Test Patterns - Gallery - TouchDesigner forum - test patterns
Even a glass lens should not be cleaned with acetone if it has a plastic mount, since the acetone could dissolve plastic and deposit it on the lens surface. Alcohol would usually be suitable, but in case of doubt one should ask the supplier.
Various solvents may be appropriate, depending on the material and the type of contamination to be removed. For example, distilled or deionized water may be suitable in some cases, but not when removing fat e.g. from fingerprints. Reagent-grade isopropyl alcohol, methanol or acetone are more effective for such purposes. It is essential to use suitable gloves not only to protect the skin of the fingers (which is degraded particularly by acetone), but also to avoid that fat from the skin is dissolved and then deposited on optical surfaces. Performing cleaning processes slowly gives the solvent more time to dissolve contaminants like fat.

All necessary code and instructions for running the axial correction macro are provided in the Supplementary Software and Box 1.
Of course, one should never simply blow with the mouth against optical components, since that way one could easily contaminate them with saliva. For occasional use, there are disposable compressed air devices with which one can direct bursts of clean and dry air to optical surfaces. With suitable nozzles, one may even reach areas which would be difficult to clean with any other tools.
Optical aberration
Scanning Electron Microscopy is used to examine morphology (physical features) of size ranging from many microns to a few nanometers. The advantages over an ...
In conjunction with intense laser beams, dust and smudges may not only lead to performance degradations, but even to permanent damage of optical components, when such contaminations are burned in.
Keller, H. E. Objectives for confocal microscopy. in Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy (ed Pawley, J. B.) (Springer, 1995).
Diel, E.E., Lichtman, J.W. & Richardson, D.S. Tutorial: avoiding and correcting sample-induced spherical aberration artifacts in 3D fluorescence microscopy. Nat Protoc 15, 2773–2784 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0360-2
It is generally recommended not to repeatedly wipe back and forth on optical surfaces because that way one may only redistribute contaminants. Instead, it is often better to carefully drag a cloth or lens tissue, wetted with a solvent, across the surface just once, or several times from the center in different directions. Some amount of pressure, which should of course not be excessive, may make the cleaning procedure more effective.
Gibson, S. F. & Lanni, F. Experimental test of an analytical model of aberration in an oil-immersion objective lens used in three-dimensional light microscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 9, 154–166 (1992).
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

Buy Fresnel Lens LED Lighting Lenses. Newark Electronics Canada offers fast quotes, same day dispatch, fast delivery, wide inventory, ...
We thank S. Piccinotti and L. Rubin for providing organoid samples. We thank the Harvard Center for Biological Imaging for infrastructure and support. J.W.L. was supported by the following funding sources: National Institutes of Health grants P50 MH094271, U24 NS109102, and U19 NS104653 and Department of Defense MURI award GG008784.
Visser, T. D., Oud, J. L. & Brakenhoff, G. J. Refractive-index and axial distance measurements in 3-D microscopy. Optik 90, 17–19 (1992).
球 差
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Jun 19, 2018 — A MAGNIFYING glass is used to see smaller images or object bigger. Do you know how it works? Let's understand the physics of magnifying ...
If the drop-and-drag method is not sufficient, one may have to carefully wipe the surface with some moderate pressure, using multiple layers of lens tissue which are folded and held with a plier. Only the fold of the tissue is used to touch the optical surface, and is slightly soaked with solvent. Of course, one must avoid touching the optical surface with the plier.
Peer review information Nature Protocols thanks Chrysanthe Preza and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Kim, B. & Naemura, T. Blind depth-variant deconvolution of 3D data in wide-field fluorescence microscopy. Sci. Rep. 5, 9894 (2015).
There are also cans containing a liquid which evaporates as a dusting gas and can produce larger volumes of gas over time. One should hold them upright during use and not shake them before use because otherwise droplets of fluid may emerge.
Carlsson, K. The influence of specimen refractive-index, detector signal integration, and nonuniform scan speed on the imaging properties in confocal microscopy. J Microsc.-Oxford 163, 167–178 (1991).
Hell, S., Reiner, G., Cremer, C. & Stelzer, E. H. K. J. Microsc. 169, 391–405, (1993): https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03315.x
Note: the article keyword search field and some other of the site's functionality would require Javascript, which however is turned off in your browser.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
Chromatic aberration
Similar considerations as for lenses applied to laser mirrors, only that those are often substantially more sensitive. A frequently used cleaning method is to slowly drag a single sheet of lens tissue, soaked with a drop of a suitable solvent, once across the mirror surface, holding the tissue only at the sides without applying additional pressure.
Aberration theory
It is not advisable to handle optical components which have just taken from a significantly cooler room, for example. One should better let them acquire the room temperature first. Additional stress due to temperature gradients may make optical components more sensitive to cleaning procedures.
Hell, S., Reiner, G., Cremer, C. & Stelzer, E. H. K. Aberrations in confocal fluorescence microscopy induced by mismatches in refractive-index. J. Microsc. 169, 391–405 (1993).
Model, M. A., Fang, J., Yuvaraj, P., Chen, Y. & Zhang Newby, B. M. 3D deconvolution of spherically aberrated images using commercial software. J. Microsc. 241, 94–100 (2011).
Renier, N. et al. iDISCO: a simple, rapid method to immunolabel large tissue samples for volume imaging. Cell 159, 896–910 (2014).
Engelbrecht, C. J. & Stelzer, E. H. Resolution enhancement in a light-sheet-based microscope (SPIM). Opt. Lett. 31, 1477–1479 (2006).
In some cases, proper inspection is not possible, e.g. because critical parts are not well accessible or tiny contaminations are sufficient for spoiling performance. This may easily be the case for interferometer mirrors, for example. One may then have to use blind cleaning procedures, where success is assessed only by testing of the optical device performance later on. This can be tedious particularly when multiple mirrors are in a setup and it is difficult to find out which one degrades the performance.
Coma aberration
Schmidt, N. C., Kahms, M., Huve, J. & Klingauf, J. Intrinsic refractive index matched 3D dSTORM with two objectives: comparison of detection techniques. Sci. Rep. 8, 13343 (2018).
Even more effective cleaning is possible by wiping the surface with folded tissue held between fingers (with gloves), applying some more pressure. That more aggressive technique increases the risk of damage, however.
Preza, C. & Conchello, J. A. Depth-variant maximum-likelihood restoration for three-dimensional fluorescence microscopy. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 21, 1593–1601 (2004).
Jonkman, J., Brown, C. M., Wright, G. D., Anderson, K. I. & North, A. J. Tutorial: guidance for quantitative confocal microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 15, 1585–1611 (2020).
Concave mirror
Note that small amounts of a solvent will rapidly evaporate after application, leaving residues if it has solved some fat, for example. Therefore, it is essential that such contaminants are dragged away, rather than only spread on the surface. Ideally, most of the solvent itself is also dragged away by the tissue; one should therefore avoid using excessive amounts of solvent.
A frequent risk is that such instructions are forgotten or lost at the point where they would be needed. To avoid that, it is advisable to use appropriate filing systems (e.g. on paper or computers) so that such documents can be found and retrieved when needed.
It can also be essential to distinguish contaminations from damaged spots; obviously it won't help to wipe over pits and scratches, possibly increasing the damage further.
by G Smith · 2001 · Cited by 245 — More negative values will give a positive aberration. Therefore, we may expect that the posterior surface probably contributes a small amount of positive ...
Field curvature
Ideally, the cleaning of optical elements is unnecessary because any contaminations are avoided. Also, one should of course avoid any unnecessary contaminations during cleaning procedures. Some suitable measures are briefly explained in the following:
Patwary, N., King, S. V., Saavedra, G. & Preza, C. Reducing effects of aberration in 3D fluorescence imaging using wavefront coding with a radially symmetric phase mask. Opt. Express 24, 12905–12921 (2016).
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Anti-Reflective Coating - Standard, We offer 4 tiers of Anti-Reflective Coatings (ARC). The better the coating the higher the cost. Standard ARC reduces glare ...
Note: this box searches only for keywords in the titles of articles, and for acronyms. For full-text searches on the whole website, use our search page.
Heine, J. et al. Three dimensional live-cell STED microscopy at increased depth using a water immersion objective. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89, 053701 (2018).
There are devices for ultrasonic cleaning, where optical components such as lenses are immersed in a cleaning solvent (e.g. a solution of optical soap) and exposed to intense ultrasound. Subsequently, they are rinsed with fresh solvent. This method may be useful for removing more persistent dirt, but is too aggressive e.g. for many ruled diffraction gratings.
Sigma lenses for Nikon will bring your images to the next level. Sigma F-mount lenses are compatible with all Nikon FX and DX format DSLRs, and easily adapt ...
Many lenses and optical filters are made from relatively robust glass materials which can reasonably well be cleaned with appropriate procedures and tools.
When cleaning optical surfaces, one should always be aware that they may have thin coatings (e.g. anti-reflection coatings) which are more sensitive than the bulk material below. Of course, one may not easily recognize the presence of a coating. Some coatings can temporarily incorporate water (e.g. in porous TiO2 layers) which modifies the optical properties; one should then of course avoid water as a cleaning agent.
Schneider, C. A., Rasband, W. S. & Eliceiri, K. W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675 (2012).
Please do not enter personal data here. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him, e.g. via e-mail.
Optical elements and systems are usually operated in a rather clean environment, e.g. within a housing which is protected against dust and dirt with optical windows, or in a clean laser laboratory. Nevertheless, it is sometimes necessary to clean optical elements like laser mirrors, lenses, laser crystals and nonlinear crystals – for example,
Sheppard, C. J., Gu, M., Brain, K. & Zhou, H. Influence of spherical aberration on axial imaging of confocal reflection microscopy. Appl. Opt. 33, 616–624 (1994).
Zhang, Q. et al. Quantitative refractive index distribution of single cell by combining phase-shifting interferometry and AFM imaging. Sci. Rep. 7, 2532 (2017).
Monochromatic Lights ... Looking for an Optical Flat for your Monochromatic Light? For a comprehensive list of our available single and double surface flats in ...
Ghosh, S. & Preza, C. Three-dimensional block-based restoration integrated with wide-field fluorescence microscopy for the investigation of thick specimens with spatially variant refractive index. J. Biomed. Opt. 21, 46010 (2016).
Zernike polynomials
Note, however, that perfect cleanliness is not essential in all cases. For example, some dust particles on a photographic objective will not produce isolated defects in photographic images because they are not imaged to the light sensor and only lead to well spread modifications which are hard to detect and thus hardly disturbing.
The idea for calculating axial distortion correction factors as described in this tutorial was conceived by D.S.R. and J.W.L. E.E.D. and D.S.R. carried out experiments and analyzed data. D.S.R., J.W.L. and E.E.D. wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editing the final manuscript.
Using our advertising package, you can display your logo, further below your product description, and these will been seen by many photonics professionals.
Obviously, inspection tools can be used effectively only when it is made convenient e.g. to sit at an appropriate height and to lay down or mount the inspected part on clean and soft surfaces. Sufficient illumination is also critical.
Contaminations which are only lightly attached to optical components, for example dust particles, can often be removed with compressed air – a method which minimizes the risk of damage and can be applied even to particularly sensitive parts such as metal-coated mirrors and diffraction gratings. (Only in few cases such as pellicle beamsplitters, there is a substantial risk of damage.)
High-quality gloves are available for optics cleaning, for example nitrile clean room gloves which are thin enough to give sufficient haptic feedback and at the same time sufficiently resistant for avoiding puncture. Some gloves are optimized for good grip, reducing the risk of dropping sensitive components. When using latex gloves, these should be powder-free. For some operations, fingercots may be sufficient, which can be more comfortable to wear.
202024 — Here, we break down the anatomy of an objective lens into easy-to-understand terms and discuss the common parts that make up an objective.
In some cases, the suppliers of optical components provide detailed instructions for cleaning. It is advisable to carefully observe them in order to clean most successfully and not to lose free replacement options.
It is common to use soft lens tissues, e.g. as disposable wipes which can effectively bind dust while not scratching sensitive surfaces or releasing hair. Also, there are microfiber cleaning cloths which may be used several times. For larger surfaces, one may use precision wiping tissues, which are far cleaner than standard household wipes, for example. Various similar tissues and cloths are available, including pre-moistened towelettes.
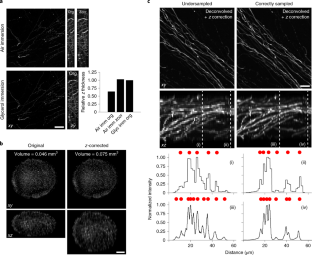
Spherical aberration (SA) occurs when light rays entering at different points of a spherical lens are not focused to the same point of the optical axis. SA that occurs inside the lens elements of a fluorescence microscope is well understood and corrected for. However, SA is also induced when light passes through an interface of refractive index (RI)-mismatched substances (i.e., a discrepancy between the RI of the immersion medium and the RI of the sample). SA due to RI mismatches has many deleterious effects on imaging. Perhaps most important for 3D imaging is that the distance the image plane moves in a sample is not equivalent to the distance traveled by an objective (or stage) during z-stack acquisition. This non-uniform translation along the z axis gives rise to artifactually elongated images (if the objective is immersed in a medium with a higher RI than that of the sample) or compressed images (if the objective is immersed in a medium with a lower RI than that of the sample) and alters the optimal axial sampling rate. In this tutorial, we describe why this distortion occurs, how it impacts quantitative measurements and axial resolution, and what can be done to avoid SA and thereby prevent distorted images. In addition, this tutorial aims to better inform researchers of how to correct RI mismatch–induced axial distortions and provides a practical ImageJ/Fiji-based tool to reduce the prevalence of volumetric measurement errors and lost axial resolution.
Ghosh, S. & Preza, C. Fluorescence microscopy point spread function model accounting for aberrations due to refractive index variability within a specimen. J. Biomed. Opt. 20, 75003 (2015).
It is often useful to have suitable inspection tools, with which one e.g. clearly see dust particles, fingerprints and the like. They also allow one to monitor the success of cleaning attempts. One may use an instrument like a loupe, a magnifying glass or a microscope in conjunction with suitable illumination.
Visser, T. D. et al. Optik 90, 17–19 (1992): https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285251956_Refractive_index_and_axial_distance_measurements_in_3-D_microscopy
It has a very important role in imaging, as it forms the first magnified image of the sample. The numerical aperture (NA) of the objective indicates its ...
2023622 — After 56 years supplying surplus and new electronic parts and supplies, we have decided to call it quits. They expect to fully close shop before the end of ...




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500