Using Coloured Filters in Black and White Photography - colorful filter
Helios cameralens
The Arena SDK includes easy to use controls for the Helios ToF camera. ArenaView allows for 2D and 3D views: 2D view allows one to see the intensity and depth of the scene from the camera’s perspective. 3D view displays a point cloud of the scene and allows users to manipulate the orientation in real-time. Additionally, settings can be changed in real-time such as false color overlay, depth range adjustments, out of range color settings and more.
A light microscope, also known as an optical microscope, is a scientific instrument that uses visible light and a series of lenses to magnify and observe small objects or organisms that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. It is one of the most commonly used tools in biology and other scientific fields.
Anti glare glasses, or lenses treated with Anti glare coatings, also known as anti reflection, reflection free, AR or MAR coatings, were developed to reduce ...
A light microscope is a type of microscope that uses visible light to magnify and observe small objects or samples. It is a widely used tool in various scientific fields, including biology, medicine, and materials science. The light microscope definition refers to the use of lenses and light sources to produce magnified images of samples.
... adapter.This simple adapter screws onto your exiting handheld and features a standard coax connector for easy connection. Radio Compatibility:• R1• GMR2 ...
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated light microscopes, such as confocal microscopes and fluorescence microscopes. These instruments utilize advanced optical techniques and components to enhance the resolution and contrast of the images obtained. Additionally, digital imaging and computer software have allowed for the capture, analysis, and storage of microscope images, enabling further research and analysis.
Phase contrast microscopes are designed to enhance the contrast of transparent specimens, such as living cells, by converting differences in refractive index into variations in brightness. This technique allows for the visualization of cellular structures that would otherwise be difficult to observe.
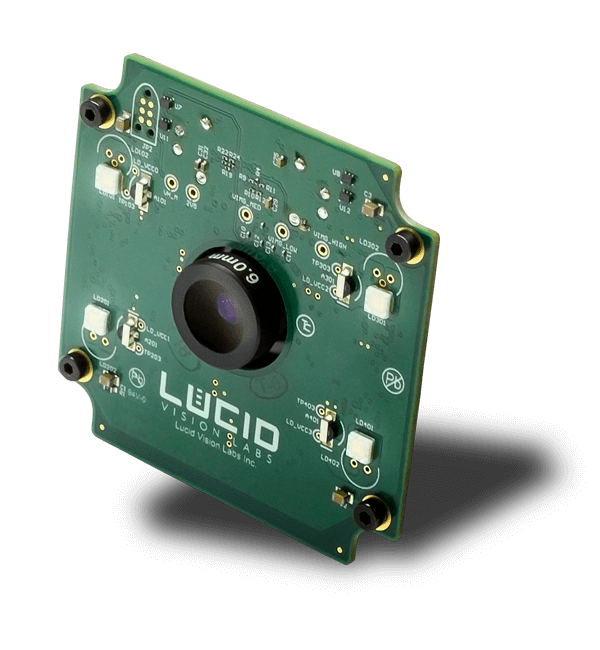
This Helios camera model (P/N: HLS003S) is designed to be connected to a host PC running either Windows or Linux. Depth information is processed on the Helios ISP and streamed through the Gigabit Ethernet connection. HLS003S: 640 x 480 at 30 FPS, Gigabit Ethernet, Working Range: up to 6m
The components of a light microscope typically include an illuminator, which provides a light source, a condenser, which focuses the light onto the specimen, an objective lens, which magnifies the image, and an eyepiece, which further magnifies the image for the observer. The microscope also has a stage where the specimen is placed and a focus adjustment mechanism to bring the specimen into sharp focus.
Resolution, on the other hand, refers to the ability of the microscope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects as separate entities. It is determined by the wavelength of the light used and the numerical aperture of the objective lens. The numerical aperture is a measure of the lens' ability to gather light and is influenced by the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen.
The Helios industrial camera detects 3D depth of objects. It features Sony’s DepthSense ToF sensor, along with 4 VCSEL laser diodes operating at 850nm. The camera calculates depth data by measuring the time it takes for light emitted from the diodes to reflect off objects in the scene and return to the sensor for each point of the image. This design results in high accuracy of < 5 mm with a precision (standard deviation) of 2 mm at 1.0 m distance.
In light microscopy, the maximum resolution is limited by the diffraction of light waves. According to the Abbe diffraction limit, the resolution is approximately half the wavelength of the light used. However, recent advancements in microscopy techniques, such as super-resolution microscopy, have pushed the limits of resolution beyond the diffraction limit. These techniques utilize fluorescent dyes and complex imaging algorithms to achieve resolutions at the nanometer scale, allowing scientists to observe cellular structures and processes in unprecedented detail.
Helios cameramanual
A light microscope is a type of microscope that uses visible light to magnify and resolve the details of a specimen. It consists of a series of lenses that work together to enlarge the image of the specimen, allowing scientists to observe and study its structure and characteristics.

Embedded model of the compact Time of Flight camera with monochromatic Sony DepthSense IMX556PLR sensor and GigE Vision interface, which allows to capture high-quality images with depth data.
Overall, sample preparation techniques for light microscopy play a crucial role in obtaining clear and detailed images of samples. These techniques continue to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and the need for more precise and accurate analysis in various scientific disciplines.
A light microscope is a type of microscope that uses visible light to magnify and observe small objects or organisms. It consists of a series of lenses that focus the light onto the specimen, allowing for detailed examination. The light microscope is one of the most commonly used tools in biological research and is essential for studying cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
The compound microscope has two systems of lenses for greater magnification, 1) the ocular, or eyepiece lens that one looks into and 2) the objective lens, or ...
Magnification refers to the ability of the microscope to make the specimen appear larger than its actual size. This is achieved by using a combination of objective lenses with different magnification powers. The total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
Basler ToFCamera
Helios is a compact Time of Flight (Tof) camera with superior depth precision with a working range of up to 6m. Unlock the potential of Time of Flight in a variety of industrial applications including robotics, 3D inspection and logistics.
Features: Resolution: 640 x 480 pixels (0.3 MP) in monochrome. Frames per second: 30 fps at full resolution. Sensor: CMOS Global Shutter sensor Sony DepthSense IMX556PLR. Video Interface: 4-Lane MIPI D-PHY CSI-2 (FFC) Lens Mount: Integrated lens with 6mm focal length (not user changeable)
time-of-flightcameraprice
In recent years, there have been advancements in sample preparation techniques for light microscopy. For example, immunostaining techniques have become more sophisticated, allowing for the visualization of specific proteins or molecules within a sample. Additionally, the development of super-resolution microscopy techniques has enabled researchers to achieve higher resolution and better visualization of subcellular structures.
The plane resolving power of typical optical microscopes is generally defined by Rayleigh's resolving power. Even if the optical system is aplanatic, when ...
Model name HLS003S-001ETX2 Product family Helios Product type Area scan 3D ToF Sensor name Sony DepthSense IMX556PLR Sensor type CMOS Sensor size (H x V), format 6.40 mm x 4.80 mm, 1/2" Pixel size (H x V) 10.0 µm x 10.0 µm Color/Mono Mono Resolution (H x V), MP 640 x 480 px, 0.3 MP Frame rate 30 fps ADC Dynamic Range Shutter Global Exposure Range Synchronization Software trigger, hardware trigger, PTP (IEEE 1588) Inputs/Outputs Image Buffer Lens Mount Integrated lens with 6mm focal length (not user changeable) Output Formats 3D Point Cloud, Intensity and Confidence Working Ranges Near mode: up to 1.5m, Far mode: up to 6m Accuracy Less than 5mm (0.3m to 1.5m) Precision Standard deviation less than 2mm at 1m Lens Field of View 59⁰ x 45⁰ (nominal) Illumination 4 x VCSEL laser diodes @ 850nm Interface 4-Lane MIPI D-PHY CSI-2 (FFC) Machine Vision Standard GigE Vision v2.0 Power Requirements Power Consumption (Maximum) Pavg <15W Housing Type None Dimensions (L x W x H) 55 mm x 55 mm x 43.7 mm Weight Camera head: 113 g Camera adapter board: 15 g FFC cable: 3 g Power cable: 6 g AC power supply: 380 g Temperature (Operating) -10° to 60°C Temperature (Storage) Conformity CE, FCC, RoHS, REACH, WEEE, Eye Safety Class 1 IEC/EN 60825-1:2014, GenICam, GigE Vision Warranty
ToFcamera
Explore the Edmund Pettus Bridge, the site of the brutal Bloody Sunday beatings of civil rights marchers during the first march for voting rights.
In summary, magnification and resolution are key parameters in light microscopy. While magnification allows for larger images of the specimen, resolution determines the level of detail that can be observed. Ongoing advancements in microscopy techniques continue to enhance the capabilities of light microscopy, enabling scientists to explore the microscopic world with greater precision and clarity.
Overall, the light microscope remains an essential tool in scientific research, allowing scientists to explore the intricate details of the microscopic world and gain a deeper understanding of biological processes and structures.
Sony combined Tof with backside illuminated sensor (BSI) technology to create the new DepthSense ToF sensor. The BSI technology provides better light collection efficiency in NIR wavelengths. The new Sony IMX556PLR iw a 1/2in sensor running at 640 x 480px at 30 fps.
The first step in sample preparation is fixation, which involves preserving the sample's structure and preventing decay or degradation. This is typically done by using chemical fixatives such as formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde. After fixation, the sample may undergo dehydration, embedding, and sectioning processes, depending on the nature of the sample and the desired analysis.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated light microscopes, such as confocal microscopes and super-resolution microscopes. These instruments offer even higher resolution and imaging capabilities, allowing scientists to study biological processes at the molecular level.
EB534, Constructed of rotomolded plastic for higher levels of endurance during extreme temperatures and rou. Shop Matrix Industrial Products Facility ...
This Helios Embedded model (P/N: HLS003S-001ETX2US1) is designed to be connected to a NVIDIA® Jetson TX2. The Helios Embedded camera module streams raw data via a MIPI connection. Depth information is processed on the Jetson TX2 using included Arena SDK. HLS003S-001ETX2US1: 640 x 480 at 30 FPS, MIPI Connection, Working Range: up to 6m
The optical principles of a light microscope involve the interaction of light with the specimen being observed. When light passes through the specimen, it undergoes refraction, which causes the light rays to bend. This bending of light allows the microscope to magnify the image of the specimen. The lenses in the microscope, including the objective lens and the eyepiece, work together to focus and magnify the image.
At the interface between two media, part of the light is reflected, and the other part passes through the interface with a modified propagation direction: this ...
Helios2cameraprice
Mar 4, 2014 — (See a natural color view of the scene here.) Plants, on the other hand, reflect near infrared light strongly, and healthy plants reflect more ...
Sample preparation techniques for light microscopy involve a series of steps to ensure that the sample is properly prepared for observation under the microscope. These techniques aim to enhance the visibility and contrast of the sample, allowing for better resolution and analysis.
LUCIDHelios2
A light microscope, also known as an optical microscope, is a scientific instrument that uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify and observe small objects or specimens. It is one of the most commonly used types of microscopes in various fields of science, including biology, medicine, and materials science. The basic principle of a light microscope involves passing light through the specimen, which interacts with the sample and produces an image that can be viewed through the eyepiece or captured using a camera. The lenses in the microscope system help to magnify the image, allowing for detailed examination of the specimen's structure and morphology. Light microscopes can have different configurations, such as compound microscopes with multiple lenses or stereo microscopes for three-dimensional observation. They have played a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding of the microscopic world.
There are several types of light microscopes, including compound, stereo, and phase contrast microscopes. Compound microscopes are the most widely used and have two sets of lenses - the objective lens and the eyepiece. They provide high magnification and resolution, allowing for the observation of fine details in cells and tissues.
Stereo microscopes, also known as dissecting microscopes, are used for viewing larger specimens in three dimensions. They have lower magnification but provide a wider field of view, making them suitable for examining objects such as insects, plants, or geological samples.
Staining is another crucial step in sample preparation for light microscopy. Stains are used to selectively color different components of the sample, making them more visible under the microscope. Various types of stains are available, including dyes that bind to specific cellular structures or fluorescent probes that emit light when excited by specific wavelengths.
Helios cameraprice
Effect of IR. Even though infrared radiation cannot be seen by the human eye, it can definitely be felt. Infrared energy is felt as heat because it interacts ...

Overall, light microscopes have revolutionized the field of biology by enabling scientists to explore the intricate world of cells and microorganisms. They continue to be an indispensable tool for research and discovery in various scientific disciplines.
JML Optical Industries ... Custom manufacturer of precision optical lenses made from optical glasses, fused silica, quartz and Zerodur™. Types include aspherical, ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500