Welcome to Bright Horizons at Lakeshore East - lakeshore magnifying glass
F-mount is a bayonet-style mount originally developed by Nikon for its 35 mm format cameras and is still found in most of its digital SLR cameras. It is commonly used with bigger sensors, e.g. full-frame or line-scan cameras. Lenses can be easily swapped out thanks to the bayonet mount, but no back focal adjustment is possible.
fov和焦距的关系
Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy. The Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy facility in the Frick Chemistry Laboratory offers state-of-the-art equipment for measuring ...
where p is the sensor pixel size (in microns), M is the lens magnification and k is a dimensionless parameter that depends on the application (reasonable values are 0.008 for measurement applications and 0.015 for defect inspection). For example, taking p = 5.5 µm and k = 0.015, a lens with 0.25X mag and WF/# = 8 has an approximate DoF = 10.5 mm.
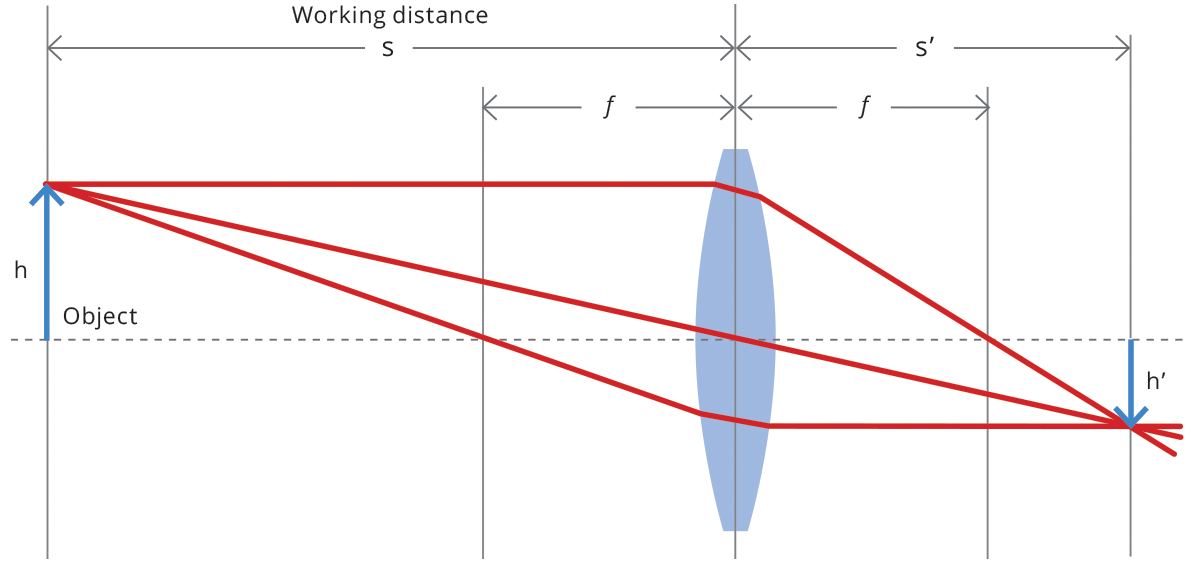
The main features of most optical systems can be calculated with a few parameters, provided that some approximation is accepted. The paraxial approximation requires that only rays entering the optical system at small angles with respect to the optical axis are taken into account. The thin lens approximation requires the lens thickness to be considerably smaller than the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces: it is thus possible to ignore optical effects due to the real thickness of the lenses and to simplify ray-tracing calculations. Furthermore, assuming that both object and image space are in the same medium (e.g. air), we get the following fundamental equation:

Typical F-numbers are F/1.0, F/1.4, F/2, F/2.8, F/4, F/5.6, F/8, F/11, F/16, F/22, etc. Every increment in the F-number (smaller aperture) reduces incoming light by a factor of 2. The given definition of F-number applies to fixed focal length lenses where the object is located ‘at infinity’ (i.e. a distance much greater than its focal length). For macro and telecentric lenses where objects are at a closer distance, instead, the working F/# (wF/#)is used. This is defined as:
Normal color image sensors have three types of color filters on the photodiode of each pixel - red, green, and blue - but Sony’s IMX454 multispectral image sensors have 8 types of filters on the photodiodes to take in light from different wavelengths. Typical multispectral cameras have a built-in spectral element, such as a prism or diffraction grating. They function by scanning a subject or camera at a constant speed to take pictures, which limits the types of scenes that can be photographed. With the IMX454, users can capture 2D images in one shot, just like with a normal camera. This means it can be used in many kinds of scenarios.
fov参数
Sep 27, 2023 — Pancake lenses suffer from fewer image quality issues than fresnel ones. There's less distortion of the geometry of the image, where the picture ...
![]()
The basic purpose of a lens of any kind is to collect the light scattered by an object and recreate an image of the object on a light-sensitive ‘sensor’ (usually CCD or CMOS based).
VAT IT02011230204 Fiscal code and registration number at Mantova Business Register 02011230204 Nr. REA: MN-216669 - Share Capital: 205.258,00 €
Each camera mount is more commonly used with certain camera sensor formats. The most typical sensor formats are listed below. It is important to remember that these are not absolute values – i.e. two cameras listed with the same sensor format may differ substantially from one another in terms of aspect ratio (even if they have the same sensor diagonal). For example, the Sony Pregius IMX250 sensor is listed as 2/3” and has an active area of 8.45 mm x 7.07 mm. The CMOSIS CMV2000 sensor is also listed as 2/3” format but has an active area of 11.26 mm x 5.98 mm.
field ofview中文
C-mount is the most common optics mount in the industrial market. It is defined by a flange focal distance of 17.526 mm, a diameter of 1” (25.4 mm) with 32 threads per inch.
The focal length is a typical characteristic of an optical system. It is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges rays of light. If collimated rays converge to a physical point, the lens is said to be positive (convex), whereas if rays diverge the focus point is virtual and the lens is said to be negative (concave). All optics used in machine vision applications are overall positive, i.e. they focus incoming light onto the sensor plane. CCTV lenses are commonly identified by their focal length, expressed in millimeters (12mm, 25mm, 35mm, etc.).
Kowa's SWIR lenses are designed to meet the needs of industries requiring precise imaging, from machine vision to security and beyond.
And the prayer offered in faith will make the sick person well; the Lord will raise them up. If they have sinned, they will be forgiven.
Multispectral cameras have a less established history than color or monochrome cameras, and there is still something to be desired in terms of the necessary environment for their development and introduction. Given this, Sony made advance arrangements for the functions that the development and introduction of the IMX454 requires, and provided a software program that includes all of them.
FOV to focal length calculator
Every optical system is characterized by an aperture stop, that determines the amount of light that passes through it. For a given aperture diameter d and focal length f we can calculate the optics F-number:
Different mechanical mounting systems are used to connect a lens to a camera, ensuring both good focus and image stability. The mount is defined by the mechanical depth of the mechanics (flange focal distance), along with its diameter and thread pitch (if present). It’s important that the lens flange focal distance and the camera mount flange distance are exactly the same, or focusing issues may arise. The presence of a threaded mechanism allows some adjustment to the back focal distance if needed. For example, in the Opto Engineering® PCHI series lenses, the back focal adjustment is needed to adjust the focus for a different field of view.
*This data has undergone signal processing in the software that comes with the sensor. Data may vary depending on the conditions and environment.
What does MTF actually mean? Find out inside PCMag's comprehensive tech and computer-related encyclopedia.
Developed by Leica Camera, the L-Mount allows photographers to combine lenses and cameras made by the five Alliance partners. A new era of creative freedom has ...
Many cameras are found not to respect the industrial standard for C-mount (17.52 mm), which defines the flange-to-detector distance (flange focal length). Besides all the issues involved with mechanical inaccuracy, many manufacturers don’t take into the due account the thickness of the detector’s protection glass which, no matter how thin, is still part of the actual flange to detector distance.
Infrared and Covert convoy LED Lighting for Military vehicles and more. Our infrared convoy signature light is now available. Forces need to more fully ...
fov是什么
Sony's multispectral image sensor has a multispectral filter formed on the photodiode of each pixel, making it possible to capture multiple wavelengths of light simultaneously, from visible light to near-infrared light. Because these sensors can capture the composition of different substances as well as subtle color differences that are imperceptible to the human eye, they can be used in applications like material sorting, contaminant detection inspection, and quality management.
Why does dispersion take place when light is passed through prism and not through glass slab? Asked by: Kavita. Answer. A light ray is refracted (bent) when ...
StarLight Opto-Electronics · Magnifying glass LL6-NW-UV365, 3 × natural white (4,000 K), 3 × UV (365 nm) · $ 920.00.
FOV to focal length
In some cases, users may need to synthesize a color image from identification results based on a multispectral image, or they may require a color image to combine with existing software designed for color images. To address these needs, Sony has built a color image generation function that creates color images that are easy to comprehend visually, based on image data from multiple different wavelengths. This function makes it possible to obtain images with natural-feeling color, without setting up a separate camera.
CS-mount is a less popular and 5 mm shorter version of the C-mount, with a flange focal distance of 12.526 mm. A CS-mount camera presents various issues when used together with C-mount optics, especially if the latter is designed to work at a precise back focal distance.
This is why a spacer kit is supplied with Opto Engineering® telecentric lenses including instructions on how to tune the back focal length at the optimal value.
Replace sunglasses lenses from home for brands like Oakley, Ray-Ban, Costa, and more. Starting at just $25, you can match your originals or upgrade to ...
By combining the IMX454, which has a multispectral filter, with Sony's specially designed signal processing software, image data of 41 wavelengths (from 450 nm to 850 nm, in 10 nm intervals) obtained from 8 types of filters can be captured in just one shot. This makes it possible to capture more specific information at a high resolution, providing more wavelength choices across the visible light and near-infrared spectrums and opening the door to a variety of applications.
A certain number of parameters must be considered when choosing optics, depending on the area that must be imaged (field of view), the thickness of the object or features of interest (depth of field), the lens to object distance (working distance), the intensity of light, the optics type (telecentric/entocentric/pericentric), etc.
For common optical systems, in thin lens approximation, the focal length is the distance over which collimated rays coming from infinity converge to a point on the optical axis.
Defect correction, noise reduction, AE (Auto Exposure) control functions, and other essential, standard camera functions that are generally supported for color or monochrome image sensors have been optimized for multispectral image sensors. This has facilitated the efficient development of multispectral cameras.
Viewangle
where s (s’ ) is the object (image) position with respect to the lens, customarily designated by a negative (positive) value, and f is the focal length of the optical system (cf. Fig. 1). The distance from the object to the front lens is called working distance, while the distance from the rear lens to the sensor is called back focal distance. Henceforth, we will be presenting some useful concepts and formulas based on this simplified model, unless otherwise stated.
Semantic segmentation is an image recognition method that uses machine learning to label each pixel within the image data to divide the regions more precisely. Performing segmentation using the wavelength information for each pixel makes it possible to identify the material composition of a subject quickly and reliably, regardless of its form and even if the color looks the same to the human eye. This enables differentiation of materials by color and estimation of the area or volume of individual materials.
Since fixed focal length lenses also follow the previous equation, it is possible to calculate the required focal length given the magnification and working distance, or the required working distance given the sensor size, field of view and focal length, etc. (some examples are given at the end of this section). For macro and telecentric lenses instead, the working distance and magnification are typically fixed.
Field of view
Mxx-mounts are different types of camera mounts defined by their diameter (e.g. M72, M42), thread pitch (e.g. 1 mm, 0.75 mm) and flange focal distance. They are a common alternative to the F-mount for larger sensors.
The focal length and the focus plane coincide only when the object is placed at an infinite distance, indeed beams from a point on the object can be considered as parallel. When instead the distance from the object is ‘short’ (rule of thumb: <10x Focal length), we are in macro mode and the focus plane is placed further away from the optical system compared to the focal length.
A common F-number value is F/8 since smaller apertures could give rise to diffraction limitations, while lenses with larger apertures are more affected by optical aberrations and distortion. A rough estimate of the field depth of telecentric and macro lenses (or fixed focal length lenses used in macro configuration) is given by the following formula:
Macro and telecentric lenses are designed to work at a distance comparable to their focal length (finite conjugates), while fixed focal length lenses are designed to image objects located at a much greater distance than their focal length (infinite conjugates). It is thus convenient to classify the first group by their magnification, which makes it easier to choose the proper lens given the sensor and object size, and the latter by their focal length.
The F-number affects the optics depth of field (DoF), that is the range between the nearest and farthest location where an object is acceptably in focus. Depth of field is quite a misleading concept because physically there is one and only one plane in object space that is conjugate to the sensor plane. However, being mindful of diffraction, aberration and pixel size, we can define an “acceptable focusing distance” from the image conjugate plane, based on subjective criteria. For example, for a given lens, the acceptable focusing distance for a precision gauging application requiring a very sharp image is smaller than for a coarse visual inspection application.
For optical systems used in machine vision, in which rays reflected from a faraway object are focused onto the sensor plane, the focal length can be also seen as a measure of how much area is imaged on the sensor (Field of View): the longer the focal length, the smaller the FoV and vice versa (this is not completely true for some particular optical systems, e.g. in astronomy and microscopy).




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500