Synonyms of fluorescence - fluorscence
An optical table is the foundation for building an optical experiment. For over 50 years, Newport's optical tables have contributed to many scientific and industrial success stories across various subjects from fundamental physics to semiconductor manufacturing. Our optical table solutions are designed to fit any performance, budget and delivery need. From very demanding applications like confocal microscopy, spectroscopy or interferometry, to applications under a small budget, Newport has the right optical table for you. When you choose a Newport optical table, you have chosen not only the proven superior performance and quality, but also our wealth of knowledge, experience and committed product support along your way. For application-specific photos, see our optical table galleries on Flickr.
Sample Size and Depth of Field: Compound microscopes are designed to observe thin, transparent specimens placed on glass slides. They offer a narrow depth of field, allowing clear focus on one plane at a time. Other microscopes, like stereo or electron microscopes, can accommodate larger specimens or samples with more depth, providing a wider depth of field.
The transmissibility curve shows the mechanical filtering properties for the isolator leg—in other words, it gives an indication of how much floor vibration will be transmitted through the leg to the table top. It is a relative measure given as a ratio of vibration at two points: one on the top of the isolator and one on the floor.
Condenser Lens: The purpose of the condenser lens is to focus the light onto the specimen. Condenser lenses are most useful at the highest powers (400x and above). Microscopes with in-stage condenser lenses render a sharper image than those with no lens (at 400x). If your microscope has a maximum power of 400x, you will get the maximum benefit by using a condenser lenses rated at 0.65 NA or greater. 0.65 NA condenser lenses may be mounted in the stage and work quite well. A big advantage to a stage mounted lens is that there is one less focusing item to deal with. If you go to 1000x then you should have a condenser lens with an N.A. of 1.25 or greater. All of our 1000x microscopes use 1.25 Abbe condenser lens systems. The Abbe condenser lens can be moved up and down. It is set very close to the slide at 1000x and moved further away at the lower powers.
Meets competitor’s top performance models, featuring 2 precision tuned dampers, field upgradeable to hybrid SmartTable performance
Moreover, because our tuned mass dampers can be tuned to very low frequencies, even Newport's doubled table tops that have low resonance frequencies can be damped –broadband damping, by contrast, could not achieve as good of a result in such a scenario.
Microscopeparts and functions
Integrity VCS featuring passively damped table top is the best value table system to support basic optical research and development applications, at universities, corporate labs and manufacturing floors. Theses systems deliver comparable damping and isolation performance to other optical platforms at a more affordable price – while also offering accessories to improve platform requirements.
Applications: Compound microscopes are commonly used in fields such as biology, medicine, and research, where detailed examination of small structures is required. Other microscopes, such as stereo microscopes, are utilized for examining larger objects or conducting dissections. Electron microscopes are used for high-resolution imaging of nanoscale structures.
What is objectivelensinmicroscope
Diaphragm or Iris: Many microscopes have a rotating disk under the stage. This diaphragm has different sized holes and is used to vary the intensity and size of the cone of light that is projected upward into the slide. There is no set rule regarding which setting to use for a particular power. Rather, the setting is a function of the transparency of the specimen, the degree of contrast you desire and the particular objective lens in use.
Optical table systems can be characterized by compliance curves for the optical table top and transmissibility curves for the isolation provided by the table supports. Taken together, these two plots show the primary performance capabilities of the optical table system. Knowing how to interpret the two graphs is vital when choosing the most appropriate table system for your application.
Historians credit the invention of the compound microscope to the Dutch spectacle maker, Zacharias Janssen, around the year 1590 (more history here). The compound microscope uses lenses and light to enlarge the image and is also called an optical or light microscope (versus an electron microscope). The simplest optical microscope is the magnifying glass and is good to about ten times (10x) magnification.
Whichlensis used inmicroscopeconvex or concave
For the most demanding applications or challenging environments, our S-2000A Stabilizer™ Series pneumatic vibration isolators with automatic re-leveling are the industry's highest performing table supports. For experiments needing lower levels of vibration isolation, SL Series LabLegs™ also provide pneumatic vibration isolation at a very affordable price when automatic re-leveling is not required. And if vibration isolation is not required, RL Series LabLegs™ offer rigid high load support of optical table tops.
Advantages of choosing separate table tops and supports include more customization – and thus, constructing the optimal system for your application and environment – higher payloads per isolator and maximum storage capacity. Disadvantages of separate table tops and supports include more difficult setup, less mobility and flexibility than combined systems, difficulty in adding casters and potentially higher prices.
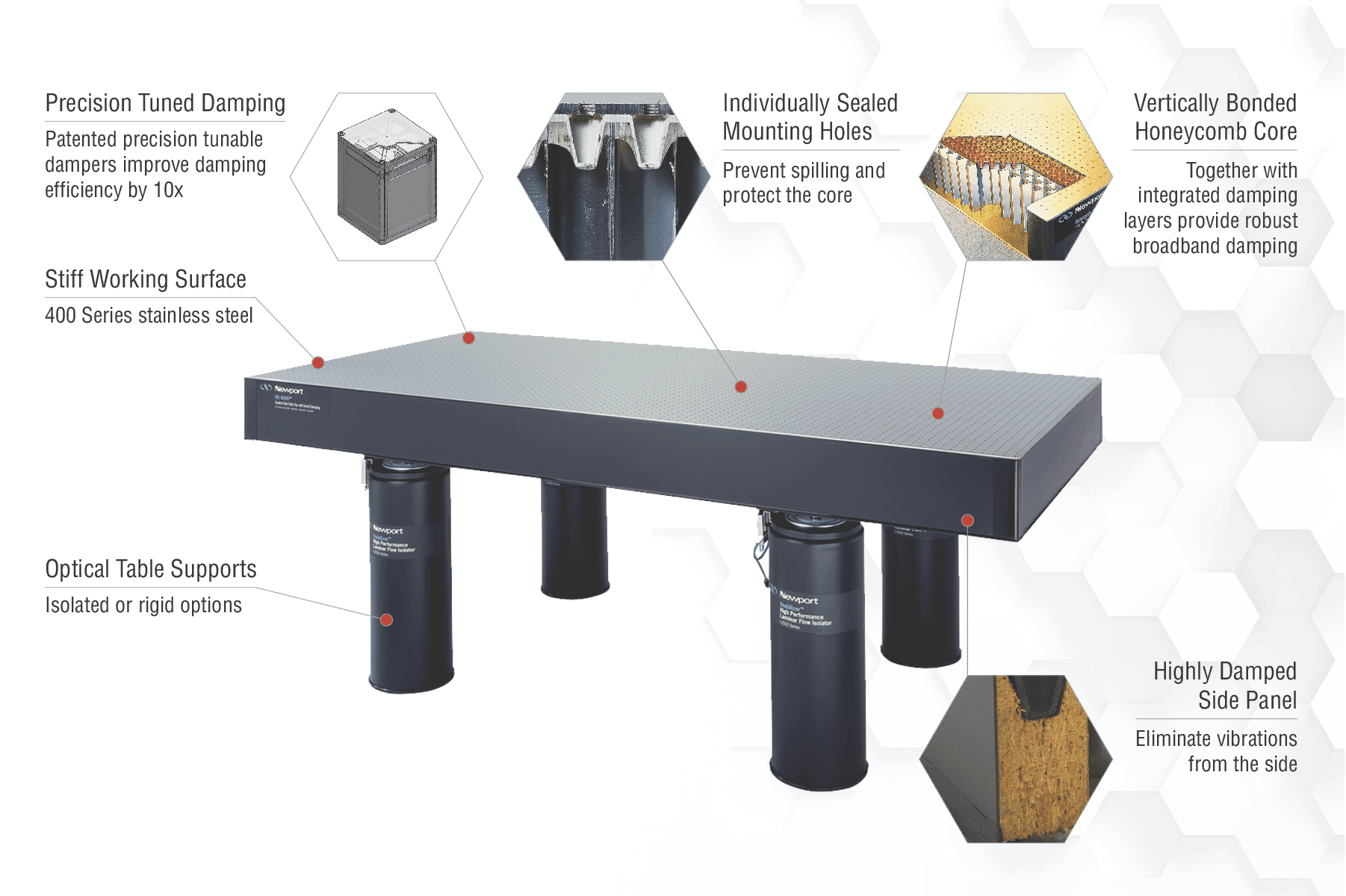
If the optical table will be in an environment subject to seismic floor vibrations – for example, from foot and vehicle traffic and building vibrations – then the type of optical table supports should be selected depending on how much vibration isolation is needed by your application. Newport offers pneumatic vibration isolators, passive air mounts and rigid legs to support optical tables.
Q: What is the typical thermal bending of optical tables and what type of table should I choose if thermal stability is needed for my application?
Lens of microscopeparts
The short answer is, yes it does matter. Thickness is considered as structural mass of a structure, and thus contributes to the overall stiffness of the optical table. Thicker optical table provides better stiffness and smaller static deflection under the load. Dynamic deflection would also be reduced, as thicker optical tables require taller honeycomb structures inside without increasing the overall mass significantly. Therefore the stiffness to mass ratio is improved so the rigid body frequency zone of the table is expanded. The most popular thickness choices are 8" (203 mm) and 12" (305 mm). For increased stiffness and minimized deflection, choose 18" (457 mm) and above. For cost effective and less demanding applications choose 6" (152 mm).
Stage with Stage Clips: The flat platform where you place your slides. Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down.
Objective Lenses: Usually you will find 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope. They almost always consist of 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x powers. When coupled with a 10x (most common) eyepiece lens, total magnification is 40x (4x times 10x), 100x , 400x and 1000x. To have good resolution at 1000x, you will need a relatively sophisticated microscope with an Abbe condenser. An Abbe condenser is composed of two lenses that control the light that passes through the specimen before entering the objective lens on the microscope. The shortest lens is the lowest power, the longest one is the lens with the greatest power. Lenses are color coded and if built to DIN standards are interchangeable between microscopes. "DIN" is an abbreviation of "Deutsche Industrial Normen". This is a German standard that has been adopted internationally as an optical standard used in most quality microscopes. A typical DIN standard microscope objective lens has a 0.7965" (20.1mm) diameter threads, 36 TPI (threads per inch), and a 55º Whitworth. Many high power objective lenses are retractable (i.e. 40XR). This means that if they hit a slide, the end of the lens will push in (spring loaded) thereby protecting the lens and the slide. All good quality microscopes have achromatic, parcentered, parfocal lenses.
How to Focus Your Microscope: The proper way to focus a microscope is to start with the lowest power objective lens first and while looking from the side, crank the lens down as close to the specimen as possible without touching it. Now, look through the eyepiece lens and focus upward only until the image is sharp. If you can't get it in focus, repeat the process again. Once the image is sharp with the low power lens, you should be able to simply click in the next power lens and do minor adjustments with the focus knob. If your microscope has a fine focus adjustment, turning it a bit should be all that's necessary. Continue with subsequent objective lenses and fine focus each time.
Broadband damping absorbs and dissipates vibration energies across a broad range of frequencies. It is widely used in anti-vibration tables to reduce the structural vibrations of the tabletop. Typically the broadband damping involves energy absorption materials such as foam, rubber or elastomers. It may also involve mass blocks/plates and rubbers installed along the side of the table to absorb moderate amount of vibrations for a broad frequency range that covers the resonances of a standard size optical table. Broadband damping does not target any specific table resonance or any specific set of frequencies; instead it absorbs and dissipates vibration energies uniformly across the frequency range. It is usually affordable and good for applications that do not require high damping performances. Newport's RPR Reliance™ Series broadband damped optical tables represented the state-of-the-art optical table tops before the advent of tuned damping, and they still offer good value for many less stringent applications.
A: Vibrations transmitted from the floor to the tabletop is handled by isolators. Those floating legs provide isolation to your experiment and eliminate surrounding floor vibrations like building sway, street traffic or even people walking nearby. Damping, on the other hand, targets tabletop and minimizes its resonances caused by the rest of your experiments or environment. This part is handled mainly by tabletop. Combined together, they kill vibrations and make your optical table the cornerstone of your experiment.
The compliance curve shows the dynamic response of the table top in a free space condition—in other words, it gives an indication of how the surface will change shape in response to vibration. Compliance curves are transfer function curves that show the position response of a point on the table surface to a time variant force applied at the same point. In practice the force is generally applied with a calibrated hammer, which outputs a signal proportional to the force with which it hits the table.
Choose products to compare anywhere you see 'Add to Compare' or 'Compare' options displayed. Compare All Close
Yes, opt-in. By checking this box, you agree to receive our newsletters, announcements, surveys and marketing offers in accordance with our privacy policy
Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: This is the part of the microscope that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change power.
Magnification: Compound microscopes are designed for higher magnifications, typically used for observing microscopic details. Other microscopes may have lower magnification capabilities, suitable for larger specimens or samples.
It's important to note that the term "other microscope parts" is quite broad and can include various microscope types with different designs and features. The above differences are generalized and may not apply to every microscope outside the category of compound microscopes.
Q: Why use composite wood for side panels? Isn’t wood more vulnerable compared to steel in terms of environmental instability?
An optical table is a stiff platform supporting vibration sensitive equipment. The most critical vibration characteristic of an optical table is its resonances. This is because the table is designed to be as stiff as possible and acts as a rigid body when its resonances are not excited. In other words, when the table is a rigid body there is no dynamic deflection, and the beam alignment on top of the table would not be disturbed. However, a typical optical table has one or sometimes two major resonances and several minor ones. Therefore, damping is needed to reduce the resonance amplitudes and minimize the system deflection when the resonances are excited by ambient vibrations. Three types of damping methodologies are available: Broadband, Tuned Mass, and Active/Hybrid.
Optical table system with frame - Meets competitor’s top performance models, featuring 2 precision tuned dampers. Casters included and tabletop could be bolted to frame using provided safety clips. Field upgradable to SmartTable active damping using IQ upgrade kits.
A: Surprisingly, we don’t want our tables to be too heavy. What matters is the stiffness to mass ratio, and we want this ratio to be as large as possible so that the table has a higher stiffness and expanded rigid body zone. Granite is very flat but it is also very heavy. The mass in granite does not contribute to its structural stiffness; therefore granite is not the ideal candidate for optical table top. Instead, honeycomb structure provides less mass and better stiffness and delivers the best vibration control performance.
Illuminator: A steady light source (110 volts) used in place of a mirror. If your microscope has a mirror, it is used to reflect light from an external light source up through the bottom of the stage.
Other tests such as non-contact laser scanning vibrometry (LSV) is also sometimes performed. However, LSV test could lead to erroneous conclusions if the test is not staged properly. It requires the laser head to be calibrated and mounted on a tall structure in order to capture the entire table surface. Moreover, it requires a calibrated reference signal for excitation in order to get meaningful data. It is used widely for testing complicated miniature structures, instead of a well-defined large structure such as optical table.
Microscopeparts
SmartTable OTS featuring actively damped table top was designed specifically for advanced applications in live cell imaging, semiconductor metrology, and precision optical alignment and testing. The integrated accessories and ergonomic designs available with the SmartTable OTS deliver exceptional performance, flexibility and upgradability. The SmartTable OTS is the only optical table system that is field upgradable with three levels of table damping performance and two levels of isolation performance, which could satisfy current requirements but also allow the flexibility needed for future performance improvement.
Table systems were born due to the increasing demand of easier set up, mobility and accessories capabilities. They usually feature a robust frame system with either rigid support or integrated isolators and could be combined with various accessories such as casters, overhead shelves, hip guards, side shelves, laser safety curtains, etc.
Illumination: Compound microscopes often have built-in illumination systems, such as a substage light source, condenser, and diaphragm, to provide transmitted light through the specimen. Other microscopes, like dissecting or fluorescence microscopes, may utilize different lighting techniques or illumination configurations.
Newport’s patented precision tuned dampers (US patent 8857585) are specially designed with precise tuning capabilities and immunity to load changes up to several hundred pounds. With each damper targeting one major resonance mode of the table, a standard optical table's resonance amplitudes are effectively reduced within a broad range of frequencies. Our RS4000 Series features 6 precision tuned dampers and delivers the best passive damping performance for applications requiring a critical level of damping, such as live cell imaging, high resolution imaging and interferometry. The RS2000 Series features 2 precision tuned dampers to selectively eliminate two fundamental structural table modes and their entire harmonics and is ideal for applications such as biomedical imaging, scanning microscopy, spectroscopy and electrophysiology.
Objective Lenses: Compound microscopes have multiple objective lenses mounted on a rotating nosepiece, typically with magnifications ranging from 4x to 100x or higher. Other microscopes, such as dissecting or stereo microscopes, usually have fixed magnification lenses.
A: Optical tables are not complex structures. Modes of rectangular plate-like structures like optical tables had been discussed and depicted in numerous handbooks and textbooks. The most direct way is to compare the compliance curves. Compliance test is the vibration control industry standard to test the vibration damping characteristics of a structure; it is well documented and has been used for decades. The test is done on all corners of the table as those tend to have the highest level of vibration.
On the other hand, combined optical table systems (INT or OTS) are easier to set up, more mobile, easier to add accessories to (such as casters and shelves) and may be more economical. Newport offers a wide variety of active damped, tuned mass damped and broadband damped tables integrated into a robust frame system with either pneumatic isolation or rigid supports. Disadvantages of combined systems include lower payloads per isolator and possible resonances introduced by the frame structure.
Objectivelens microscopefunction
1. Ocular eyepiece lens to look through. 2. Objective lens, closest to the object. Before purchasing or using a compound microscope, it is important to know the functions of each part. This information is presented below. Links will take you to additional information and images.
A: Side panels and edge finish for optical tables do more than just covers. They should contribute to the overall damping performance of the table. The advantage of steel is that it is stiff and provides good environmental stability. The drawbacks are: Like many other hard metals with high elasticity and high density, steel tends to allow vibration or ringing and would resonate with very little natural damping. The wood, on the other hand, is very good at natural damping and eliminate vibrations. This is why ringing bells are always made out of steel/metal and high end hi-fi speakers that require acoustic damping are almost all enclosed by composite wood. But wood is not without any drawbacks – it tends to be more vulnerable than steel under difficult environmental factors. Considering the pros and cons from each side and the fact that optical tables are generally used in house and under controlled environment, Newport decides to use composite wood with moisture protective paint layers which provides superior damping and prevent the side panels from introducing vibrations to the tabletop.
Eyepiece/Ocular: Compound microscopes commonly have a pair of eyepieces that provide binocular vision. Other microscopes may have a single eyepiece or sometimes no eyepieces at all.
Optical table tops and supports can be selected and ordered separately as stand-alone items, or they can be ordered as frame based combined systems.
Lens of microscopeuses
Compound microscopes and other types of microscopes differ in their design and functionality. Here are the key differences between compound microscope parts and those of other microscopes:
Lens of microscopeprice
Hybrid damping combines the advantages of both active damping and tuned mass damping. The active system is able to further reduce vibrations on top of a good foundation created by precision tuned dampers, delivering optical tables and systems with the minimum resonance peaks. Hybrid damping system is the most advanced damping technique for optical tables and provides the best performance optical tables ever in the market. They are ideal for the most demanding applications such as nanostructure studies and fabrication; long exposure holography, spectroscopy and microscopy; ultrafast studies; live cell imaging; and any application that involves constant load changes.
A tuned mass damper is a device consists of a mass, a spring, and a damper that is attached to a structure in order to reduce the dynamic response of the structure. It is tuned to a particular structural frequency so that when the table resonance is excited, the damper will resonate out of phase with the structural motion of the structure. Vibration energy is then dissipated by the damper inertia force acting on the structure. TMD is the most effective method among all known passive damping methods, as it concentrates damping efforts where it's needed at the frequencies of dominant resonance modes. It is widely used in various industries for its efficiency and effectiveness of damping, such as the famous Grand Canyon Skywalk, Taipei 101 Building, and NASA's Ares I rocket. Different from broadband damping which absorbs a moderate amount of vibration energy equally over the broad band, TMD targets resonances and as a result is much more effective.
Q: What is the difference between vibration damping and isolation? Why do I need isolators when I already have an optical table top?
Rack Stop: This is an adjustment that determines how close the objective lens can get to the slide. It is set at the factory and keeps students from cranking the high power objective lens down into the slide and breaking things. You would only need to adjust this if you were using very thin slides and you weren't able to focus on the specimen at high power. (Tip: If you are using thin slides and can't focus, rather than adjust the rack stop, place a clear glass slide under the original slide to raise it a bit higher).
Newport introduced the first commercially available actively damped optical tables in 2005. Different from broadband or tuned mass damping that absorbs vibrations passively, Newport’s SmartTable® line of products feature active damping with patented IQ technology (US patent 7320455, 8196891, 8807515, 9086112, 8276873, 8231098, 8651447 and 8857585) that senses vibration in real time and immediately sends out signals to actuators to counteract and cancel the vibrations. It effectively addresses the resonances of optical tables by incorporating two pairs of sensor and actuator in the optical table design and uses an external controller to coordinate the signal processing, enabling the fast and accurate damping response for optical tables. It has a much shorter settling time than passive system and reduces all table resonances within the entire active bandwidth. For more information about active damping, see our technical note Active Vibration Damping.
A: Under localized heat sources (laser, lamp, etc.), all standard optical tables in the market are very likely to bend a little bit (µrads) because the thermal gradient exists between top and bottom skin, which are thermally isolated by air – no matter whether it is an “all-steel symmetrical isotropic” design. If minimum thermal expansion is absolutely needed, the best way is to isolate your thermal source from tables, or choose Super Invar™ as your table material.
If our standard optical tables and isolation systems do not quite meet the requirements for your application or environment, please contact us to discuss a custom solution. For over 50 years our extensive design and manufacturing capabilities have delivered customized, damped platforms to numerous academic and industrial customers. Our capabilities include custom shaped granite, honeycomb or Invar structures, non-magnetic honeycomb tables, cleanroom and vacuum compatible structures with either broadband or tuned dampers for optimal stability and vibration reduction. For more information, please see Custom Vibration Isolation Solutions.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500