Testing Color Contrast in Non-Web Documents and Images - image color test
Numerical Aperture calculator
*Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademarks of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, these products.†Next Generation Science Standards and NGSS are registered trademarks of Achieve. Neither Achieve nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
Having said that, from a purely scientific point of view (and it would be interesting to learn if the ‘official’ Zeiss .czi format definition differs from this), the ‘effective’ numerical aperture would be the angle of acceptance of illumination (refractive index of the medium taken into account as per the Abbe formula) that was permitted during the experiment regardless of the maximum NA specs of the lens.
Numerical apertureofoptical fiber
Na of a lensformula
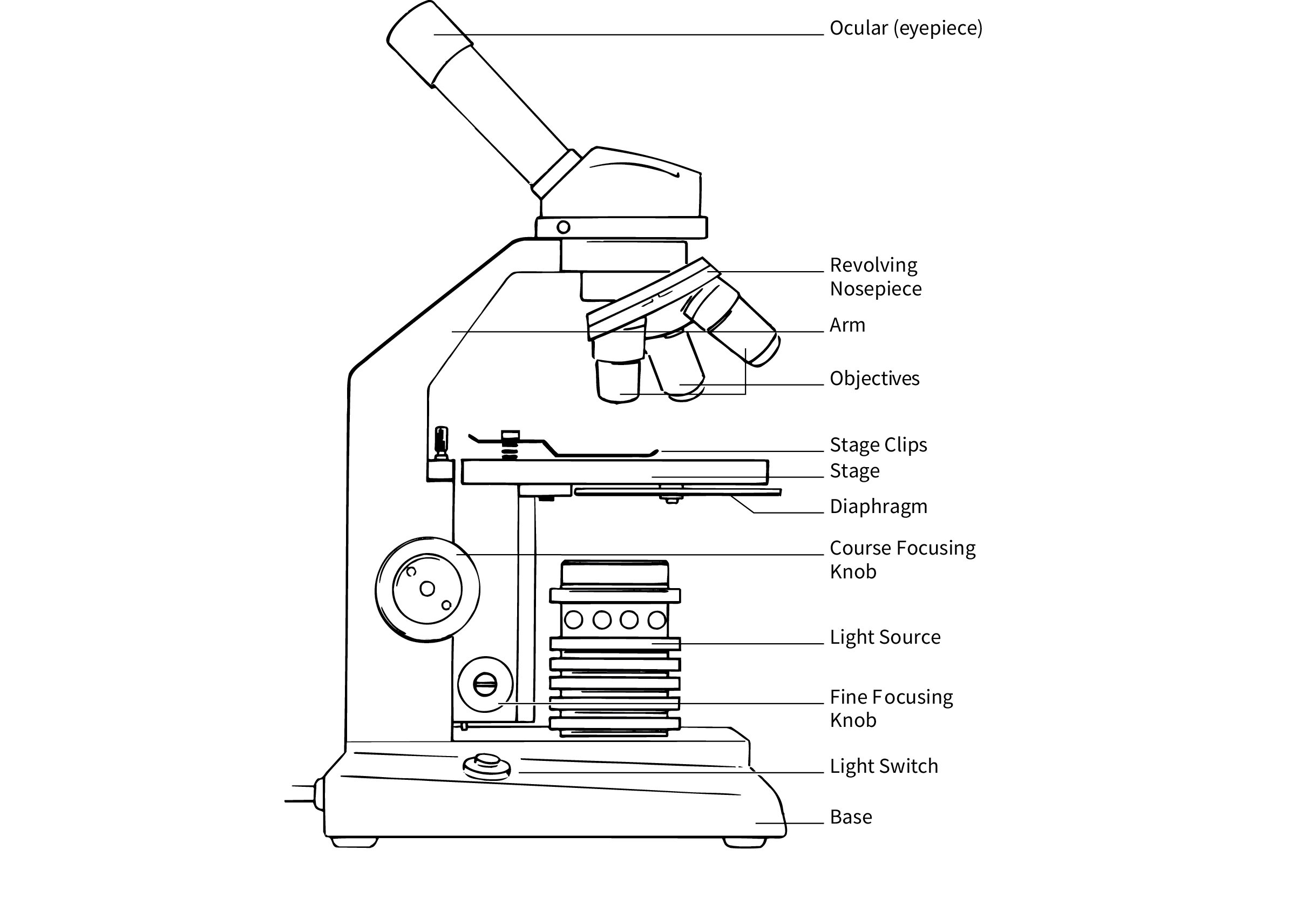
Compound microscopes are tools which allow the human eye to view tiny objects that would otherwise not be observable. Becoming familiar with the functional parts and terms of the compound microscope is a great way to increase you understanding. See below for these parts and terms for a compound microscope.
Hi, Going through a .czi metadata to extract some information I ran into both the NA 0.95 of the lens and a value set as the effective Numerical aperture a smaller value at 0.8. I wonder if anyone here can help me find this difference and from there to know which one theoretically is the one to be considered in the computatation of the point spread functio.

I much prefer open source software, hardware and documentation for scientific transparency. The companies can still make money selling their expensive stuff - open source doesn’t mean they have have to give their kit (or software) away for free.
Numerical aperture formula
The most common laboratory scopes, the compound microscope (also referred to as light or compact microscope) and the stereomicroscope (also referred to as a dissecting microscope), have different uses.Compound microscopes have a glass lens contained in the ocular (the eyepiece typically has 10X magnification), and a lens in each objective (4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X are the common objectives found in microscopes used in education, although not all microscopes have a 100X objective). Magnification is simply the ratio of the object size viewed through the lens to that of the actual size of the object.
Essentially a compound microscope is a high magnification microscope that uses 2 lenses to compound (multiply) the level of magnification. The first lens is referred to as the objective lens and typically has a 4x, 10x, 40x or 100 magnification ability). The second lens is known as the eyepiece lens. This lens compounds or multiplies the magnification of the objective lens by another 10x resulting in a total magnification of 40x, 100x, 400x and 1000x.In short, a compound microscope is a high power microscope that uses two lenses to increase magnification of tiny objects that would otherwise not be observable.
Numerical apertureofmicroscope
The NA of the lens is the maximum NA rating it can practically handle using the immersion medium for which is was designed (air, water, glycerol, DIN oil, etc.). You can easily reduce this in practice for any experiment by (e.g.) stopping down the condenser iris and/or using a different mounting and immersion medium to the one for which the NA of the lens was measured at during the lens design and manufacture stage (e.g. using water or glycerol immersion instead of DIN oil with a lens designed for DIN oil immersion will reduce the effective NA of the experiment with that lens to below its rated standard).

Hello and welcome to the Forum! I cannot give you a definitive answer but an opinion. This is because Zeiss ZEN is very much NOT open source software and you need to get a license just to get access to their file format details but maybe someone here already has this or knows the answer more definitively.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500