Winter Festival of Lights - Niagara Falls Canada - illuminated lights
Multispectralimaging archaeology
Feature Control Frame: To control the flatness of a surface, a feature control frame (FCF) is used to apply the tolerance to the desired surface.
Spectral bands: Multispectral imaging systems use sensors or cameras equipped with filters or detectors that selectively capture light at specific wavelengths or bands. The number and positions of these bands are predetermined based on the requirements of the application.
Multispectralimage example
Data analysis: Multispectral images can be processed to create composite images or to extract specific information based on the different spectral bands. Techniques such as vegetation indices, band ratios, and image classification are commonly used.
Multispectral imagerysoftware
Multispectral imaging is a technique that involves capturing and analyzing images at multiple discrete spectral bands within the electromagnetic spectrum. Unlike hyperspectral imaging, which acquires data across a continuous range of wavelengths, multispectral imaging is characterized by capturing information at several specific, predefined bands. This allows for the extraction of spectral signatures and information from different parts of the spectrum.

To apply a flatness control to a surface, the FCF may point to the surface, or can point to or rest on the extension line that extends from the surface. The FCF is placed in the view where the surface is viewed as a line. The FCF shown below applies a flatness tolerance to the entire surface. This surface must lie between two parallel planes that are spaced 0.2 mm apart.
Multispectralimaging in agriculture
Satellite imaging: Many Earth-observing satellites use multispectral sensors to capture information for scientific, environmental, and military purposes.
Multispectralimaging satellites
Remote sensing: In Earth observation, multispectral imaging is commonly used for mapping land cover, monitoring vegetation health, and studying environmental changes.
Landsat satellites: Landsat satellites, for example, capture imagery in multiple bands, including visible, near-infrared, and thermal-infrared bands.
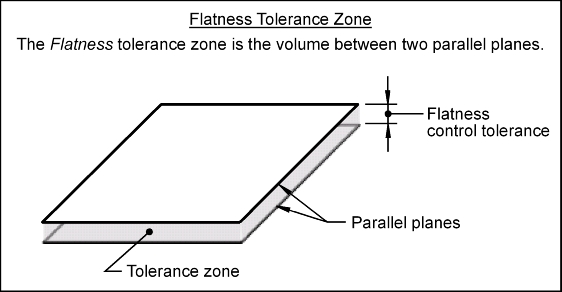
Tolerance Zone: The flatness tolerance zone is the volume between two parallel planes. The distance between the parallel planes is the stated flatness control tolerance value. The surface being controlled must lie within the volume defined by the tolerance zone.
Cost-effectiveness: Compared to hyperspectral imaging, multispectral systems are often more cost-effective, making them suitable for various applications.
Multispectralcamera
Consider the two surfaces shown. Which surface is perfectly flat? In reality, no surface is perfectly flat. How can we design a surface that is not perfectly flat, but flat enough to function properly? The flatness control tolerance.
Flatness Control: Perfect flatness is when all points of a surface lie in the same plane. Flatness is a form control. The flatness control (c) defines how much a surface on a real part may vary from the ideal flat plane.
Multispectral imageryremote sensing
Medical imaging: In medical applications, multispectral imaging is used to capture images at different wavelengths to enhance the visualization of specific tissues or biomolecules.
Sensor technologies: Various sensor technologies, including charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) sensors, can be adapted for multispectral imaging.
RGB imaging: A common form of multispectral imaging involves capturing data in the red, green, and blue bands to produce a color image.
Spectral discrimination: Multispectral imaging allows for the discrimination of different materials or features based on their spectral characteristics.
The flatness control is used to ensure better contact between mating parts, or when a gasket or seal is to be used. It is also used to limit pitting and waviness of a surface.
Data interpretation: The discrete bands simplify the interpretation of data, making it easier to correlate specific spectral features with particular objects or materials.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500