Shop Lenses Online| OM SYSTEM Canada - lenses for sale
Trigeminal neuralgia. Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain disorder of one or both of the trigeminal nerves, which relay sensory information between your brain and areas of your forehead, cheek and lower jaw. This nerve disorder causes extreme facial pain that feels like an electric shock.
Laguerre Gaussbeam
Dose planning. The results of the brain scans are fed into a computerized planning system that enables the radiosurgery team to plan the appropriate areas to treat, dosages of radiation and how to focus the radiation beams to treat the areas.
Children are often anesthetized for the imaging tests and during the radiosurgery. Adults are usually awake, but you may be given a mild sedative to help you relax.
Stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain and spine is typically completed in a single session. Body radiosurgery is used to treat lung, liver, adrenal and other soft tissue tumors, and treatment typically involves multiple (three to five) sessions.
Dr. Parney: I've had one patient send me a picture of himself golfing in the same day that he had Gamma Knife done. Now that's a little extreme, but I think most patients are really surprised at how smoothly this goes.
Beamshaper
Form FactorThe anamorphic effect is described by the form factor F, which Âindicates the relative diameter change of the parallel beam.The target value is calculated from the ratio of the beam diameters Ã⥠and Ã|| of the Âcollimated beam.
Head frame placement. Before the procedure begins, you'll have a lightweight frame attached to your head with four pins. This frame will stabilize your head during the radiation treatment and serve as a point of reference for focusing the beams of radiation. Some types of brain radiosurgery may not require head frame placement.
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM). AVMs are abnormal tangles of arteries and veins in your brain. In an AVM, blood flows directly from your arteries to veins, bypassing smaller blood vessels (capillaries). AVMs may disrupt the normal flow of blood and lead to bleeding (hemorrhage) or stroke.
It is not surgery in the traditional sense because there's no incision. Instead, stereotactic radiosurgery uses 3D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Imaging for brain AVMs may include CT scans, MRI scans, cerebral angiograms or some combination of these tests.
Beamexpander
If a head frame is required, you'll receive numbing shots in the four places on your scalp where the pins will be inserted — two points on your forehead and two at the back of your head. Your hair will not be shaved, and you may be given a special shampoo to cleanse your scalp and help the frame stay in place.
How to design a Gaussian to top hatbeamshaper
Acoustic neuroma. An acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma), is a noncancerous tumor that develops along the main balance and hearing nerve leading from your inner ear to your brain.
Simulation. A radiation oncologist will conduct a simulation to determine the best placement of your body to align it with the radiation beams. Your body will be held very tightly and still by an immobilization device. Tell your doctor if you have claustrophobia.
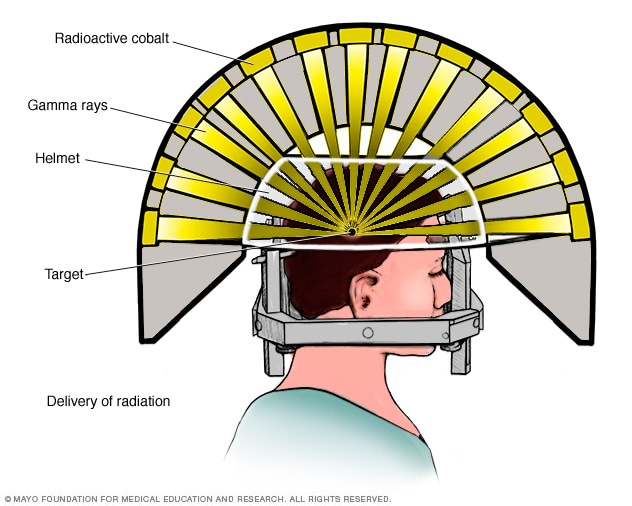
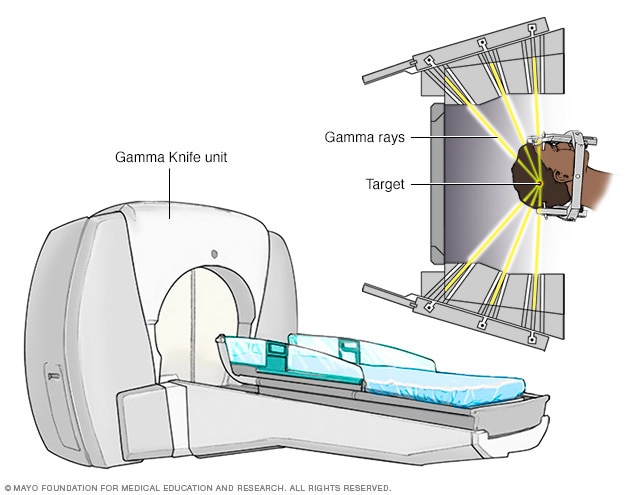
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other problems in the brain, neck, lungs, liver, spine and other parts of the body.
Since then, the use of stereotactic radiosurgery has expanded widely to treat a variety of neurological and other conditions, including:
Unlike the Gamma Knife, the LINAC machine moves and rotates around the target during treatment to deliver radiation beams from different angles. The treatment takes less than an hour.
Ms. Dixon: It reminded me of having a tooth filled. It's that, yeah, it stings. It's like up bee sting. And then there's pressure.
Stereotactic radiosurgery doesn't involve surgical incisions, so it's generally less risky than traditional surgery. In traditional surgery, you may have risks of complications with anesthesia, bleeding and infection.
A circular beam profile may be preferred over the elliptical profile usually provided by laser diodes or by tapered amplifiers. Anamorphic optics act one-dimensionally on the elliptical profile of the colliÂmated beam. They can be used to
Preparation for stereotactic radiosurgery or radiotherapy for other parts of the body also involves several steps, including:
Gamma Knife radiosurgery uses multiple tiny beams of radiation to shrink tumors. The left brain scan shows a pretreatment image of a noncancerous tumor — an image enhanced by the use of a special dye, called a contrast agent. At six months after treatment (middle image), the tumor appears slightly larger but doesn't take up as much of the contrast agent — isn't as bright in the center. This indicates a positive treatment effect. At seven years (right scan), the tumor appears much smaller.
The Anamorphic Beam-shaping ÂOptics type 5AN are cylinder lens systems and, therefore, can be additionally used to correct the astigmatic difference âAs of the laser diode or tapered amplifier through a refocusing of the optical system. Coupling efficiencies to single-mode fibers of 80% or more are possible when using anamorphic beam-shaping optics (depending on the beam characteristics of the laser diode or tapered amplifier).
Around 50 years ago, stereotactic radiosurgery was pioneered as a less invasive and safer alternative to standard brain surgery (neurosurgery), which requires incisions in the skin, skull, and membranes surrounding the brain and brain tissue.
In a cerebral angiogram, a doctor inserts a small tube in a blood vessel in your groin and threads it to the brain using X-ray imaging. A doctor injects dye through the blood vessels to make them visible on X-rays. Your doctor may inject a dye into a blood vessel during CT or MRI scans to view the blood vessels and highlight blood circulation.
You may have a tube that delivers fluids to your blood stream (intravenous, or IV, line) to keep you hydrated during the day if you are not allowed to eat or drink during the procedure. A needle at the end of the IV is placed in a vein, most likely in your arm.
When doctors use stereotactic radiosurgery to treat tumors in areas of the body other than the brain, it's sometimes called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR).
Doctors use three types of technology to deliver radiation during stereotactic radiosurgery in the brain and other parts of the body:
Your in-depth coping with cancer guide will be in your inbox shortly. You will also receive emails from Mayo Clinic on the latest about cancer news, research, and care.
Dr. Parney: People often think of it like a laser beam and it's not quite like that. But it is very tightly focused and really down to the millimeter level. It is such a high dose and so tightly focused that we can't have people move their head at all during the procedure.
Dr. Pollock: Once the frame is in place, we go upstairs for imaging which could be an MRI, could be a CAT scan or potentially a cerebral angiogram.
Debbie Dixon, Mayo Clinic Patient: I've undergone Gamma Knife two times for two separate meningiomas. Gamma Knife is kind of a misnomer because there's no knives.
Ms. Dixon: Nothing. Nothing. No sound. No, no sensation. And I say are you doing it? When are you going to start? Yeah, we're doing it. I mean, it was it was the most anticlimactic thing ever.
Brain tumor. Stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife, is often used to treat noncancerous (benign) and cancerous (malignant) brain tumors, including meningioma, paraganglioma, hemangioblastoma and craniopharyngioma.
Pituitary tumors. Tumors of the bean-sized gland at the base of the brain (pituitary gland) can cause a variety of problems. The pituitary gland controls hormones in your body that control various functions, such as your stress response, metabolism, growth and sexual function.
Bring any medications you are currently taking with you to the treatment center and ask about what you should do about taking your medications on the day of the procedure.
This planning process may take an hour or two. During that time, you can relax in another room, but the frame must remain attached to your head. If you are doing LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain, typically you would be sent home during the planning process and treatment would be delivered a few days later.
Dr. Pollock: We are not beside you, but at the same time, we can see you all the time. You can speak to us. We watch your oxygen. We watch your breathing. There is communication. At any point during a procedure, the procedure can be stopped and we can come in and have you sit up and take a break. When you're finished, you'll come out of this device. We take this frame off your head and a short while later, you're ready to go home.
Doctors may inject a dye into a blood vessel to view the blood vessels in your brain and highlight blood circulation. In some cases, you may have an MRI scan and a CT scan.
Gaussianbeam
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
The precision of stereotactic radiosurgery means there's minimal damage to the healthy surrounding tissues. In most cases, radiosurgery has a lower risk of side effects compared with other types of traditional surgery or radiation therapy.
Tumors. Imaging for tumors may include computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In a CT scan, a series of X-rays create a detailed image of your brain. In an MRI scan, a magnetic field and radio waves create detailed images of your brain.
This downloads section only includes general downloads for the complete series.Please access the individual product pages (using the product configurator, the product list, order options or the search button if you have a complete order code). Here you will find specific downloads including technical drawings or stepfiles.
Like other forms of radiation, stereotactic radiosurgery works by damaging the DNA of the targeted cells. The affected cells then lose the ability to reproduce, which causes tumors to shrink.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
Preparation for stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy may vary depending on the condition and body area being treated but usually involves the following steps:
Dr. Parney: That allows us to rely on our computers to know where the tumor or the lump or the vascular malformations were going to treat, where that is in space relative to the frame. When we go ahead with the treatment, they just lie there. They get the treatment. Most people won't feel anything at all, just like getting an x-ray or any of the radiation treatments that people have undergone.
Stereotactic radiosurgery may stop the growth or minimize the size of an acoustic neuroma with little risk of permanent nerve damage.
If you don’t receive our email within 5 minutes, check your SPAM folder, then contact us at newsletters@mayoclinic.com.
If you are using a Gamma Knife machine, you'll lie on a bed that slides into the machine, and your head frame will be attached securely to the bed frame. The machine does not move during treatment; instead, the bed moves within the machine. The procedure may take less than an hour to about four hours, depending on the size and shape of the target. If treating with LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain the treatment will be quicker.
Pi shaper
There's a variety of devices that are used to perform stereotactic radiosurgery. The Gamma Knife is used only to treat the brain and head and upper neck, whereas the linear accelerators are more versatile and can also be used to treat the head but can treat below the neck and the parts of the body as well.
Laserbeamhomogenizer
The specialized equipment focuses many small beams of radiation on a tumor or other target. Each beam has very little effect on the tissue it passes through, but a targeted dose of radiation is delivered to the site where all the beams intersect.
Researchers are also exploring the use of stereotactic radiosurgery to treat other conditions, including melanoma of the eye, breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, epilepsy and psychological disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Subscribe for free and receive an in-depth guide to coping with cancer, plus helpful information on how to get a second opinion. You can unsubscribe at any time. Click here for an email preview.
Preparation for Gamma Knife and LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain is very similar (except for the first step — a head frame is not needed for LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery) and involves three steps:
The high dose of radiation delivered to the affected area causes tumors to shrink and blood vessels to close off over time following treatment, robbing the tumor of its blood supply.
Flat-topbeam
Stereotactic radiosurgery is usually an outpatient procedure, but the entire process will take most of a day. You may be advised to have a family member or friend who can be with you during the day and who can take you home.
When the tumor puts pressure on the nerve, a person can experience hearing loss, dizziness, loss of balance and ringing in the ear (tinnitus). As the tumor grows, it can also put pressure on the nerves affecting sensations and muscle movement in the face.
Ian Parney, M.D., Ph.D., Neurosurgery, Mayo Clinic: In some cases, this is something to manage the metastatic brain tumor burden for patients but isn't something that wouldn't necessarily cure them. Other tumors, this is definitely a cure.
The steps immediately prior to treatment may vary depending on the location of your treatment area and the type of equipment being used to deliver the radiation.
You don't need a head frame with LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain. The radiosurgery typically can be delivered with a soft plastic mask that forms to your face. The advantage of this approach is it facilitates multiple (three to five) treatments and avoids the uncomfortableness of frame placement.
Bruce Pollock, M.D., Neurosurgery, Mayo Clinic: Stereotactic radiosurgery is an outpatient-based radiation procedure. You're going to walk in, have this done, and walk out again. And that's the way we want people to think about radiosurgery.
Gamma Knife radiosurgery uses multiple tiny beams of radiation to shrink tumors. The left brain scan shows a pretreatment image of a noncancerous tumor — an image enhanced by the use of a special dye, called a contrast agent. At six months after treatment (middle image), the tumor appears slightly larger but doesn't take up as much of the contrast agent — isn't as bright in the center. This indicates a positive treatment effect. At seven years (right scan), the tumor appears much smaller.




 Ms.Cici
Ms.Cici 
 8618319014500
8618319014500