser for long periods of time outside a cleanroom, it should be sealed in a container to prevent dust accumulation.
Light that enters the skin is either absorbed or scattered and reflected back out of your hand. When this happens to a laser beam, the scattering is called ...
Operating Limits are Determined by the Heat LoadIdeally, the slope of the L-I curve would be linear above the threshold current, which is around 270 mA in Figure 1. Instead, the slope decreases as the driving current increases, which is due to the effects from the rising temperature of the lasing region. Rollover occurs when the laser is no longer effective in converting additional current to laser light. Instead, the extra driving creates only heat. When the current is high enough, the strong localized heating of the laser region will cause the laser to fail.
Conversely, heat in the lasing region can be absorbed by electrons. This boost in energy can scatter electrons away from the path leading down the laser's energy steps. Later, scattered electrons typically lose energy as heat, instead of as photons.
For this system, we obtained M2 = 1.2 ± 0.08 in the parallel direction and M2 = 1.3 ± 0.2 in the perpendicular direction. While this is just one example, we believe these results to be representative of well-collimated mid-IR lasers manufactured by Thorlabs, as corroborated by supplementary measurements we have performed in-house.
Heat Build UpLasers are not 100% efficient in forcing electrons to surrender their energy in the form of photons. The electrons that lose their energy as heat cause the temperature of the lasing region to increase.
Partner with us to reach an enthusiastic audience of students, enthusiasts and professional videographers and filmmakers. Click here to contact a sales representative and request a media kit.
At our semiconductor manufacturing facility in Jessup, Maryland, we build fully packaged mid-IR lasers and gain chips. Our engineering team performs in-house epitaxial growth, wafer fabrication, and laser packaging. We maintain chip inventory from 3 µm to 12 µm, and our vertically integrated facilities are well equipped to fulfill unique requests.






 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500