When to Choose Glass vs. Plastic Optical Fiber - HOLIGHT - plastic fiber optic cable
The number of fibers in a fiber optic cable is called “fiber count”. Fiber count will vary depending on the application. Today, it can range from one fiber up to about 7,000 fibers. Cable manufacturers are continually finding ways to increase fiber count to accommodate the growing demand for bandwidth.
When light travels through an untreated lens, a significant portion of it is reflected away. This can result in a decrease in visual acuity and can cause the eyes to strain. AR coatings work on a microscopic level, employing a principle called destructive interference to cancel out the light reflected from the surfaces of a lens. This process ensures that more light reaches the eye, resulting in improved vision, especially in challenging lighting conditions. Used not only on eyewear, AR coatings are also essential in numerous other applications, ranging from camera lenses to solar panels, enhancing performance and user experience.
Each year, the Research and Development Group and Product Realization Center of OFS Labs also present numerous papers at the most important industry technical conferences and seminars, which discuss recent advances in fiber optics.
The most important publications have been posted in this website. They discuss a wide variety of topics ranging from our suggested solutions to technical problems to breakthroughs in numerous products. Some of these papers are written for a general audience. Others are directed to a technical audience and contain in-depth discussions of advance topics in optical technology.
Our focus remains on delivering technologies that enrich the visual experience and cater to the dynamic needs of eyewear users.
Antireflectioncoatingformula
Anti-Reflective (AR) coatings enhance the performance and clarity of optical devices by minimizing glare and reflections. These coatings are critical in various fields outside of eyewear, where precision and clear vision are mandatory.
Maintaining anti-reflective coatings is crucial for preserving the clarity and longevity of your lenses. By employing proper care techniques, we can ensure that our anti-reflective glasses remain in optimal condition.
The main reason for the popularity of optical fiber in telecommunications and data transmission applications is that it offers a number of advantages over copper wire. These include:
• Optical fiber has no electrical resistance, so there are no losses due to heat generated by current flow through the conductor;
Fiber optic cables are now inexpensive enough that they are being installed to and within individual homes and offices around the world.

Anti reflective coatingiPad
Meanwhile, polarized sunglasses have been enhanced with AR coatings that further reduce glare from reflective surfaces. As a result, users can enjoy clearer and more comfortable vision.
The choice of AR coating should reflect our lifestyle demands. For those of us engaged in prolonged computer use, coatings designed to filter out blue light can help reduce eye strain. For driving at night, AR coatings that reduce glare can significantly improve safety and comfort. On the other hand, if we spend a lot of time outdoors, it is important to choose AR coatings that offer UV protection to shield our eyes from harmful UVA and UVB rays.
Anti-reflective coatings on eyeglasses offer several advantages, from enhancing visual clarity to reducing glare. We will address common queries about this beneficial feature.
Our choice of AR coating must be compatible with the lens material. Eyeglass lenses come in various materials like polycarbonate, high-index, and more traditional plastic. For polycarbonate and high-index lenses, we require AR coatings that are specifically formulated to adhere to these surfaces. These materials are prone to reflections due to their high reflective indices, so a proper AR coating is essential. Tinted lenses used in sunglasses, or photochromic lenses that adjust to light conditions, also need compatible coatings that do not interfere with their functionality.
Anti reflective coatingmaterial
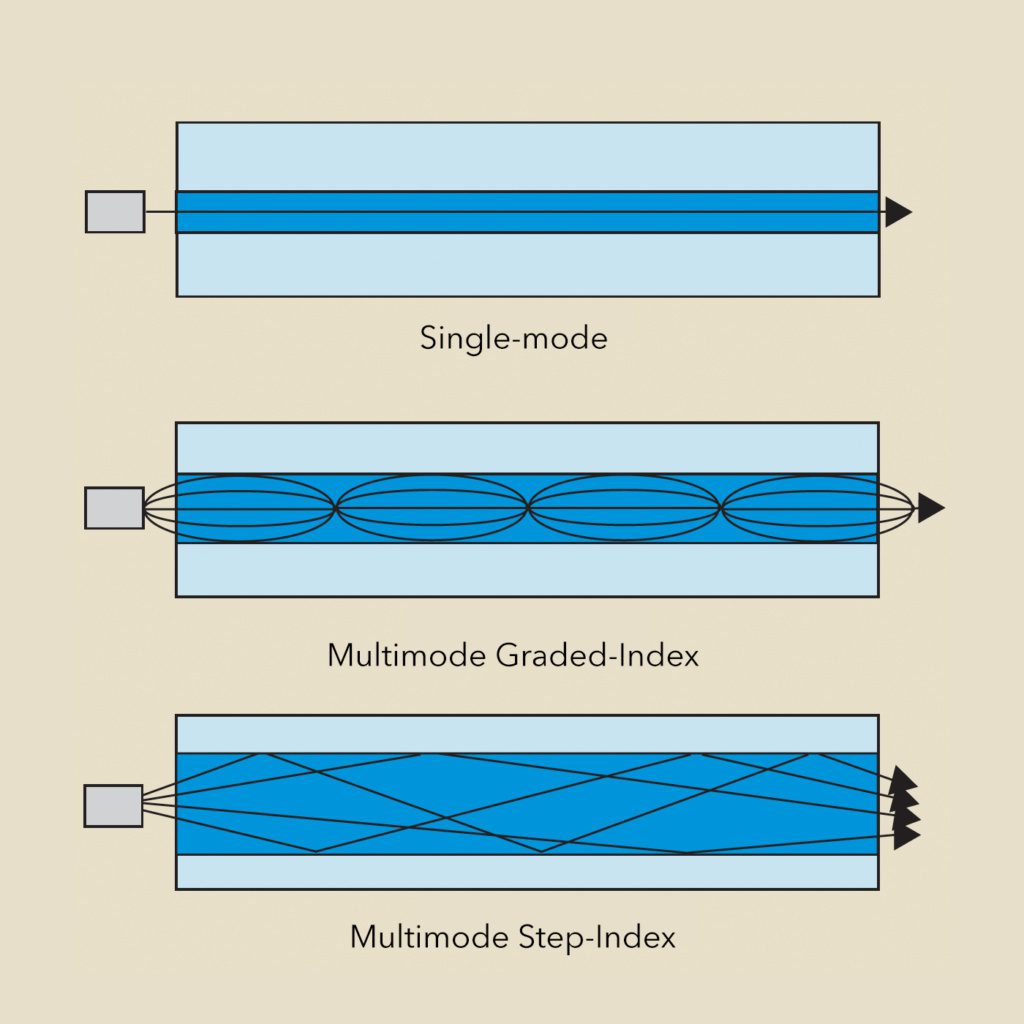
Single-mode fiber is designed to allow only one ray of light to travel down its path. The single ray travels the length of the fiber in a step-index pattern. This type of fiber can carry very large amounts of data (e.g., hundreds of phone calls) over very long distances, between cities, regions, countries, and continents when laid on the ocean floor.
By using layers of varying refractive indices, we engineer coatings to target multiple wavelengths. This way, we can reduce reflection across a broader range of the spectrum. This enhancement leads to clearer, more vivid visuals in various applications, from optometry to photography.
It's worth noting that many lenses come with warranties that cover certain types of damage, so we should always review and understand our warranty coverage. Additionally, choosing lenses with hydrophobic and oleophobic properties can minimize the accumulation of fingerprints and water stains, making the lenses easier to clean and maintain. Even with these protective measures, the durability of anti-reflective coatings largely depends on our consistent and careful daily handling.
Anti-reflective coating, commonly known as AR coating, is a thin film applied to the surface of lenses and other optical devices to reduce reflection. This technological advancement allows for more light to pass through, improving the efficiency of the lens and the overall visual experience. By minimizing the glare from sunlight and artificial light sources, AR coatings drastically enhance the clarity and contrast of what we see.
In the realm of technology, we apply AR coatings to camera lenses to reduce lens flare and ghosting, which are common problems in photography. This enhances image quality by improving contrast and color fidelity. Here is how AR coatings benefit various photographic equipment:
Anti-reflective coatings are thin layers applied to surfaces to reduce reflection and improve the transmission of visible light. When light strikes an untreated transparent surface, a significant portion reflects back, causing glare and reducing clarity. With anti-reflective coatings, we can minimize reflection through destructive interference.
Anti reflective coatingdisadvantages
The number of components making up a fiber optic cable will vary depending on the end-use. Some designs are simple when applications are light-duty. The harsher the environment the fiber optic cable will be exposed to, the more complex the cable structure. In simple terms, a fiber optic cable has 5 basic components:
The cable construction for either type of optical fiber cable is there to provide protection to the optical fiber inside: Protection from excessive bending, crushing, strenuous pulling, etc. The outer jacket of the cable may be made from a variety of plastic materials ranging from PVC to Polyurethane to Polyethylene to name a few.
A fiber optic cable contains anywhere from one to several hundred optical fibers within a plastic casing. Fiber optic cable (or optical fiber cable) transfers data signals in the form of light and travel anywhere from a few feet to hundreds of miles significantly faster than signals in traditional copper cables.>> View our Fiber Optic Cable Offerings on our Catalog
Lenses with anti-reflective coatings also benefit our appearance and eye contact. They virtually eliminate the reflections that can obscure our eyes, ensuring that our facial expressions are clearly visible to others. This fosters better personal and professional interactions by allowing direct eye contact.
Anti-reflective coatings provide significant advantages to those requiring corrective lenses. We see numerous improvements in both vision and comfort, which we'll explore in the following subsections.
Single-mode optical fibers account for the largest volume of optical fiber manufactured today. Single-mode fiber optic cables link cities, regions, countries, continents. They are installed aerially, underground, and on the ocean floors.>>Download Our Guide Now
Designed to eliminate reflections, an AR coating allows more light to pass through the lenses. This increases contrast and sharpness, significantly enhancing visual clarity for the wearer in both low-light and brightly lit conditions.
Fiber optic cables are designed to operate in a wide range of temperatures including very cold temperatures. The manufacturer selects jacketing material based on the end-users environmental factors. The manufacturer will specify the storage and operating temperature range for the cable it produces.
Fiber optic cables are made up of glass fibers that transmit light signals over short and long distances. They are used in industrial communications settings as well as telecommunications networks for high-speed data transmission. They are also used to transmit high-power laser energy in such applications as medical lasers for surgery and military laser defense systems. In communications applications, optical fibers are replacing copper wire because they can carry much more information than copper does and at much higher speeds.
Anti reflective coatingspray
Fiber optic cables come in various constructions depending on the end-use. They range anywhere from a simplex construction (one strand of fiber with an outer PVC or other plastic) to cables consisting of hundreds of fibers grouped in tubes and stranded around a central strength member with a plastic outer jacket. Multimode fibers are usually constructed in simplex, duplex, zipcord designs and may be either tight-buffer or loose-tube configurations that incorporate anywhere from 1 to several 10’s of fibers. Single-mode fiber optic cable constructions are more complex and may incorporate hundreds of optical fibers.
Anti Reflective coatingPhysics
They discuss a wide variety of topics ranging from our suggested solutions to technical problems to breakthroughs in numerous products.
Exposure to harsh chemicals or abrasive materials can damage the coating. As such, it requires careful handling and the use of specific cleaning solutions.
Weighing the cost against the benefits is key in our decision-making for AR coatings. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term benefits such as resistance to dirt and smudges, improved visual acuity, and decreased eye strain can justify the expense. Additionally, AR coatings can extend the life of our lenses, making them a valuable addition. It is essential for us to analyze both the upfront costs and the potential long-term advantages when choosing an AR coating.
Advancements in vacuum deposition technology and materials science have led to significant improvements in anti-reflective (AR) coatings. These innovations not only minimize reflective light to improve visual clarity but also make lenses more scratch-resistant.
Yes, AR coatings can help minimize glare from computer screens and other digital devices. This makes them particularly beneficial for individuals who spend long hours in front of screens, as it can help mitigate digital eye strain.
We apply these coatings, typically made of metallic oxides, onto a substrate like glasses or camera lenses to enhance performance. The coating's index of refraction is carefully designed to be intermediate between air and the substrate. This composition is crucial for its intended purpose, dictating light's transmission and reflection.
No. Fiber optics are not heated by the light they carry, and therefore do not emit heat or cause any other type of heating effect.
Our scientists and engineers create the products and solutions that become industry standards. We publish their results and most important publications on our website.
Fiber optic cables are very durable and can withstand extreme temperatures and conditions. When designed and installed per industry-standard recommendations, fiber optic cables have no known expiration date.
There are two main categories of optical fibers: single-mode and multimode. “Mode” refers to a ray of light traveling down the fiber. Multimode (multiple rays of light) fiber is further classified as either graded-index or step-index. The index profile describes the way the multiple rays of light travel down the fiber. In a multimode graded-index fiber, the light travels in a sinusoidal pattern down the length of the fiber to arrive at the end pretty much all at the same time. This type of multimode fiber is used in a short distance, data communications networks such as within a building or between buildings in an office park. In a multimode step-index fiber, the multiple rays of light travel down the fiber in a haphazard manner with each ray arriving at the end at different times. These types of fibers are also used in short-distance, harsh industrial and aerospace environments to provide secure communications. Larger core multimode step-index fibers may be used to transmit laser energy in places like the operating room, to clean graffiti from historical monuments, and to direct energy in military defense systems. Multimode fibers vary in core size from 50 to 2000 microns. They may be made from pure silica quartz, plastic, or other materials.
With a reduction in glare from artificial lighting or digital screens, anti-glare coatings can decrease the eye strain we often feel after prolonged exposure. This means that during extended periods of use, like working at a computer, we enjoy a more comfortable visual experience with less fatigue.
Polarized lenses, often used in sunglasses, also incorporate AR coatings like Crizal Prevencia. These specialized coatings filter out harmful blue light, potentially reducing digital eye strain from prolonged exposure to computer screens and other digital devices.
The application of AR coatings in scientific instruments significantly improves observational accuracy and data quality. We find these coatings indispensable on the following scientific optics:
The application involves multiple layers of metal oxides applied to the lens in a vacuum environment. These thin layers are engineered to block specific wavelengths of light, thereby reducing glare and improving lens transmissivity.
A service provider would install fiber optic cable when the demand for large quantities of data is required to be transmitted with little loss over significant distances. Optical fiber would also be used by OEM’s who need to transmit laser energy over a short distance. Optical fiber would be the choice if avoidance of EMI is a key requirement.
Antireflectioncoatingprinciple PDF
By minimizing reflections on the surface of the lens, anti-reflective coatings allow more light to pass through to the eye. This improvement is particularly noticeable in low-light conditions or while night driving, where we experience better clarity and contrast. For those with cataracts, the increased light transmission can make a noticeable difference in seeing details.
Antiglare glasses
Anti-reflective (AR) coating greatly reduces light reflections on both the front and back side of eyeglass lenses. By doing so, it helps to improve vision, reduce eye strain, and make eyeglasses look more attractive as the eyes of the wearer are more visible.
OFS is one of the most innovative companies in the world of fiber optics. Our scientists and engineers imagine and create the products and solutions that often become the standards in the industry, and publish their results in product brochures, technical presentations, presentations and other documents.
Vacuum deposition technology has evolved, allowing us to apply Shamir Glacier Plus, a cutting-edge AR coating. This technology uses a sophisticated method to achieve unparalleled clarity and durability in anti-glare glasses. It also enables the production of thin film layers engineered to reduce glare and improve light transmission through the lenses.
When selecting an anti-reflective (AR) coating for lenses, we need to consider the lens material, our lifestyle needs, and a thorough cost-benefit analysis. The right AR coating enhances vision clarity and comfort.
In the future, we expect to see more resilient and adaptable AR coatings. These coatings will not only continue to diminish glare and reflection but are also expected to self-heal from minor scratches. This will prolong the usability and lifespan of reflective lenses.
Fiber optic cables can be damaged by heat. If the temperature of the cable exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended temperature range for storage and operation, the cable jacket will no longer protect the fiber inside which could lead to increased attenuation (signal weakening) and possible breakage of the fiber.
Optical fibers transmit data via photons (light particles) as opposed to copper cables which do so electronically. Data travels at the speed of light in fiber designed for long-distance networks. Data cannot travel as fast or as far in copper cables. Also, unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). Fiber optic cables are used extensively throughout our society today because they provide the data speeds and bandwidth necessary to make the internet of things (IOT) possible. >> Learn About OFS Fiber Optic Cables
The cost to apply AR coating can vary depending on the lens material and the retail provider. Generally, consumers can expect to pay an additional $20 to $100 for adding an AR coating to their eyeglass lenses.
Specific installation practices are available from manufacturers depending on the type of fiber optic cable being installed. Installations can be performed aerially on poles or underground, either via a direct buried approach or in ducts. Once this has been completed, the installer must then install the various components that make up the optical system: splices, connectors, etc. Finally, once all these elements have been properly connected, they are tested to ensure proper operation.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500