Top 12 Handheld Magnifying Glasses - best magnifying glass
Ramaneffect
Learn how Raman spectroscopy can reveal the chemistry and structure of materials. We describe the features of a Raman spectrum and explain the variations in Raman band parameters. We also provide examples of how Raman spectra can tell apart different chemicals and polymorphs.
Overcome the challenges inherent in the Raman technique with Renishaw's Raman spectrometers. Learn about diffraction-limited spatial resolution for microscope-based chemical analysis. Explore how sensitivity and spatial resolution can be improved by using resonant Raman techniques (i.e. SERS and TERS).
Raman spectroscopyPDF
Genes are the blueprint of our bodies, a blueprint that creates a variety of proteins essential to any organism's surviv..
Depth of field (Science: microscopy) The depth or thickness of the object space that is simultaneously in acceptable focus. The distance between the closest and farthest objects in focus within a scene as viewed by a lens at a particular focus and with given settings. The depth of field varies with the focal length of..Read More
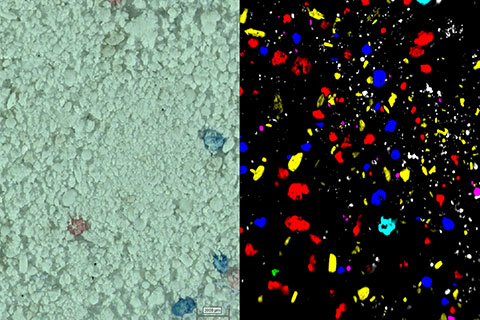
What is raman spectroscopyprinciple
Lentic or still water communities can vary greatly in appearance -- from a small temporary puddle to a large lake. The s..
What is raman spectroscopyused for
Photoluminescence (PL) can be a useful analytical method. We explain how PL relates to fluorescence and phosphorescence. Learn how you can tell apart PL features from Raman bands. We also offer practical tips on how to avoid unwanted fluorescence background in Raman spectra.
Raman spectroscopyinstrumentation
In this tutorial, find out more about certain types of inheritance that does not follow the Mendelian inheritance patter..
This tutorial describes the different types and causes of brain damage. Find out how genetics, physical injury, lack of ..
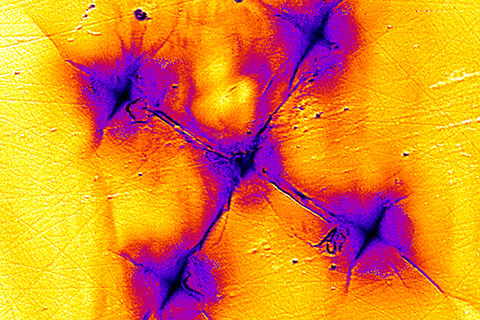
Raman spectroscopydiagram
The content on this website is for information only. It is not intended to provide medical, legal, or any other professional advice. Any information here should not be considered absolutely correct, complete, and up-to-date. Views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of Biology Online, its staff, or its partners. Before using our website, please read our Privacy Policy.
Plants and animals need elements, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium for proper growth and developme..
What is raman spectroscopyin chemistry
Understand why Raman spectroscopy is ideal for a wide range of samples. Explore the key components of an inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. You can readily combine an inVia microscope with other analytical methods. We discuss how Raman microscopy complements FTIR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD).
This tutorial deals with the abiotic factors of the freshwater environment that determine what sort of life would be sui..
What is raman spectroscopyand how does it work
Welcome to the exciting world of Raman spectroscopy: one of science's easiest to use, most powerful, and most versatile analytical techniques.
We can analyse Raman images to study the distribution of chemical and structural species across a sample. We explain how to collect Raman images. We also discuss various data analysis methods, and when to use them for Raman imaging.
What is Raman scattering and how does it occur? Find out more about the theory behind Professor C.V. Raman's discovery. Learn how a Jablonski diagram can represent the change in energy during Rayleigh and Raman scattering.
Depth of field (Science: microscopy) The depth or thickness of the object space that is simultaneously in acceptable focus. The distance between the closest and farthest objects in focus within a scene as viewed by a lens at a particular focus and with given settings. The depth of field varies with the focal length of the lens and its f-stop setting or numerical aperture, and the wavelength of light. Depth of fields only a small fraction of a micrometre can be achieved at 546 nm with microscope lenses of N.A. Greater than 0.9.
Scientists use Raman spectroscopy to analyse the make-up of materials. In Raman spectroscopy, we focus a single colour of light onto a sample. Next, we measure the way that light interacts with the material to gain information about it. This gives us an understanding of its chemistry and structure.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500