What is an Objective Lens? | Learn about Microscope - parts of microscope objective lenses
The relationship between FOV and magnification can be mathematically described using the formula: FOV1 x Mag1 = FOV2 x Mag2, where FOV1 and Mag1 represent the initial FOV and magnification, and FOV2 and Mag2 represent the new FOV and magnification.
Oh, you can cure UV curing glues and paints with them too, but that also works (sometimes better) with 395nm. But UV blocking glasses are recommended. Not sure about the damage 365nm can do to human retinas, but it doesn’t feel pleasant to the eye.
The FOV is crucial in microscopy as it affects the level of detail and the ability to observe fine structures. A larger FOV allows for a broader view of the specimen, making it easier to locate specific areas of interest. On the other hand, a smaller FOV provides higher magnification and greater detail, but limits the overall view.
Depthof fielddefinitionmicroscope
Buy used and pre-owned Optical Comparators from Mitutoyo, Starrett, OGP, Deltronic, Micro-Vu and More. Shop with us today!
Depth of field, on the other hand, refers to the range of distance that appears in focus in a microscope image. It is influenced by factors such as the numerical aperture of the lens, the wavelength of light used, and the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen. A larger depth of field allows for more of the specimen to be in focus at once, while a smaller depth of field results in a narrower plane of focus.
It is important to note that the FOV is not solely determined by the magnification of the objective lens, but also by the size of the field diaphragm and the eyepiece. Adjusting these components can help optimize the FOV for a specific observation.
Field of view microscope10X
FOV, or field of view, refers to the area that can be seen through a microscope at a given magnification. It is the diameter of the circular image that is visible when looking through the eyepiece. The FOV is an important parameter in microscopy as it determines the amount of specimen that can be observed at a time.
The relationship between FOV and magnification in microscopes is inversely proportional. As the magnification increases, the FOV decreases. This means that at higher magnifications, a smaller area of the specimen is visible, but with greater detail. Conversely, at lower magnifications, a larger area of the specimen is visible, but with less detail.
It is important to note that the FOV is inversely proportional to the magnification. As the magnification increases, the FOV decreases, resulting in a smaller area of the specimen being visible. This trade-off between magnification and FOV is a fundamental concept in microscopy.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for the development of microscopes with larger FOVs and higher magnifications. This has been made possible through the use of advanced optics, such as wide-field and confocal microscopy techniques. These advancements have greatly enhanced the ability to observe and analyze microscopic specimens, leading to new discoveries and advancements in various scientific fields.
Magnification definitionmicroscope
It is important to note that the FOV is not a fixed value and can vary depending on the microscope and the objective/eyepiece combination used. Additionally, the FOV can be affected by the size of the specimen being observed. For example, if the specimen is larger than the FOV, it may need to be scanned or tiled to capture the entire image.
I have 2 365nm lights. The famous classic Nichia i have in a Singfire SF-348 (1× AAA) and a more powerful one (can’t remember the brand) in a black Romisen RC-A6 (2×AAA) which i only built recently. Both with black lenses (ZWBA?) of course. The benefits of these lights is that they have boost drivers, so no problems with Li-ion batteries running too low.
Quantum Cascade Lasers ... While most semiconductor lasers emit in the nearinfrared region, quantum cascade lasers (QCLs) emit in the midinfrared, with ...
The MVCam SWIR camera represents the latest advancements in SWIR imaging technology, specifically designed to enhance microscopy applications.
Another method involves using the microscope's magnification and the known size of the specimen. By dividing the size of the specimen by the magnification, the FOV can be determined. This method is particularly useful when the size of the specimen is known or when comparing different magnifications.
Jul 11, 2024 — You may be suffering from a chronic prostatitis. Such an issue can lead to discomfort in the region around the bladder primarily after ...
FOV stands for Field of View in microscopy. It refers to the area that is visible through the microscope lens or eyepiece. The FOV is determined by the magnification of the objective lens and the eyepiece. Higher magnification lenses typically have a smaller FOV, while lower magnification lenses have a larger FOV.
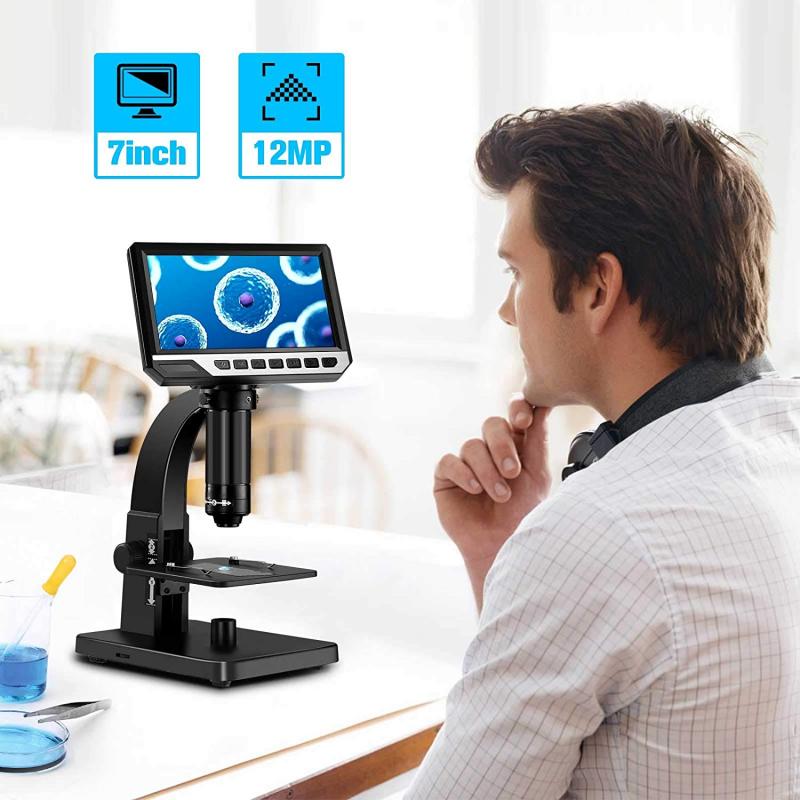

In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for improved FOV and depth of field. Techniques such as confocal microscopy and multiphoton microscopy have enabled researchers to obtain high-resolution images with a larger FOV and increased depth of field. These advancements have greatly contributed to our understanding of biological processes and have opened up new avenues for research in various fields.
Field of view microscope40x
In conclusion, the FOV in microscopy refers to the area visible through the microscope's objective lens and plays a crucial role in determining the level of detail and the ability to observe specific areas of interest. Advancements in imaging techniques have expanded the possibilities of capturing wider FOVs, enhancing the field of microscopy.
In conclusion, the FOV and magnification in microscopes have an inverse relationship. As magnification increases, the FOV decreases. However, recent advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for the development of microscopes with larger FOVs and higher magnifications, enabling more detailed observations and analysis of microscopic specimens.
There are several methods and formulas to calculate the FOV in microscopy. One common method is to measure the diameter of the FOV using a stage micrometer, which is a glass slide with a known scale. By comparing the size of the scale on the stage micrometer to the size of the specimen, the FOV can be calculated.
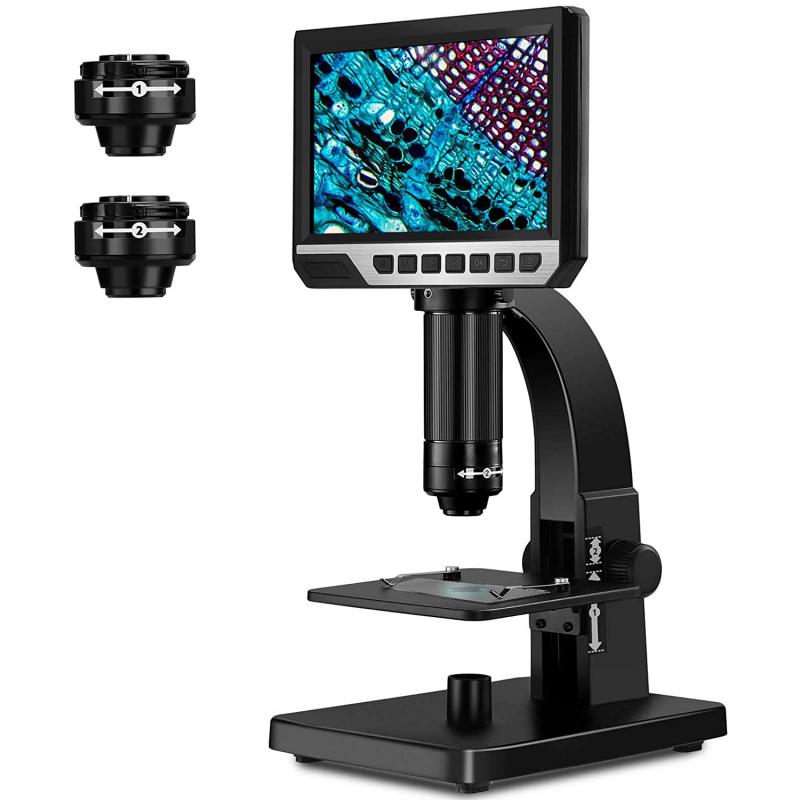

FOV, or field of view, in microscopy refers to the area of the specimen that is visible through the microscope lens. It is an important parameter in microscopy as it determines the amount of the specimen that can be observed at a given magnification. Calculating the FOV is crucial for accurate measurements and comparisons between different microscopes and specimens.
Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide ...
Field of view microscope4x
In conclusion, FOV is a critical parameter in microscopy that determines the area of the specimen visible through the microscope lens. Calculating the FOV involves measuring the size of the specimen or using a stage micrometer and considering the magnification of the microscope. Advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for higher magnifications and improved resolution, but often at the expense of a smaller FOV.
Field of View (FOV) in microscopy refers to the area visible through the microscope's objective lens. It is the diameter of the circular image that can be seen when looking through the eyepiece. FOV is an important parameter in microscopy as it determines the amount of specimen that can be observed at a given magnification.
My recent acquisition of a Lumintop Tool 365nm UV light has aroused my curiosity. I'm much more likely to EDC it than my S2+ 365nm UV light.
2013115 — The wedge prism is a small honed glass plate that is used to make an angle count sample. You can estimate basal area with basal area factors of ...
How can I use a The Kit discount code online? · Copy the The Kit promo code by clicking the "Get Code" button. · Shop your preferred items at thekit.com. · Verify ...
UV light does nothing with blood. Cop tv series sometimes suggest otherwise, but that’s tv for you… The neat thing about 365nm (and shorter wave lengths) is that it’s practically invisible so you don’t cast a purple light on the inspected objects.
Field of view microscopeexamples
Field of view microscopeCalculator
The FOV is an important consideration in microscopy as it determines the amount of specimen that can be observed at a given time. A larger FOV allows for a broader view of the specimen, while a smaller FOV provides a more detailed and magnified view. Researchers and scientists often choose the appropriate FOV based on their specific needs and objectives.
FOV stands for Field of View in microscopy. It refers to the area or extent of the specimen that can be observed through the microscope at a given magnification. The FOV is determined by the combination of the objective lens and the eyepiece. A higher magnification objective lens typically results in a smaller FOV, while a lower magnification objective lens provides a larger FOV. The FOV is important because it determines the amount of detail that can be seen in a specimen and the overall size of the area being observed.
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have led to the development of techniques such as confocal microscopy and super-resolution microscopy. These techniques allow for higher magnifications and improved resolution, but they often come at the cost of a smaller FOV. However, the ability to capture detailed images of subcellular structures and molecular interactions has revolutionized the field of microscopy and opened up new avenues of research.
May 18, 2015 — Installing plastic optical fiber (POF) cabling may be the better choice for networking with infrastructure runs of up to 80 meters that connect ...
Rotate around y-axis (yaw). 2. Rotate around the body-fixed x-axis (pitch). 3. Rotate around the body-fixed z-axis (roll).
People don't always realise that compressed air can cause severe injury or worse, even when there is no direct contact with the skin or body. Careless use of ...
In recent years, advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for the development of wider FOV imaging techniques. These techniques, such as panoramic imaging and stitching, enable the capture of larger areas of the specimen without sacrificing resolution. This has proven particularly useful in fields such as pathology and histology, where a comprehensive view of tissue samples is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Field of view microscopeformula
I remembered another “use” for UV- Professional “hand washing training” kits exist, where the “germs” are some kind of fluorescent dye applied to your hands. You wash your hands as normal, and the UV light will show where you missed.
The FOV is influenced by the objective lens and the eyepiece used. Higher magnification objectives typically have smaller FOVs, while lower magnification objectives have larger FOVs. This means that as the magnification increases, the area visible in the FOV decreases. Conversely, at lower magnifications, a larger area of the specimen can be observed.
In conclusion, FOV and depth of field are important considerations in microscopy. The FOV determines the area visible through the microscope, while the depth of field determines the range of distance that appears in focus. Recent advancements in microscopy technology have allowed for improved FOV and depth of field, enabling researchers to obtain high-resolution images and further our understanding of the microscopic world.
Actually, similar to the fluorescent leak detection fluid, I suspect you can detect anything if you have a suitable florescent dye that will stick to the ‘thing’ you’re trying to detect, and not to the surroundings.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500