What Is An Eyepiece On A Microscope? - eyepiece ocular lens function
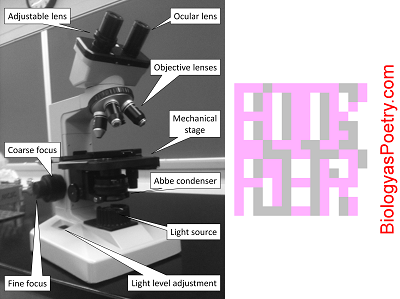
Iris diaphragmvs condenser
Figure legend: The iris diaphragm is found within the condenser, here labeled 'Abbe condenser'. It is responsible for controlling the amount of light that passes from the condenser to the specimen or, more specifically, the width of the light beam. Narrower widths provide greater contrast but also less light. The 'trick' is to effectively balance these therefore conflicting desirables as you adjust the degree to which the iris diaphragm is opened.
If the iris diaphragm is closed too far then the specimen will be too dark to clearly view. If it is too far open then the specimen will appear to be "washed out" and perhaps also barely visible. An all too common error is to not sufficiently close the iris diaphragm and thereby fail to see the specimen due to insufficient contrast, even if the specimen otherwise is in focus. As magnification is increased, particularly as top magnification is attempted using the oil immersion lens, then increased illumination often is required, necessitating additional opening of the iris diaphragm.
What is the iris diaphragmused for

Device that controls the amount of light that exits the condenser of a microscope, thereby controlling the illumination of the specimen and, more relevantly, the degree of contrast between specimen and background.
What is the iris diaphragmin microscope
Target Line pairs a jumbo cylindrical lens with a low-profile, ultra-sleek frame design for an incredible field of view. We flattened the brow line of the frame to create a seamless integration with Oakley helmets. Available in three sizes, this …
Target Line pairs a jumbo cylindrical lens with a low-profile, ultra-sleek frame design for an incredible field of view. We flattened the brow line of the frame to create a seamless integration with Oakley helmets. Available in three sizes, this Sutro-inspired design offers style and function for any face size. Target Line L is designed for a large-sized fit.
In light microscopy the iris diaphragm controls the size of the opening between the specimen and condenser, through which light passes. Closing the iris diaphragm will reduce the amount of illumination of the specimen but increases the amount of contrast. The pathway of light through a compound microscope is: light source → condenser → iris diaphragm → stage → object/specimen → objective lens → ocular lens → eye or camera.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500