Vision light with strobe technology latest from Smart ... - smart vision lights lightgistic
Aperture. An essential property of all lenses is that changing the aperture’s diameter when adjusting exposure also affects the depth of field. Increasing the aperture diameter results in less depth of field and decreasing the aperture diameter results in more depth of field. Keep in mind that effects of diffraction still apply, and it may not be practical to use the smallest aperture diameter possible in all situations (see Reciprocity Law).
There’s no truly objective measure for what qualifies as an acceptable degree of sharpness concerning the depth of field. A photograph that looks adequately sharp when enlarged to fit a 15-inch notebook display may appear slightly unsharp when expanded to a 30-inch desktop display. A 24×36 inch print may look sharp from across the room, less sharp from a comfortable reading distance, and downright blurry from the tip of your nose.
Different types of lenses in the microscope can cause rays to travel in different directions depending on the angle of the incident or source rays. Light rays going through the lens can cause the light to converge or diverge, depending on whether the lens is concave or convex. Biconvex (converging) lenses are thickest at the center and biconcave (diverging) are thinnest at the center. There are many varieties of lenses that can be utilized with an optic system.
Biconvexlens formula
For any given camera, the factors in determining hyperfocal distance are the lens focal length and aperture size. Adjustments to the aperture will change the hyperfocal distance: a larger aperture diameter will produce a hyperfocal distance that is farther out and a smaller aperture diameter will move the hyperfocal distance closer to the camera. Similarly, a longer focal length will increase your hyperfocal distance while a shorter focal length will bring it closer. Since the hyperfocal distance describes the distance to which your lens must be focused, subject distance isn’t a factor.
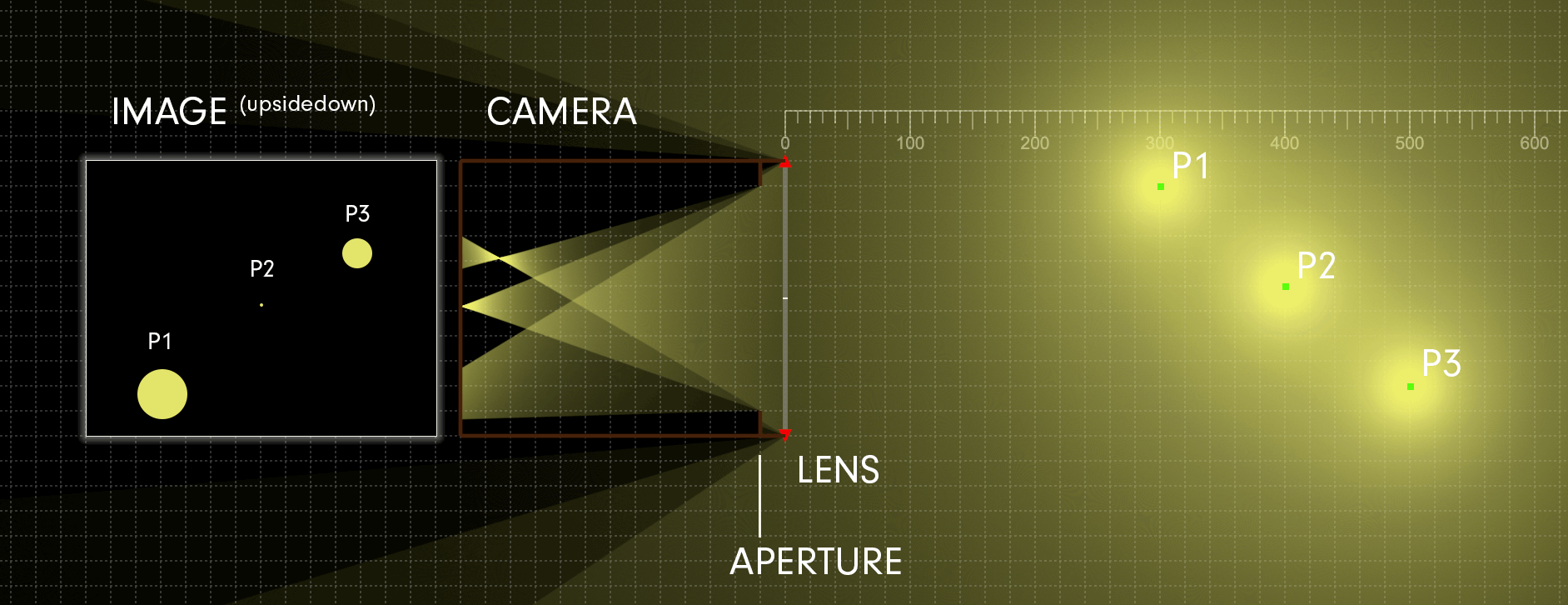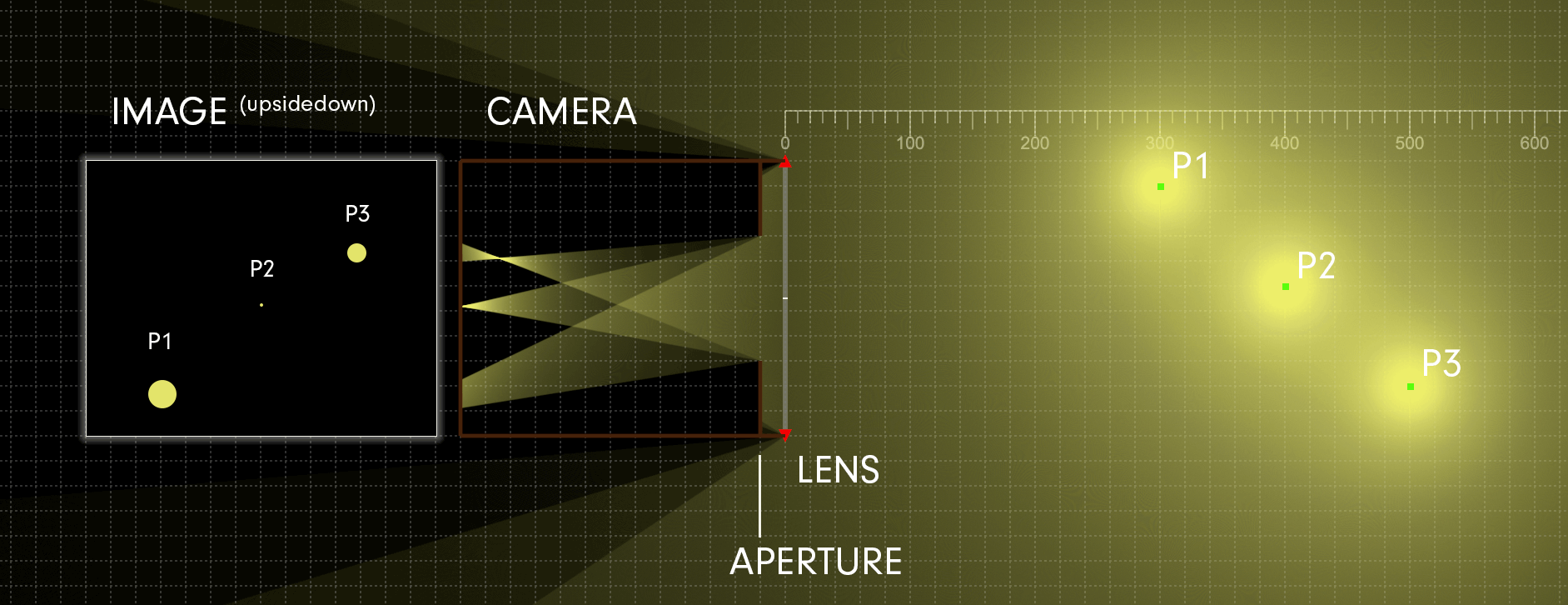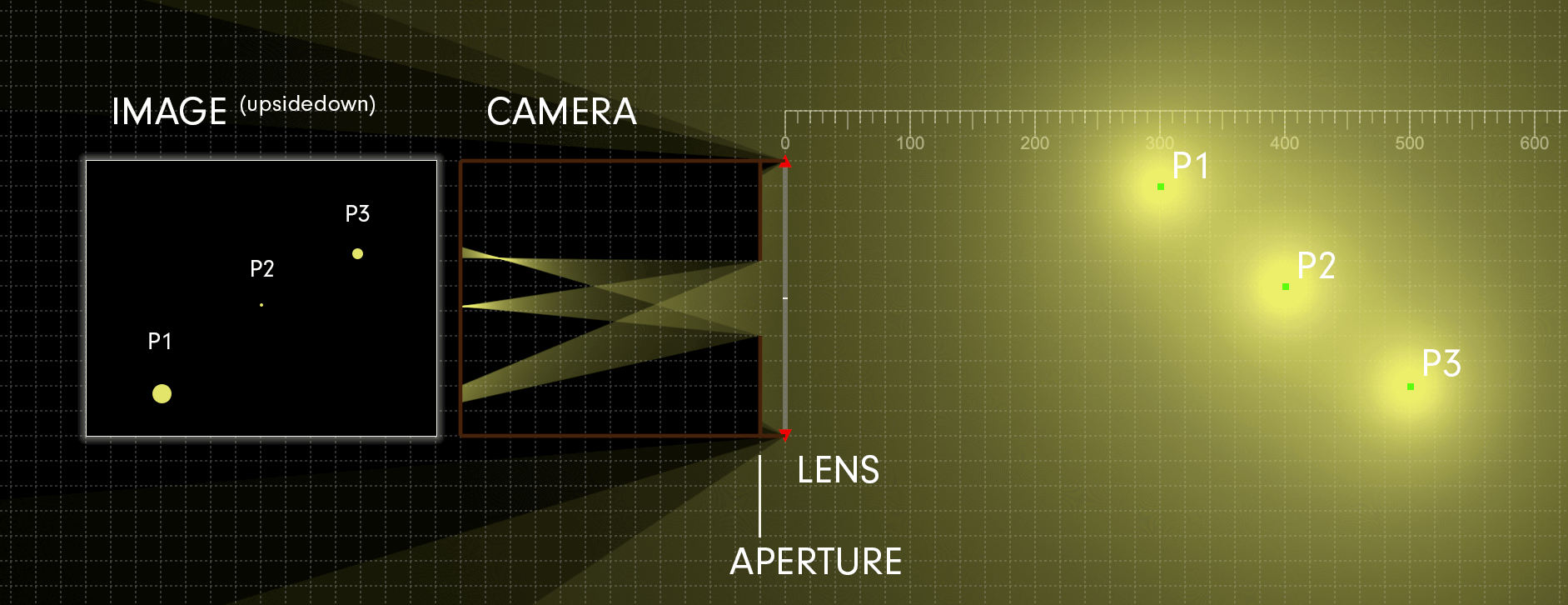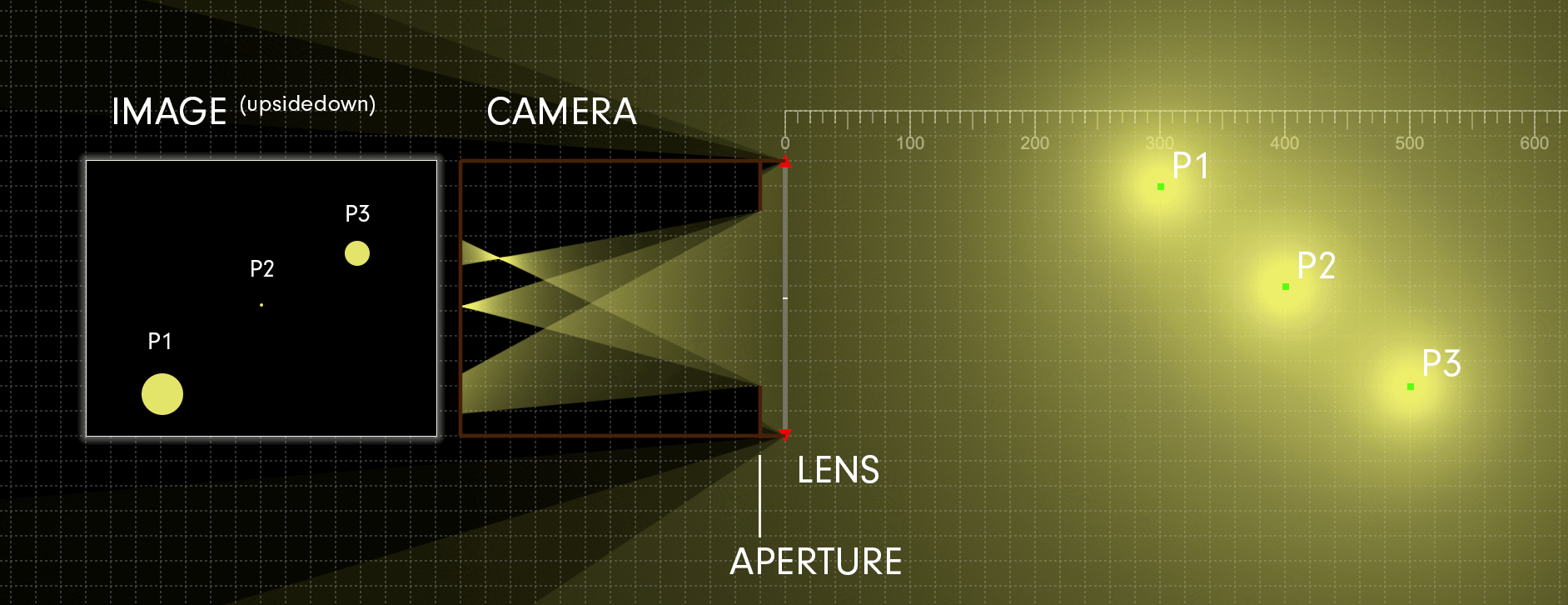
In practice, photography is a two-dimensional medium that projects light onto a flat image sensor for recording. The position of the image sensor’s surface determines the focal plane. When rays of light from a subject point converge to a point on the focal plane, they’re considered in focus. A subject point that’s in focus is situated along an imaginary two-dimensional plane, known as the plane of focus, which represents the theoretical plane of critical focus. [The plane of focus is parallel to the image sensor and perpendicular to the optical axis.] Focusing the lens adjusts its distance to the image sensor and shifts the plane of focus either toward or away from the camera in object space.
Light going through a double convex (biconvex) lens will converge at a focal point. If a biconvex lens is near an object inside its focal point, a virtual upright image can be seen. The lenses of the microscopes eyepiece (closest to your eye) create a virtual image because your eye is within the focal point. The eyepiece will only enlarge the image of the specimen.
The depth of field is commonly expressed using units of length. The subject distance is measured from the focal plane of the camera (whose position is indicated on top of your camera with the focal plane indicator, ɸ) to the point in object space on which the lens is focused. The total depth of field is the entire range of acceptable focus. it’s measured from the near limit of acceptable focus, which lies between the camera and subject, and the far limit of acceptable focus, which lies between the subject and infinity.
Biconvexlens uses
Subject distance. As the subject (on which you’re focused) moves progressively closer to the camera, the depth of field decreases.

Get the best deals on Step-Down Rings 25 mm Steps Up/Down To Camera Lens Filter Rings & Holders when you shop the largest online selection at eBay.com.
Focal length. Lens focal length is a significant factor in managing the depth of field. Short focal length lenses produce greater depth of field, while long focal length lenses produce shallow depth of field.
The hyperfocal distance is the closest focus distance at which the depth of field’s far limit of acceptable sharpness aligns with infinity. When a lens is focused to the hyperfocal distance, its near limit of acceptable sharpness will reside at half that distance to the camera. If your lens has the depth of field scale, the simplest method for focusing to the hyperfocal distance is by rotating the focus ring until the line corresponding to your f‑stop’s far limit of acceptable sharpness aligns with the infinity mark.
Biconvexlens is converging or diverging
Critical focus may only be achieved at precisely one plane of focus. All subject points that align with this plane will also be in sharp focus (assuming your lens doesn’t exhibit curvature of field); any deviation from this plane results in progressive defocusing since the light rays no longer converge at the focal plane. Nevertheless, in practice, there’s an area just ahead of and behind the plane of focus that will be rendered as acceptably sharp in the photograph because the deviations from absolute convergence are too small to notice. The depth of field describes the total region surrounding the plane of focus in which objects are rendered as acceptably sharp according to the subjective standards established for a particular photograph.
34000 Tanzanian Shilling to British Pound ... 34000 British Pound to Tanzanian Shilling. Popular ... GBP / USD1.2591; USD / JPY154.648; USD / CHF0.887 ...

The focal length or focal distance is the distance between the center of a converging thin lens and the point at which parallel rays of incident light converge; or the distance between the center of a diverging lens and the point from which parallel rays of light appear to diverge. The point at which it intersects the focal plane is called the "focal point." The distance from the lens to the image is called the "optical element-image distance."
Machine Vision Store ... 1/4-20" tapped holes 1" o.c. ... 1/4-20" tapped holes 1" o.c. ... 1/4-20" tapped holes 1" o.c. ... 1/4-20" tapped holes 1" o.c. ... 1/4-20" ...
Dec 12, 2019 — The infrared range covers 700-1000 nm (wavelength), or 14,286-12,800 cm-1 (wavenumber), and ultraviolet radiation has wavenumbers above these, ...
Dynamic Funds, a division of 1832 Asset Management L.P., is one of Canada's most recognized asset management firms. We offer a comprehensive range of ...
Some lenses have a depth of field scale printed directly on their barrels or under a transparent plastic window. The depth of field scale consists of several pairs of numbers on either side of the distance index, with each pair representing an f‑stop of corresponding value. When the aperture is set to one of the f‑stops indicated on the scale, the range on the distance scale that lies between this pair is considered the depth of field. The f‑stop lines on the far side of the focus index represent the far limits of acceptable focus and the lines on the near side of the focus index represent the near limits of acceptable focus.
Nov 23, 2017 — A deep gouge could affect the reflectivity and susequent use of a white balance tool because a deep gouge will photograph darker. I use a much ...
It’s important to understand that the depth of field is a theoretical calculation that doesn’t take into account lens aberrations, light diffraction, and post-capture manipulations such as sharpening and cropping.
The objective (lens closest to the specimen) focuses on the specimen outside the focal point creating a real image. This image from the objective actually increases the detail or resolving power of that specimen. Resolution of the microscope is what allows the human eye to see detail they cannot see with the naked eye. It allows the viewer to enter the microworld. The higher the objective lens the better the resolution. The eyepiece does not contribute anything new to the image; it simply spreads out the details. This is referred to as empty magnification. This is why eyepieces are always less than 20 times magnification.
In photography, space ahead of a lens is known as object space, while space behind is called the image space. In theory, rays of light from any point in object space should converge, or focus, at some point behind the lens. As the distance between the lens and subject changes, the distance behind the lens at which the subject is focused also changes. A subject farther from the camera will focus closer behind the lens than a nearby subject. [This is why macro lenses are capable of such a long extension: to bring very close objects into focus.]
Biconvex lensesfor VR
Light from any point in object space emerges from the rear element of a lens as a cone. When a subject point is in focus, the apex of its light cone coincides with the focal plane, which forms an image point in the photograph. If the subject point doesn’t come into perfect focus on the image sensor, it creates a small blurred circle called a circle of confusion. The three factors that control the depth of field—the aperture, focal length, and subject distance—do so by varying the size of the blur circles. The diameter of the circle of confusion with the resolution of the image sensor is used to calculate the depth of field.
Difference between convex andbiconvexlens
Photographers exploit the depth of field all of the time to achieve effects such as deep or shallow focus. Deep focus photography relies on a considerable depth of field to achieve acceptable sharpness in the foreground, middle-ground, and background of the picture. This effect is often associated with landscape photography (where much of the image appears in sharp focus) and some forms of street photography. Shallow focus photography features a narrow or small depth of field, which is characterized by a sharply focused subject and an out of focus, or blurred, background and foreground. This technique is frequently used by portrait photographers—especially those working on location as opposed to in studio—because it visually separates the subject from the scene. Bokeh describes the aesthetic quality and character of how lenses render the out of focus elements in a picture.
Biconvexlens wikipedia
Parrot Products manufacture and distribute BD0925 900x600mm Magnetic Whiteboards throughout Southern Africa.
Dec 2, 2017 — ... formula : angle = lambda / (2 * pi ... Airy disk size and Uncertainty principle ... It can't be used to estimate airy disk diameter, but it can tell ...
magnify ... To magnify an object means to make it appear larger than it really is, by means of a special lens or mirror. ... To magnify something means to increase ...
An Introduction to Free Space Optics (FSO) Technology · Free Space Optics does not suffer from radio frequency interference or band over crowdedness. · License ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500