Vision Forward Lighted Stand Magnifiers - magnifying glass with light on stand
Overcome the challenges inherent in the Raman technique with Renishaw's Raman spectrometers. Learn about diffraction-limited spatial resolution for microscope-based chemical analysis. Explore how sensitivity and spatial resolution can be improved by using resonant Raman techniques (i.e. SERS and TERS).
Raman spectroscopy principlePDF
BEAMSHOT® is proud to introduce our newest hand held Greenbeam tactical laser pointer, slimmer and lighter than our GreenBeam 100, this pointers compact on the go design make this product the ideal chose for professional who depend on their equipment. This product was designed with the working environment of today's military in mind. True daylight visibility allows rapid deploying teams to accurately communicate critical target and obstacle positions. When your message must be perfectly clear, a visual aid you can count on becomes a vital tool. Our 532nm wavelength GreenBeam 50 laser pointer provides 100 meters of daylight visibility and a 1 mile nighttime range.
Raman spectroscopyapplications
1. 532nm green laser beam at 1 mile nighttime range.2. 20 time brighter than red lasers pointers.3. Powered by 2 AA batteries that provides approximate 6 hours continuous laser use.4. Exceptional glass laser lens produce better beam focus for more accurate target acquisition.5. Light weight compact design make this laser shock resistant and waterproof.
Raman spectroscopydiagram
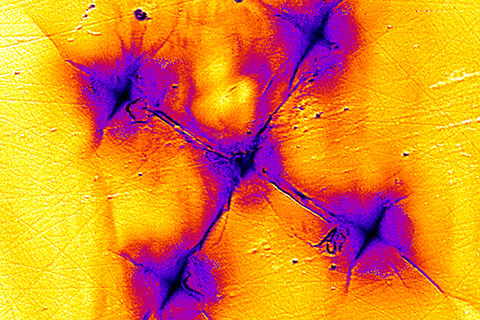
Photoluminescence (PL) can be a useful analytical method. We explain how PL relates to fluorescence and phosphorescence. Learn how you can tell apart PL features from Raman bands. We also offer practical tips on how to avoid unwanted fluorescence background in Raman spectra.
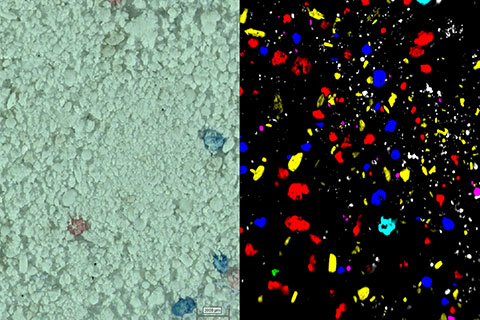
We can analyse Raman images to study the distribution of chemical and structural species across a sample. We explain how to collect Raman images. We also discuss various data analysis methods, and when to use them for Raman imaging.
Raman spectroscopy principleand instrumentation PDF
Welcome to the exciting world of Raman spectroscopy: one of science's easiest to use, most powerful, and most versatile analytical techniques.
Scientists use Raman spectroscopy to analyse the make-up of materials. In Raman spectroscopy, we focus a single colour of light onto a sample. Next, we measure the way that light interacts with the material to gain information about it. This gives us an understanding of its chemistry and structure.
Learn how Raman spectroscopy can reveal the chemistry and structure of materials. We describe the features of a Raman spectrum and explain the variations in Raman band parameters. We also provide examples of how Raman spectra can tell apart different chemicals and polymorphs.
Raman spectroscopy
Understand why Raman spectroscopy is ideal for a wide range of samples. Explore the key components of an inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. You can readily combine an inVia microscope with other analytical methods. We discuss how Raman microscopy complements FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
What is Raman scattering and how does it occur? Find out more about the theory behind Professor C.V. Raman's discovery. Learn how a Jablonski diagram can represent the change in energy during Rayleigh and Raman scattering.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500