The Airy Disc - airy disc
The photometer is a precise measuring instrument that fulfils the highest requirements for light measurements. In accordance with DIN 5032-7, it fulfils the ...
RMSF - root mean square wavefront distortion in comparison with the closest plane; PVF - peak-to-valley wavefront distortion in comparison with the closest plane; D - focusing coefficient of the sample; B4 - 4-th order Zernike coefficient of zonal error; PVZ - peak-to-valley value of zonal error; RMS(W-Z) - root mean square wavefront distortion without zonal error; s - wavefront reconstruction inaccuracy;
The purpose of the illuminator is to provide even, high intensity light at the place of the field aperture, so that light can travel through the condensor to ...
For some applications like CO2-laser optics wavefront shape maintenance is very important. For such optics we check transmitted wavefront distortion (TWD) with interferometer measurements using the following procedure:
Note: this box searches only for keywords in the titles of articles, and for acronyms. For full-text searches on the whole website, use our search page.
Germanium windowscost
Note: the article keyword search field and some other of the site's functionality would require Javascript, which however is turned off in your browser.
Measured at 10.6 µm, interferometer pattern is transferred to personal computer. At the first stage we remove noise and boost contrast of the image using a regular graphics software (see Fig. 3).
Germaniumlens
Some of our skincare has optical diffusers, which disperse light to help minimize the appearance of skin imperfections or uneven tone around the eyes.
Good optical transmission is very important for optical elements; it is the most important parameter for pyrometric applications. However, for the elements of imaging systems it is not enough to have good transmission only. That is why for such elements we carry out more complicated tests.
In the 1860s, optical waves were identified with electromagnetic waves by James Clerk Maxwell. However, a lot of productive research in wave optics was already possible before that, i.e., without understanding the detailed physical nature of light waves.
We use the highest optical grade monocristalline germanium for optical production. However, before coating, we always check the transmission of polished windows in the range of 2.0 - 14.0 µm over clear aperture (see Fig. 1).
Maximal diameter of the lenses that can be processed with the sufficient parameters for the thermography application is 150 mm.
Modern applications of wave optics can be mathematically based on Maxwell's equations as the most fundamental basis; one can directly derive a wave equation from it, which is a second-order differential equation in time and space. For monochromatic light, one obtains the Helmholtz equation. In many cases one uses simplified equations which are approximate but fairly accurate in certain limited domains. For example, one can often neglect the second-order derivative with respect to the <$z$> coordinate for fields propagating largely in <$z$> direction. One also often uses the paraxial approximation. Scalar wave models, ignoring the transverse nature of electromagnetic waves, are also widely used in optics, e.g. for calculating fiber modes. For some applications, one requires more sophisticated models for a full description of electromagnetic wave propagation.
Fig. 1.2. Transmission spectrum of a Ge window with the diameter of 180 mm and thickness of 12.7 mm with BBAR coating (3.0 - 5.0 µm and 8.0 - 12.0 µm).
Thorlabsgermaniumwindow
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Shop by Digi-Flyer · Order by Item NumberOrder by Item #; Featured Shops. Featured Shops; Holiday Shop · Teacher Gift Books · Educator Shop · Featured on ...
Germaniumglass properties
Frequently, numerical software is used for simulating light propagation based on some kind of wave equation. While this approach can in principle be fairly general, computation time and memory requirements can be excessive when not using various restricting assumptions – for example, that light propagates essentially only in one direction. As far as geometrical optics are sufficient for realistic descriptions, that approach is often preferred over wave optics because it is computationally much less demanding.
Fresnels. Show: All Manufacturers, AAdynTech, Altman Stage Lighting, Aputure, Arri, Desisti Lighting, ETC - Electronic Theatre Controls ...
FTIRwindows
Polarization, also called wave polarization, is an expression of the orientation of the lines of electric flux in an electromagnetic field ( EM field ).
Fig. 3. Interferometer graph of transmitted wavefront after noise removal and contrast boost. Window with the diameter of 50.8 mm, thickness of 5 mm.
A very important concept in wave optics is Fourier optics, which essentially means the application of transverse spatial Fourier transforms. This allows both for an intuitive qualitative explanation of various phenomena and design techniques and for quantitative calculations. Such calculations can partly be done with analytical means only.
For several applications like CO2-laser output couplers, parallelism of the window surfaces is very critical. Routine mechanical methods do not allow checking of small wedges, as their accuracy is not sufficient. Interferometer methods allow us to measure the wedge value with accuracy of 1.5 seconds of arc.
Wave optics is usually understood to be a completely classical approach, not taking into account any quantum effects. Quantum optics works with extended theories, where the electromagnetic field is treated on a new basis. Wave properties of light continue to play a central role, although some kind of particle character (→ photons) also became apparent.
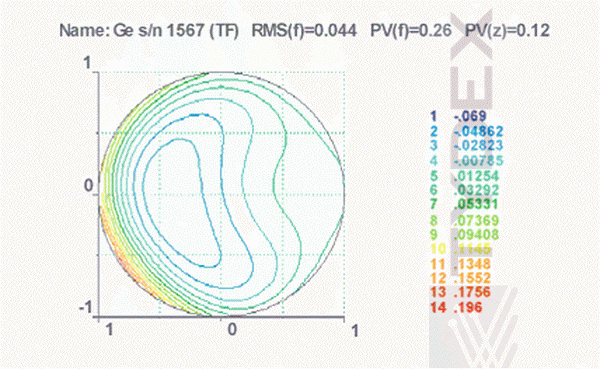
Fig. 5. Reconstructed wavefront compensation of surfaces imperfection presented on a planar plot. Value of TWD over clear aperture 36 mm is equal to 0.14 lambda PVF at 10.6 µm. It corresponds to the value d(n)=3*10-4 over the window aperture. Window diameter = 50.8 mm, thickness = 5.0 mm.
A related term is physical optics, which may be interpreted as the same as wave optics, or in a more restricted sense when certain approximations are applied. The term emphasizes that such wave-based models are physically more realistic than geometrical optics, even if they are not based on full Maxwell's equations.
Germaniumtransmission
BESTLASERPOINTERS.COM. Odin 5000mw High Power Blue Burning Laser Pointer Best 5w Laser For Burning Stuff · YOUTUBE.COM. Odin 3 Watts High Power Blue Burning ...
The material control of Germanium lenses is carried out the same way as for the windows. The control of the spherical surfaces accuracy, however, is made with use of the test glasses. For the radii of curvature (ROC) calculation and the production of the lenses we use the list of available test glasses.
First, we measure the coefficient of internal scattering. This coefficient determines the part of energy that deviates from incident beam direction after transmitting through the window (routine spectrophotometer measurements cannot separate radiation spreading at different angles). Test beam wavelength is 2.5 µm and it is known that for longer wavelengths scattering losses are smaller. Thus, this coefficient can serve as an adequate parameter for estimation of the material internal quality. The aperture diameter of testing setup is about 35 mm. In cases when it is significantly smaller than the window aperture we measure internal scattering in several spots lying on the perpendicular radii (see Tab. 1 and Fig. 2).

Function of the Excitation Filter in a Fluorescence MicroscopeThe excitation filter plays a crucial role in the operation of a fluorescence microscope.
TWD depends on material optical homogeneity and flatness of surfaces. Sometimes it is required to separate the contribution of each factor and provide separate data for optical homogeneity and surfaces flatness.
Early attempts to scientifically describe light and optical phenomena were based on corpuscular theories (developed by René Descartes, Isaac Newton and others), assuming light to consist of small particles which at least in free space travel along straight lines with a velocity. That fits to geometrical optics, where light is represented by geometrical rays. From the 17th century on, scientists like Robert Hooke and Christiaan Huygens followed more closely the evidence for the wave nature of light, and this finally led to the wave theory of light (wave optics), which was mathematically worked out by Huygens (with publication in 1690, see Ref. [1]) and later on in more detail by the civil engineer Augustin-Jean Fresnel. Wave optics was not immediately accepted as an appropriate model for describing the nature of light; only in the early 19th century, it became really widely accepted in the scientific community, particularly after observation of the so-called Arago spot by Dominique-François-Jean Arago, with important contributions from Augustin-Jean Fresnel. Based on wave theory, one could now well describe the following important optical phenomena:
Fig. 1.1. Transmission spectrum of a Ge window with the diameter of 180 mm and thickness of 12.7 mm without BBAR coating (3.0 - 5.0 µm and 8.0 - 12.0 µm).
Following operations are performed by a specially designed interferometer graph analysis software. First, we determine the coordinates of fringes. Then we approximate fringes with two-dimensional power polynomials. After that calculation of TWD, parameters and measurements accuracy estimation are provided (see Table 2). Finally we reconstruct wavefront topography and present it on planar and 3-d plots (see Fig. 4).
Tydex produces BBAR coated Germanium optics for pyrometry and thermography. All elements are strictly tested to provide the best quality of the material and the coating.
Germanium Windows12
Jan 6, 2023 — Applications · 1. Optical power meters · 2. LD monitors · 3. Radiation thermometers · 4. Flame monitors (flame detection) · 5. Moisture ...
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
The lenses and the windows can be coated with various types of anti-reflection and protective coatings including hard carbon coating (“diamond-like coating” or DLC).
Interferometer measurement of surfaces flatness is provided at 0.633µm, in a phase-measuring regime. Then interferometer graphs are processed in the same way as described above. The data of surfaces flatness is presented in the same form as data of TWD (planar and 3-d plots, table of parameters).
Germanium Windows11

Fig. 6. Comparative transmission curves of Ge windows (4.5mm thick) coated with different types of anti-reflection and protective coatings.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
Edmund Optics services its customers through two specialized solutions: its Marketplace and its Advanced Manufacturing services! The Edmund Optics Marketplace ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500