The Evolution of the Canon Lens Mount (Video) - lens mounts
Fiber optic cables offer numerous advantages over copper cables, including greater bandwidth and higher speed, as well as immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Fiber optics is a technology that sends data as pulses of light through strands of glass. This method allows high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal loss, making it essential for modern data networks, telecommunications, and the internet.
Thanks to this combination of specialized layers, light can travel largely unimpeded throughout the cable network. A receiver then receives the signal at the end of a link.
Another trend is the use of fiber optics to help meet the demands of 5G networks. This will provide faster and more reliable wireless connectivity, especially in areas with high data demand. Fiber optics will be the backbone for 5G, 5.5G, 6G, and beyond.
Higher performance, longer distances, data centers where the higher cost of supporting electronics is not an issue
From bringing high-speed internet to your fingertips to powering connectivity in smart cities, fiber optics might be one of the most versatile forms of technology currently in existence. Here are a few ways in which it’s used:

The future of fiber optics is exciting, with ongoing research and development aimed at further improving the technology.
The primary purpose of fiber optic technology is to enable the transmission of large amounts of data at high speeds and with greater reliability. This capability is crucial for supporting the vast, interconnected networks that form the backbone of our digital society, allowing for efficient communication and access anywhere, any time.
The importance of fiber optics for fast data transmission is clear, but there's still so much more this technology can do. Continuing to develop the potential of fiber optics not only promises faster communications but also opens doors to entirely new possibilities — from environmental monitoring to improving safety in our interconnected world.
The demand for higher data transmission capacity and speeds continues to grow as network applications expand and organizations collect more data (images, voice, video, etc.) than ever before. This requires cabling that delivers higher bandwidth support. Fiber optic infrastructure is increasingly the go-to medium for datacom networks.
Streaming a movie, making a phone call, or getting an endoscopy may seem like disparate experiences, but they share a common thread: They’re connected by an invisible network of optical fibers. In this guide, we’ll take you through the ins and outs of this powerful technology. You’ll learn what fiber optics are used for, how fiber optic cables work, and the benefits they offer.
RM2011, 20/F, SCITECH Tower, 22 Jianguomenwai Avenue, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China 地址:北京市朝阳区建国门外大街22号赛特大厦20层2011室 联系电话:400-8103435 沪ICP备11037028号-15
Additionally, the miniaturization of fiber optic components and the development of flexible fibers will unlock new applications in Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
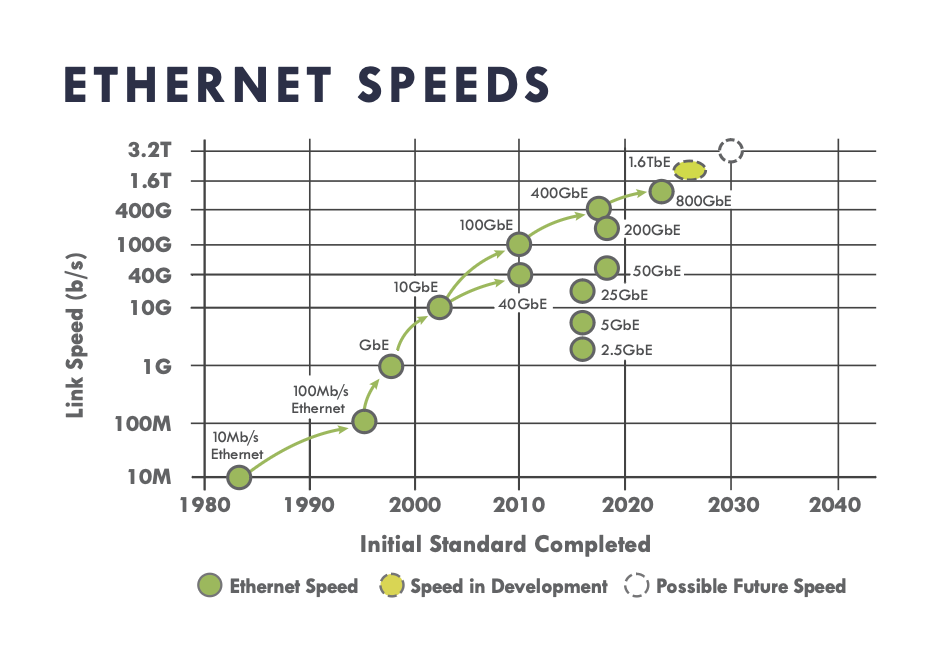
Data transmission rates have been doubling about every five years, as shown in the graph below from the Ethernet Alliance. The big trend is higher data rates through the same fiber optic cables, which will be instrumental in powering 4K and 8K video, virtual reality applications, and other data-intensive technologies.
Fiber optic cabling has some challenges. Although fiber is cost competitive with copper, the electronics needed by a fiber network are more expensive. Fiber optic cable also requires specialized tools, safety rules, and skills in installation, maintenance, and repair; these can be managed with proper equipment, training, and support.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500